Löwenstein–Jensen medium
The Löwenstein–Jensen medium, more commonly known as LJ medium, is a growth medium[1] specially used for culture of Mycobacterium species, notably Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Löwenstein-Jensen medium used for growing M. tuberculosis in a McCartney bottle. | |
| Acronym | LJ medium |
|---|---|
| Uses | Culturing |
| Related items | Petri dish Growth medium |
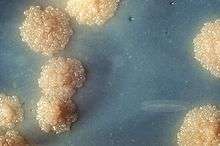
When grown on LJ medium, M. tuberculosis appears as brown, granular colonies (sometimes called "buff, rough and tough"). The medium must be incubated for a significant length of time, usually four weeks, due to the slow doubling time of M. tuberculosis (15–20 hours) compared with other bacteria.
Composition
The usual composition[2] as applicable to M. tuberculosis is:
- Malachite green
- Glycerol
- Asparagine
- Potato starch
- Coagulated eggs
- Mineral salt solution
- Potassium dihydrogen phosphate
- Magnesium sulfate
- Sodium citrate
The original formulation included starch, which was later found to be unnecessary, so omitted.
Low levels of penicillin and nalidixic acid are also present in LJ medium to inhibit growth of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, to limit growth to Mycobacterium species only. Presence of malachite green in the medium inhibits most other bacteria. It is disinfected and solidified by a process of inspissation. Presence of glycerol enhances the growth of M. tuberculosis.
If the slopes are made on test tubes, they must be stored in cold and used within a month.
For cultivation of M.bovis, glycerol is omitted and sodium pyruvate is added.
The medium appears green, opaque, and opalescent.
Uses
- For diagnosis of mycobacterial infections
- For testing antibiotic susceptibility of isolates
- For differentiating different species of Mycobacterium (by colony morphology, growth rate, biochemical characteristics, and microscopy)
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Mycobacterium bovis |
|---|---|
| Eugonic, rough tough and buff | Dysgonic |
| Aerobic | Microaerophillic |
| Glycerol enhancement + | Glycerol enhancement - |
| Pyruvate enhancement + | Pyruvate enhancement - |
| Niacin production + | Niacin production - |
Alternatives
Alternative culture media
While the LJ medium is the most popular means of culturing mycobacteria, as recommended by the International Union against Tuberculosis, several alternative media have been investigated.[3]
Solid media
- Egg-based – Petragnani medium[4] and Dorset medium
- Middlebrook 7H10 agar
- Middlebrook 7H11 agar
- Blood-based – Tarshis medium
- Serum-based – Loeffler medium
- Potato-based – Pawlowsky medium
Liquid media
- Dubos' medium
- Middlebrook 7H9 broth
- Proskauer and Beck's medium
- Sula's medium
- Sauton's medium
Rapid detection techniques
The chief limitation of culture-based techniques is the time it takes to culture positivity, which can be several months. Several new molecular technologies have emerged in recent years to secure more speedy confirmation of diagnosis.
- Polymerase chain reaction
- GeneXpert MTB/RIF
- Loop-mediated isothermal amplification
References
- Elbir H, Abdel-Muhsin AM, Babiker A (February 2008). "A one-step DNA PCR-based method for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex grown on Löwenstein–Jensen media". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 78 (2): 316–7. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.2008.78.316. PMID 18256436.
- Composition of LJ medium
- Textbook of Microbiology by Ananthanarayan and Panicker, Sixth Edition
- Martin, R. S.; Sumarah, R. K.; Robart, E. M. (November 1975). "Comparison of Four Culture Media for the Isolation of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: a 2-Year Study" (PDF). Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 2 (5): 438–440.