VDSCP: Vitamin D Standardization-Certification Program
Osteoporosis and other bone diseases affect millions of U.S. residents and are a major cause of disability. Half of all women and as many as a quarter of men age 50 years and older will have an osteoporosis-related fracture in their lifetime.1
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient long-known for its role in maintaining bone health. People who are deficient in vitamin D are at higher risk for osteoporosis. Laboratory tests for vitamin D are used to determine a person’s vitamin D status, and to identify persons with vitamin D deficiency. These tests must be accurate to ensure correct diagnoses and treatment of patients with vitamin D deficiency.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) improves the detection and diagnosis of bone diseases by ensuring that laboratory tests for vitamin D are accurate and reliable. CDC’s Vitamin D Reference Method Laboratory and the Vitamin D Standardization–Certification Program (VDSCP) work to
- provide reference measurements for total 25-hydroxyvitamin D (sum of 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 and 25-hydroxyvitamin D3),
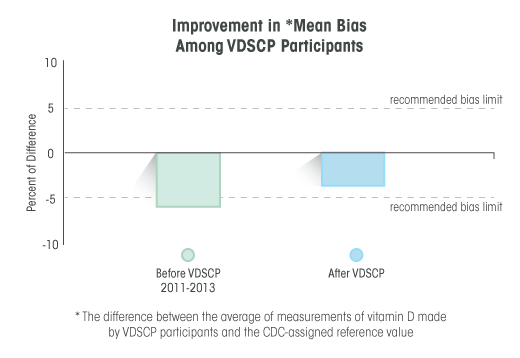
- assess the accuracy and precision of vitamin D tests, and monitor their performance over time, and
- provide technical support to external quality assurance programs, proficiency testing programs, and research studies that ensure vitamin D tests are accurate and reliable.
What is vitamin D?
The biologically active form of vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) is a hormone whose main function is to keep serum calcium and phosphorus concentrations in blood within normal ranges.
In patient care and public health assessments, vitamin D is defined as the sum of 25-hydroxyergocalciferol (25-hydroxyvitamin D2) and calcifediol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3). Our bodies convert both compounds to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Levels of 25-hydroxyergocalciferol and calcifediol in blood describe a person’s vitamin D status.
How is vitamin D status assessed?
Blood tests for assessing a person’s vitamin D status measure two forms: 25-hydroxyergocalciferol (25-hydroxyvitamin D2) and calcifediol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3). These major circulating forms reflect the cumulative effects of exposure to sunlight and dietary intake of vitamin D (the two ways people get vitamin D), and therefore, clinicians use them to determine vitamin D status.
What role does the Vitamin D Reference Method Laboratory play in vitamin D assessment?
CDC’s Vitamin D Reference Laboratory uses a highly accurate and precise reference method for measuring 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 and 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (total 25-hydroxyvitamin D). It uses this reference method to assign reference values to serum samples.
What is the function of the Vitamin D Standardization-Certification program?
CDC’s Vitamin D Standardization-Certification Program (VDSCP) evaluates the accuracy and reliability of vitamin D tests using well-established procedures, and certifies those that have a certain accuracy and precision.
What is standardization and a standardized test?
Standardization is an activity in which the accuracy, precision, and other analytical performance parameters of a laboratory test are assessed against analytical performance goals by an independent, impartial, qualified organization. Thus, a standardized laboratory test is a test that demonstrated, through an independent and impartial assessment, an analytical performance, such as accuracy and precision, which meets specific analytical performance goals.
1Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. 2016. Arthritis, osteoporosis, and chronic back conditions. In: Healthy People 2020. Washington, DC [accessed 2017 May 18]. Available from https://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/topics-objectives/topic/Arthritis-Osteoporosis-and-Chronic-Back-Conditions.
- Page last reviewed: July 6, 2017
- Page last updated: July 6, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir
