Population Movements
Central American Refugee Health Profile
Drivers of Immigration
Historically, the primary drivers of immigration from El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras to the United States have been family reunification and the economy; however, civil war throughout the region in the 1980s also prompted immigration. Recently, extreme poverty and increasing violence have spurred a new wave of immigration1.
Increased instability and growing gang violence have been particularly unsettling for families and have pushed many children, often unaccompanied by an adult, to flee to the United States. The numbers of unaccompanied minors who arrived in the U.S. from El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras significantly increased from 2009 to 2014 (Figure 2). While the number of unaccompanied minors arriving in the United States decreased from 2014 to 2015, more than 23,000 children arrived in 2015 from El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras, with an additional 11,000 from Mexico9. The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) reports that unaccompanied minors presenting at border stations have health issues, often associated with the difficult journey or crowded, unsanitary, and environmental conditions experienced prior to arrival in the United States. The majority of health conditions reported include scabies, lice, rash illness, diarrhea, and respiratory infections10.
Figure 2: Unaccompanied Minors Encountered at U.S. Border, 2009-2015
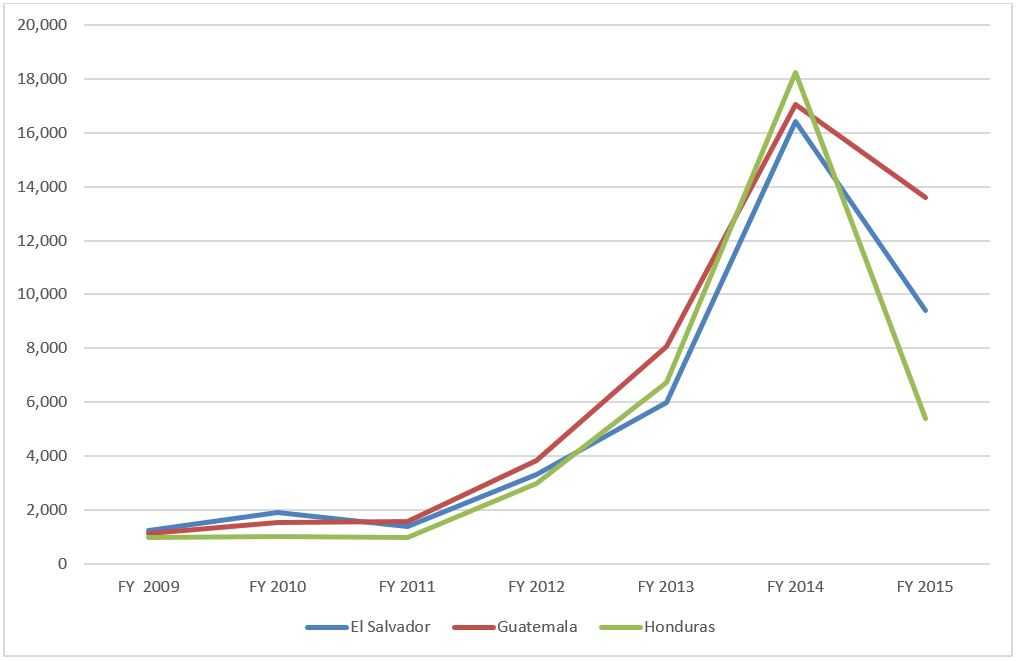
Source: U.S. Customs and Border Protection. http://www.cbp.gov/newsroom/stats/southwest-border-unaccompanied-children
The Central American Minors Refugee/Parole Program
Because of the large number of minors crossing the southwestern border, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) in the Department of Homeland Security initiated the Central American Minors (CAM) Refugee/Parole Program in December 2014. The CAM program allows for refugee and parolee processing in El Salvador, Honduras, and Guatemala, and provides qualifying minors with safe and legal means of entering the United States11.
To be eligible for refugee status under the CAM program, minors and their parents must meet strict requirements. The child must meet the following criteria:
- The child (biological, stepchild, or legally adopted) of the qualifying parent
- Unmarried
- Under 21 years old
- A Guatemalan, Honduran, or Salvadoran national living in his or her country of nationality
Additional information regarding the CAM program, including detailed steps outlining the refugee application process, can be found at the USCIS website and the Department of Homeland Security website. Additional information on how minors may qualify for humanitarian parole through the CAM program is also available at these sites.
Refugee and Parole Status
The 1951 Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees defined a refugee as a person who “owing to a well-founded fear of being persecuted for reasons of race, religion, nationality, membership of a particular social group, or political opinion, is outside the country of his nationality, and is unable to or, owing to such fear, is unwilling to avail himself of the protection of that country”12. Additional information on international refugee status can be found here. For the U.S. legal definition of a refugee please refer to Section 101(a)(42) [PDF - 1 page] of the Immigration and Nationality Act. In contrast, parole status allows an individual, who may otherwise be inadmissible or ineligible for admission to the United States, to enter the U.S. legally for a specified period of time13. For additional information on parole status, please refer to the USCIS website. If granted refugee status through the CAM program, individuals have access to federal benefits, including health insurance coverage through Refugee Medical Assistance (RMA) or Medicaid. Those granted parolee status are not eligible to receive the same benefits.
References
-
Cultural Orientation Resource Exchange, Backgrounder: Central American Minors. 2015.
-
Central Intelligence Agency. Guatemala. The World Factbook [cited 2015 March];
Available from: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/gt.html. -
Central Intelligence Agency. El Salvador. The World Factbook [cited 2015 March];
Available from: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/es.html. -
Central Intelligence Agency. Honduras. The World Factbook [cited 2015 March];
Available from: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ho.html. -
United States Department of State, Guatemala, in International Religious Freedom Report for 2012. 2012.
-
Stansifer, C.L., Guatemala, in Encyclopaedia Britannica. 2015.
-
Moncada R, J., W. Clegern, and R. Woodward, Honduras, in Encyclopaedia Britannica. 2014.
-
Zimmerman, L., Women in Latin America. Roger Thayer Stone Ceter for Latin American Studies, Tulane University.
-
U.S. Customs and Border Protection. Southwest Border Unaccompanied Alien Children Statistics FY 2015. 2015 [cited 2015 November];
Available from: http://www.cbp.gov/newsroom/stats/southwest-border-unaccompanied-children/fy-2015. -
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Unaccompanied Children: Health Information for Public Health Partners.
-
Langlois, J., Written testimony of USCIS Refugee, Asylum and International Operations Associate Director Joseph Langlois for a Senate Committee on the Judiciary, Subcommittee on Immigration and The National Interest hearing titled “Eroding the Law and Diverting Taxpayer Resources: An Examination of the Administration's Central American Minors Refugee/Parole Program”. 2015.
-
Article 1, Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees, Editor. 1951.
-
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services. Humanitarian Parole. 2015 [cited 2015 November];
Available from: http://www.uscis.gov/humanitarian/humanitarian-parole. -
Central Intelligence Agency. Physicians density. [cited 2016 March 17];
Available from: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2226.html. -
World Health Organization, Health workforce, infrastructure, essential medicines. 2009.
-
World Bank, Universal Healthcare on the rise in Latin America. 2013.
-
Pan American Health Organization, Health Systems Profile: Honduras, in Monitoring and Analyzing Health Systems Change/Reform. 2009.
-
Brown, S. Considering Curanderismo: the place of traditional Hispanic folk healing in modern medicine. 2008 [cited 2016 September];
Available from: http://www.bc.edu/clubs/mendel/ethos/archives/2008/brown.shtml. -
UNICEF, Country statistics 2015.
-
The World Bank, HealthStats 2016.
-
UNICEF. At a glance: Guatemala. 2013 [cited 2015 November]; Available from: http://www.unicef.org/infobycountry/guatemala_statistics.html.
-
Geneva Declaration Secretariat, Global Burden of Armed Violence 2011: Lethal Encounters. 2011, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge.
-
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, Women on the Run: First-hand accounts of refugees fleeing El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Mexico. 2015.
-
Manjoo, R., Special Rapporteur on violence against women finalizes country mission to Honduras and calls for urgent action to address the culture of impunity for crimes against women and girls. 2014, United Nations Human Rights, Office of the High Commissioner.
-
Marilena Adams, T., Chronic violence and non-conventional armed actors: a systematic approach. 2014.
-
Bakrania, S., Organised violence and its impacts in Central America's northern triangle. 2013, GSDRC Applied Knowledge Services.
-
American Academy of Pediatrics. Immigrant Toolkit. [cited 2015 December]; Available from: https://www.aap.org/en-us/about-the-aap/Committees-Councils-Sections/Council-on-Community-Pediatrics/Pages/Section-1-Clinical-Care.aspx.
-
Pan American Health Organization and World Health Organization, Chikungunya and dengue fever in the Americas, in Epidemiological Alert. 29 August 2014.
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chikungunya Virus. 2016 [cited 2016 March 11]; Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/chikungunya/index.html.
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All Countries & Territories with Active Zika Virus Transmission. 2016 [cited 2016 December];
Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/geo/active-countries.html. -
Gatherer, D. and A. Kohl, Zika virus: a previously slow pandemic spreads rapidly through the Americas. J Gen Virol, 2016. 97(2): p. 269-73.
-
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, Rapid risk assessment: Zika virus epidemic in the Americas: potential association with microcephaly and Guillain-Barré syndrome. 2015, ECDC: Stockholm.
-
World Health Organization. Tuberculosis profile: El Salvador. 2015 [cited 2015 November];
Available from: https://extranet.who.int/sree/Reports?op=Replet&name=%2FWHO_HQ_Reports%2FG2%2FPROD%2FEXT%2FTBCountryProfile&ISO2=SV&LAN=EN&outtype=html. -
World Health Organization. Tuberculosis profile: Guatemala. 2015 [cited 2015 November];
Available from: https://extranet.who.int/sree/Reports?op=Replet&name=%2FWHO_HQ_Reports%2FG2%2FPROD%2FEXT%2FTBCountryProfile&ISO2=GT&LAN=EN&outtype=html. -
World Health Organization. Tuberculosis profile: Honduras. 2015 [cited 2015 November];
Available from: https://extranet.who.int/sree/Reports?op=Replet&name=%2FWHO_HQ_Reports%2FG2%2FPROD%2FEXT%2FTBCountryProfile&ISO2=HN&LAN=EN&outtype=html. -
Calvo, F.N., et al, Reunión de la Comisión Intergubernamental de la Iniciativa de los Países de Centroamérica (IPCA) para la Interrupción de la Transmisión Vectorial, Transfusional y Atención Médica de la Enfermedad de Chagas.
-
Bern, C., et al., Trypanosoma cruzi and Chagas' Disease in the United States. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2011. 24(4): p. 655-81.
-
Bern, C., Chagas' Disease. N Engl J Med, 2015. 373(19): p. 1882.
-
Hotez, P.J., L. Woc-Colburn, and M.E. Bottazzi, Neglected tropical diseases in Central America and Panama: review of their prevalence, populations at risk and impact on regional development. Int J Parasitol, 2014. 44(9): p. 597-603.
-
Hotez, P.J., et al., The neglected tropical diseases of Latin America and the Caribbean: a review of disease burden and distribution and a roadmap for control and elimination. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2008. 2(9): p. e300.
-
World Health Organization. PCT Databank. 2014 [cited December 2015];
Available from: http://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/preventive_chemotherapy/databank/en/. -
Schneider, M.C., et al., Elimination of neglected diseases in latin america and the Caribbean: a mapping of selected diseases. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2011. 5(2): p. e964.
-
Schar, F., et al., Strongyloides stercoralis: Global Distribution and Risk Factors. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2013. 7(7): p. e2288.
-
Bhattarai, R., et al., Estimating the non-monetary burden of neurocysticercosis in Mexico. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2012. 6(2): p. e1521.
-
Botero, D., et al., Taeniasis and cysticercosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am, 1993. 7(3): p. 683-97.
-
Medina, M.T., et al., Reduction in rate of epilepsy from neurocysticercosis by community interventions: the Salama, Honduras study. Epilepsia, 2011. 52(6): p. 1177-85.
-
Cook, D.M., et al., A retrospective analysis of prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites among school children in the Palajunoj Valley of Guatemala. J Health Popul Nutr, 2009. 27(1): p. 31-40.
-
Chero, J.C., et al., Hymenolepis nana infection: symptoms and response to nitazoxanide in field conditions. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, 2007. 101(2): p. 203-5.
-
Drugs for Parasitic Infections. 3rd ed. 2013, New Rochelle, NY: The Medical Letter.
-
World Health Organization. Guatemala. Noncommunicable Disease Country Profiles 2014 [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://www.who.int/nmh/countries/gtm_en.pdf [PDF - 1 page]. -
World Health Organization. Country Cooperation Strategy, Guatemala. [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/136864/1/ccsbrief_gtm_en.pdf [PDF - 1 page]. -
World Health Organization. El Salvador. Noncommunicable Disease Country Profiles 2014 [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://www.who.int/nmh/countries/slv_en.pdf [PDF - 1 page]. -
World Health Organization. Country Cooperation Strategy, Honduras. 2013 [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/136893/1/ccsbrief_hnd_en.pdf [PDF - 2 pages]. -
The World Bank. Nutrition at a Glance, El Salvador. [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://siteresources.worldbank.org/NUTRITION/Resources/281846-1271963823772/ElSalvador91311web.pdf [PDF - 2 pages]. -
The World Bank. Nutrition at a Glance, Guatemala. [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://siteresources.worldbank.org/NUTRITION/Resources/281846-1271963823772/Guatemala.pdf [PDF - 2 pages]. -
The World Bank. Nutrition at a Glance, Honduras. [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://www-wds.worldbank.org/external/default/WDSContentServer/WDSP/IB/2013/05/10/000333037_20130510152029/Rendered/PDF/771720BRI0Box000honduras0April02011.pdf [PDF - 2 pages]. -
The World Bank. Data by country. [cited 2015 December]; Available from: http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.DYN.IMRT.IN/countries.
-
World Health Organization. The worldwide prevalence of anaemia, 1993-2005. [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/43894/1/9789241596657_eng.pdf [PDF - 51 pages]. -
American Academy of Pediatrics. State Medicaid Payment for Caries Prevention Services by Non-Dental Professionals. 2013;
Available from: http://www2.aap.org/oralhealth/docs/OHReimbursementChart.pdf [PDF - 12 pages]. -
US Preventive Services Task Force. Dental caries in children from birth through age 5 years: screening. May 2014;
Available from: http://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/Page/Document/RecommendationStatementFinal/dental-caries-in-children-from-birth-through-age-5-years-screening. -
Central Intelligence Agency. The World Factbook. [cited 2015 December]; Available from: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/resources/the-world-factbook/index.html.
-
Martin-Herz, S.P., et al. Developmental screening with recent immigrant and refugee children: a preliminary report. 2012;
Available from: http://ethnomed.org/clinical/pediatrics/developmental-screening-with-recent-immigrant-and-refugee-children. -
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Developmental monitoring for health professionals. [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/childdevelopment/screening-hcp.html. -
American Academy of Pediatrics. Recommendations for preventative pediatric health care. [cited 2015 December];
Available from: https://www.aap.org/en-us/Documents/periodicity_schedule_oral_health.pdf [PDF - 2 pages]. -
National Newborn Screening & Global Resource Center. [cited 2015 December]; Available from: http://genes-r-us.uthscsa.edu/%3Cfront%3E.
-
World Health Organization. Lead: assessing the environmental burden of disease at national and local levels. [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://www.who.int/quantifying_ehimpacts/publications/en/leadebd2.pdf?ua=1 [PDF - 73 pages]. -
Rivera, M.F., Prevalence of lead intoxication in public schools in Tegucigalpa. Revista Medica Hondureña, 1997. 65(3).
-
De Burgos, H., The site of lead: social poisoning in El Salvador. Anthropoligica, 2015. 57(1): p. 185-198.
-
Vigeh, M., H. Saito, and S. Sawada, Lead exposure in female workers who are pregnant or of childbearing age. Ind Health, 2011. 49(2): p. 255-61.
-
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, Children on the Run: Unaccompanied children leaving Central America and Mexico and the need for international protection.
-
Pan American Health Organization, Guatemala, in Health in the Americas, 2012 Edition: Country Volume. 2012.
-
Working with Immigrant-Origin Clients: An Update for Mental Health Professionals. 2013, American Psychological Association.
-
World Food Programme. El Salvador. 2016 [cited 2016 March 15]; Available from: https://www.wfp.org/countries/el-salvador/overview.
-
Lutter, C. and C. Chaarro, Malnutrition in infants and young children in Latin America and the Caribbean: Achieving the Millennium Development Goals. 2008, PAHO: Washington DC.
-
UNICEF, Stunting prevalence among children under five. June 2015.
-
World Food Programme. Guatemala. 2016 [cited 2016 March 15]; Available from: https://www.wfp.org/countries/guatemala.
-
World Health Organization, Global prevalence of vitamin A deficiency in populations at risk 1995-2005. WHO Global Database on Vitamin A Deficiency. . 2009, World Health Organization: Geneva.
-
World Food Programme. Honduras. 2016 [cited 2016 March 15]; Available from: https://www.wfp.org/countries/honduras.
-
FAO, The state of food insecurity in the world: economic crises-impacts and lessons learned. 2009.
-
Rivera, J.A., et al., Childhood and adolscent overweight and obesity in Latin America: a systematic review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2014. 2: p. 321-32.
-
UNICEF, W.H.O. and World Bank, Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates: Levels and Trends. 2015.
-
Webber, L., et al., High rates of obesity and non-communicable diseases predicted across Latin America. PLoS One, 2012. 7(8): p. e39589.
-
World Health Organization, Global Infobase. 2016.
-
World Health Organization, Global Database on BMI. 2005.
-
Popkin, B.M., M.K. Richards, and C.A. Montiero, Stunting is associated with overweight in children of four nations that are undergoing the nutrition transition. J Nutr, 1996. 126(12): p. 3009-16.
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Defining childhood obesity. [cited 2015 December]; Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/obesity/childhood/defining.html.
-
American Academy of Pediatrics. Blood Pressure Tables for Children and Adolescents. [cited 2015 December];
Available from: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-pro/guidelines/current/hypertension-pediatric-jnc-4/blood-pressure-tables.
- Page last reviewed: January 25, 2017
- Page last updated: January 25, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir