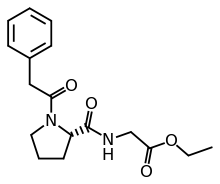
N-Phenylacetyl-L-prolylglycine ethyl ester
N-Phenylacetyl-l-prolylglycine ethyl ester is promoted as a nootropic and is a prodrug of cycloprolylglycine.[1] Other names include the brand name Noopept (Russian: Ноопепт), developmental code GVS-111; proposed INN omberacetam.[1][2][3]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Noopept |
| Other names | N-Phenylacetyl-l-prolylglycine ethyl ester; GVS-111 |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H22N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 318.367 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Its synthesis was first reported in 1996.[1] It is orally available, and as of 2017 its metabolism and elimination half-life were not well understood, as cycloprolylglycine had not been measured in humans following administration.[1]
As of 2017 there had been many studies conducted in cells and in animal models, and there had been one clinical trial with 41 subjects, which compared Noopept and piracetam in people with traumatic brain injury.[1]
References
- "Noopept Information". Examine.com. Retrieved 6 April 2017.
- "Proposed INN List 117" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. 31 (2): 308. 2017.
- "GVS 111". AdisInsight. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.