Epelsiban
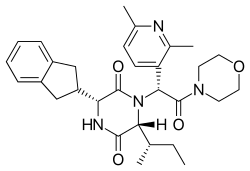
Epelsiban (INN,[1] USAN,[2] code name GSK-557,296-B) is an orally bioavailable drug which acts as oxytocin receptor antagonist. It is being developed by GlaxoSmithKline for the treatment of premature ejaculation in men and as an agent to enhance embryo or blastocyst implantation in women undergoing embryo or blastocyst transfer associated with in vitro fertilization (IVF).[3] Epelsiban has high affinity for the oxytocin receptor (Ki = 0.13 nM) with >31,000-fold selectivity over the related vasopressin receptors.[4][5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H38N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 518.6 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 67" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 62. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- USAN Council (2011). "Statement on a Nonproprietary Name Adopted by the USAN Council" (PDF). Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- Mahar KM, Stier B, Fries M, McCallum SW (November 2015). "A single- and multiple-dose study to investigate the pharmacokinetics of epelsiban and its metabolite, GSK2395448, in healthy female volunteers". Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development. 4 (6): 418–26. doi:10.1002/cpdd.210. PMID 27137713.
- Borthwick AD, Liddle J, Davies DE, Exall AM, Hamlett C, Hickey DM, Mason AM, Smith IE, Nerozzi F, Peace S, Pollard D, Sollis SL, Allen MJ, Woollard PM, Pullen MA, Westfall TD, Stanislaus DJ (January 2012). "Pyridyl-2,5-diketopiperazines as potent, selective, and orally bioavailable oxytocin antagonists: synthesis, pharmacokinetics, and in vivo potency". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 55 (2): 783–96. doi:10.1021/jm201287w. PMID 22239250.
- Northwick AD, Liddle J (January 2013). "Retosiban and Epelsiban: Potent and Selective Orally available Oxytocin Antagonists". In Domling A (ed.). Methods and Principles in Medicinal Chemistry: Protein-Protein Interactions in Drug Discovery. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. pp. 225–256. ISBN 978-3-527-33107-9.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.