Cigarette Smoking Among Adults with Disabilities
On This Page
Cigarette smoking kills almost one in five adults each year. In 2010, approximately 17% of deaths were from smoking.
Tobacco use is the leading preventable cause of death in the United States.
The percentage of adults who smoke cigarettes is higher among people with disabilities than people without disabilities.
Percentage of U.S. Adults who Currently Smoke Cigarettes by Disability Status, 2011
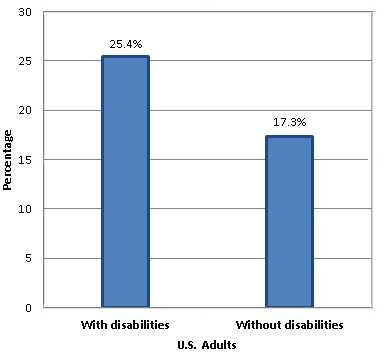
Current cigarette smoking is significantly higher among adults with a disability (25.4%) compared to adults without a disability (17.3%).1
1 2011 National Health Interview Survey
Smoking & Adults with Disabilities
Disparities in Cigarette Smoking Among Adults with Disabilities Fact Sheet.
Public Health Programs and Campaigns
Access to proven smoking cessation treatments and services and public information campaigns may significantly reduce health care costs and save the lives of people, including those with disabilities. Evidence shows that access to comprehensive tobacco control programs can reduce smoking rates, tobacco-related deaths, and diseases caused by smoking.
To reduce and prevent smoking among people with disabilities, public health programs can:
- Include disability in public health surveys and research activities
- Update existing health promotion campaigns or programs with targeted smoking cessation messages for people with disabilities
- Include people with disabilities in health promotion activities

The Ohio Disability and Health Program and the Ohio Department of Health’s Tobacco Program teamed up to create smoking cessation materials that target people with disabilities.
The Michigan Tobacco Quitline is unique in its barrier-free approach to cessation assistance.

New Hampshire provides tips to help people with disabilities quit smoking.
What is CDC Doing to Reduce Smoking among People with Disabilities?
CDC provides funding to 19 State Disability and Health Programs that work to improve the health and wellness of people with disabilities by including them in health promotion activities to reduce smoking. For example,
The Ohio Disability and Health Program collaborated with the Ohio Department of Health’s Tobacco Use Prevention and Cessation Program (TUPCP) to encourage people with disabilities to use the Ohio Tobacco Quit Line.
- The highlights of the program include:
- Collaborating with TUPCP to add a disability screener question to the Quitline intake form to track people with disabilities who use the service. The addition of this identifier allows the program to track change in use of the Quitline by people with disabilities over time.
- Collaborating with TUPCP to create a mass media campaign to raise awareness of the Quitline among people with disabilities. Focus groups were held to gather feedback from the disability community in the development of effective marketing materials. During the 3-month campaign, the proportion of callers with a disability who called the Quitline, relative to all callers, increased by 25%.
- Engaging in a Tobacco Cessation Community of Practice that included TUPCP and National Jewish Health (provider of Ohio Tobacco Quitline). This work resulted in National Jewish Health requiring disability sensitivity training for Tobacco Quitline counselors.
Members of the Disability and Health and Tobacco units at the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services (MDHHS) are working together to promote the Michigan Tobacco Quitline among people with disabilities.
- The highlights of the program include:
- Training vocational service specialists—those who work directly with employees—at Peckham Industries. Peckham is the largest vocational rehabilitation agency in Lansing (Michigan’s capitol), and the agency employs quite a few people with disabilities. Among other employee services, Peckham assists employees who wish to quit tobacco. Since the training, Peckham has changed its policies so that all employees who wish to quit tobacco are automatically referred to the Michigan Tobacco Quitline.
- Partnering with a creative advertising class at Michigan State University, students were asked to design posters and other print materials that creatively illustrate the differences in smoking rates for various groups of people and the importance of accessible smoking cessation resources. This raised awareness about access and inclusion among the students and provided strong visual messages that MDHHS is using to promote the Michigan Tobacco Quitline among people with disabilities.
The New Hampshire Disability and Public Health Program developed materials that can be used by healthcare providers to support people with disabilities who want to quit smoking.
- The highlights of the program include:
- Developing a smoking cessation brochure [] that offers tips to help people with disabilities quit smoking.
- Exploring the possibility of including disability identifiers on the state’s Quitline intake form.
- Providing technical assistance and offering training to the New Hampshire Tobacco Prevention and Cessation Program (TPCP) to improve inclusion and accessibility of the program.
Resources
- Vital Signs
- Smoking and Tobacco Use
- Disability & Health
- Healthy Living
- CDC’s Disability and Health Data System
- Page last reviewed: August 2, 2017
- Page last updated: August 2, 2017
- Content source:




 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir