Metisazone
Methisazone (USAN) or metisazone (INN) is an antiviral drug that works by inhibiting mRNA and protein synthesis, especially in pox viruses. It has been used in the past to treat smallpox.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(1-Methyl-2-oxoindol-3-ylidene)amino]thiourea | |
| Other names
Metisazone | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.016 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | D008720 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C10H10N4OS |
| Molar mass | 234.28 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| J05AA01 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Methisazone has been described as being used in prophylaxis since at least 1965.[2][3]
Synthesis
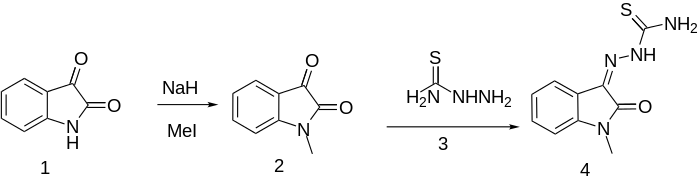
Methisazone synthesis: Bauer, Sadler, Br. J. Pharmacol. 15, 101 (1960); GB 975357 (1964 to Wellcome Foundation).
When isatin is treated with sodium hydride and methyl iodide, the acidic hydrogen is alkylated to product 2. Then, reaction of the ketone carbonyl with thiosemicarbazide (3) leads to methisazone (4).
References
- Methisazone, Merriam-Webster's Medical Dictionary
- do Valle, LA; de Melo, PR; de Gomes, LF; Proença, LM (13 Nov 1965). "Methisazone in prevention of variola minor among contacts". Lancet. 2 (7420): 976–8. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92840-0. PMID 4159212.
- Weiss MM, Weiss PD, Mathisen G, Guze P (December 2004). "Rethinking smallpox". Clin. Infect. Dis. 39 (11): 1668–73. doi:10.1086/425745. PMID 15578369.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.