Clevudine
Clevudine (INN) is an antiviral drug for the treatment of hepatitis B (HBV). It is already approved for HBV in South Korea and the Philippines. It is marketed by Bukwang Pharmaceuticals in South Korea under the tradenames Levovir and Revovir.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
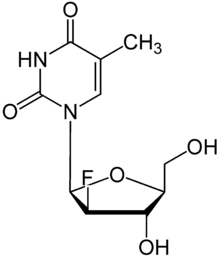
| Formula | C10H13FN2O5 |
| Molar mass | 260.219 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Under license from Bukwang, Pharmasset was developing the drug, but its phase III clinical trial (international, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, 96-week QUASH studies) was terminated due to some myopathy cases in patients. Its approval in South Korea was revoked following these findings. Researchers in South Korea are testing clevudine at lower doses in combination with adefovir for continued use.[2]
It is a nucleoside analog.[3]
References
- WHO International Working Group for Drug Statistics Methodology (August 27, 2008). "ATC/DDD Classification (FINAL): New ATC 5th level codes". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2008-09-05.
- Tak WY, Yang JM, Kim BI, Baik SK, Cheon GJ, Byun KS, Kim DY, Yoo BC, et al. (May 2014). "A randomized, open-label study comparing low-dose clevudine plus adefovir combination therapy with clevudine monotherapy in naïve chronic hepatitis B patients". Hepatology International. 8 (3): 375–381. doi:10.1007/s12072-014-9537-5. PMC 4116600. PMID 25101150.
- Lee HS, Chung YH, Lee K, et al. (May 2006). "A 12-week clevudine therapy showed potent and durable antiviral activity in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B". Hepatology. 43 (5): 982–8. doi:10.1002/hep.21166. PMID 16628625.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.