We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Stroke (main)
From WikEM
(Redirected from Stroke syndromes)
Contents
Background
- Vascular injury that reduces cerebral blood flow to specific region of brain causing neuro impairment
- Accurate determination of last known time when patient was at baseline is essential
Ischemic stroke causes (87% of all strokes)
- Thrombotic (80% of ischemic CVA)
- Atherosclerosis
- Vasculitis
- Vertebral and carotid artery dissection
- Polycythemia
- Hypercoagulable state
- Infection
- Embolic (20% of ischemic CVA)
- Valvular vegetations
- Mural thrombi
- Arterial-arterial emboli from proximal source
- Fat emboli
- Septic emboli
- Hypoperfusion
- Cardiac failure resulting in systemic hypotension
Hemorrhagic stroke causes (13% of all strokes)
- Intracerebral
- Hypertension
- Amyloidosis
- Anticoagulation
- Vascular malformations
- Cocaine use
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Berry aneurysm rupture
- Arteriovenous malformation
Stroke Types
Clinical Features
Anterior Circulation
Internal Carotid Artery
- Tonic gaze deviation towards lesion
- Global aphasia, dysgraphia, dyslexia, dyscalculia, disorientation (dominant lesion)
- Spatial or visual neglect (non-dominant lesion)
Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)
Signs and Symptoms:
- Contralateral sensory and motor symptoms in the lower extremity (sparing hands/face)
- Urinary incontinence
- Left sided lesion: akinetic mutism, transcortical motor aphasia
- Right sided lesion: Confusion, motor hemineglect
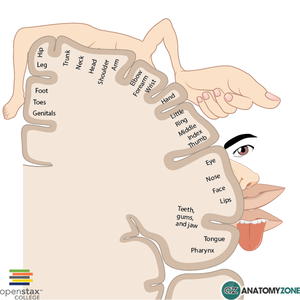
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
Signs and Symptoms:
- Hemiparesis, facial plegia, sensory loss contralateral to affected cortex
- Motor deficits found more commonly in face and upper extremity than lower extremity
- Dominant hemisphere involved: aphasia
- Nondominant hemisphere involved: dysarthria w/o aphasia, inattention and neglect side opposite to infarct
- Contralateral homonymous hemianopsia
- Gaze preference toward side of infarct
Posterior circulation
- Blood supply via the vertebral vertebral artery
- Branches include, AICA, Basilar artery, PCA and PICA
Signs and Symptoms:
- Crossed neuro deficits (i.e., ipsilateral CN deficits w/ contralateral motor weakness)
- Multiple, simultaneous complaints are the rule
- 5 Ds: Dizziness (Vertigo), Dysarthria, Dystaxia, Diplopia, Dysphagia
- Isolated events are not attributable to vertebral occlusive disease (e.g. isolated lightheadedness, vertigo, transient ALOC, drop attacks)
Basilar artery
Signs and Symptoms:
- Quadriplegia, coma, locked-in syndrome
- Sparing of vertical eye movements (CN III exits brainstem just above lesion)
- Thus, may also have miosis b/l
- One and a half syndrome (seen in a variety of brainstem infarctions)
- "Half" - INO (internuclear opthalmoplegia) in one direction
- "One" - inability for conjugate gaze in other direction
- Convergence and vertical EOM intact
- Medial inferior pontine syndrome (paramedian basilar artery branch)
- Ipsilateral conjugate gaze towards lesion (PPRF), nystagmus (CN VIII), ataxia, diplopia on lateral gaze (CN VI)
- Contralateral face/arm/leg paralysis and decreased proprioception
- Medial midpontine syndrome (paramedian midbasilar artery branch)
- Ipsilateral ataxia
- Contralateral face/arm/leg paralysis and decreased proprioception
- Medial superior pontine syndrome (paramedian upper basilar artery branches)
- Ipsilateral ataxia, INO, myoclonus of pharynx/vocal cords/face
- Contralateral face/arm/leg paralysis and decreased proprioception
Superior Cerebellar Artery (SCA)
- ~2% of all cerebral infarctions[1]
- May present with nonspecific symptoms - N/V, dizziness, ataxia, nystagmus (more commonly horizontal)[2]
- Lateral superior pontine syndrome
- Ipsilateral ataxia, n/v, nystagmus, Horner's syndrome, conjugate gaze paresis
- Contralateral loss of pain/temperature in face/extremities/trunk, and loss of proprioception/vibration in LE > UE
Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA)
Signs and Symptoms:
- Common after CPR, as occiptal cortex is a watershed area
- Unilateral headache (most common presenting complaint)
- Visual field defects (contralateral homonymous hemianopsia, unilateral blindness)
- Visual agnosia - can't recognize objects
- Possible macular sparing if MCA unaffected
- Motor function is typically minimally affected
- Lateral midbrain syndrome (penetrating arteries from PCA)
- Ipsilateral CN III - eye down and out, pupil dilated
- Contralateral hemiataxia, tremor, hyperkinesis (red nucleus)
- Medial midbrain syndrome (upper basilar and proximal PCA)
- Ipsilateral CN III - eye down and out, pupil dilated
- Contralateral paralysis of face, arm, leg (corticospinal)
Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (AICA)
- Lateral inferior pontine syndrome
- Ipsilateral facial paralysis, loss of corneal reflex (CN VII)
- Ipsilateral loss of pain/temp (CN V)
- Nystagmus, N/V, vertigo, ipsilateral hearing loss (CN VIII)
- Ipsilateral limb and gait ataxia
- Ipsilateral Horner syndrome
- Contralateral loss of pain/temp in trunk and extremities (lateral spinothalamic)
Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA)
Signs and Symptoms:
- Lateral medullary/Wallenberg syndrome
- Ipsilateral cerebellar signs, ipsilateral loss of pain/temp of face, ipsilateral Horner's syndrome, ipsilateral dysphagia and hoarseness, dysarthria, vertigo/nystagmus
- Contralateral loss of pain/temp over body
- Also caused by vertebral artery occlusion (most cases)
Internal Capsule and Lacunar Infarcts
- May present with either lacunar c/l pure motor or c/l pure sensory (of face and body)[3]
- Pure c/l motor - posterior limb of internal capsule infarct
- Pure c/l sensory - thalamic infarct (Dejerine and Roussy syndrome)
- C/l motor plus sensory if large enough
- Clinically to cortical large ACA + MCA stroke - the following signs suggest cortical rather than internal capsule[4]:
- Gaze preference
- Visual field defects
- Aphasia (dominant lesion, MCA)
- Spatial neglect (non-dominant lesion)
- Others
- I/l ataxic hemiparesis, with legs worse than arms - posterior limb of internal capsule infarct
Anterior Spinal Artery (ASA)
Superior ASA
- Medial medullary syndrome - displays alternating pattern of sidedness of symptoms below
- Contralateral arm/leg weakness and proprioception/vibration
- Tongue deviation towards lesion
Inferior ASA
- ASA syndrome
- Watershed area of hypoperfusion in T4-T8
- B/l pain/temp loss in trunk and extremities (spinothalamic)
- B/l weakness in trunk and extremities (corticospinal)
- Preservation of dorsal columns
Differential Diagnosis
Stroke-like Symptoms
- Stroke
- Seizures/postictal paralysis (Todd paralysis)
- Syncope
- Hypoglycemia
- Hyponatremia
- Meningitis/encephalitis
- Hyperosmotic Coma
- Labyrinthitis
- Drug toxicity
- Lithium, phenytoin, carbamazepine
- Bell's Palsy
- Complicated migraine
- Meniere Disease
- Demyelinating disease (MS)
- Conversion disorder
- Transient global amnesia
Weakness
- Neuromuscular weakness
- UMN:
- Spinal cord disease:
- Infection (Epidural abscess)
- Infarction/ischemia
- Trauma (Spinal Cord Syndromes)
- Inflammation (Transverse Myelitis)
- Degenerative (Spinal muscular atrophy)
- Tumor
- Peripheral nerve disease:
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Toxins (Ciguatera)
- Tick paralysis
- DM neuropathy (non-emergent)
- NMJ disease:
- Muscle disease:
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Dermatomyositis
- Polymyositis
- Alcoholic myopathy
- Non-neuromuscular weakness
- Can't miss diagnoses:
- ACS
- Arrhythmia/Syncope
- severe infection/Sepsis
- Hypoglycemia
- Periodic paralysis (electrolyte disturbance, K, Mg, Ca)
- Respiratory failure
- Emergent Diagnoses:
- Symptomatic Anemia
- Severe dehydration
- Hypothyroidism
- Polypharmacy
- Malignancy
- Other causes of weakness and paralysis
- Acute intermittent porphyria (ascending weakness)
- Can't miss diagnoses:
Evaluation
Always obtain blood glucose, which is commonly overlooked (more embarrassing if you give tPA)
Stroke Work-Up
- Labs
- POC glucose
- CBC
- Chemistry
- Coags
- Troponin
- T&S
- ECG
- In large ICH or stroke, may see deep TWI and prolong QT, occ ST changes
- Head CT (non-contrast)
- Also consider:
- CTA brain and neck (to check for large vessel occlusion for potential thrombectomy)
- Pregnancy test
- CXR (if infection suspected)
- UA (if infection suspected)
- Utox (if ingestion suspected)
MR Imaging (for Rule-Out CVA or TIA)
- MRI Brain with DWI (without contrast) AND
- Cervical vascular imaging (ACEP Level B in patients with high short-term risk for stroke):[8]
- MRA brain (without contrast) AND
- MRA neck (without contrast)
- May instead use Carotid CTA or US (Carotid US slightly less sensitive than MRA)[9] (ACEP Level C)
Management
- Depends on type
- Ischemic vs Hemorrhagic
- Acute vs subacute vs old
Disposition
- Admit for acute or subacute stroke
See Also
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
- Thrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke (tPA)
- CVA (Post-tPA Hemorrhage)
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
- Cervical Artery Dissection
- NIH Stroke Scale
- Cerebellar Stroke
- Focal neurologic signs
External Links
References
- ↑ Macdonell RA, Kalnins RM, Donnan GA. Cerebellar infarction: natural history, prognosis, and pathology. Stroke. 18 (5): 849-55.
- ↑ Lee H, Kim HA. Nystagmus in SCA territory cerebellar infarction: pattern and a possible mechanism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013 Apr;84(4):446-51.
- ↑ Rezaee A and Jones J et al. Lacunar stroke syndrome. Radiopaedia. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/lacunar-stroke-syndrome.
- ↑ Internal Capsule Stroke. Stanford Medicine Guide. http://stanfordmedicine25.stanford.edu/the25/ics.html
- ↑ Mullins ME, Schaefer PW, Sorensen AG, Halpern EF, Ay H, He J, Koroshetz WJ, Gonzalez RG. CT and conventional and diffusion-weighted MR imaging in acute stroke: study in 691 patients at presentation to the emergency department. Radiology. 2002 Aug;224(2):353-60.
- ↑ Suarez JI, Tarr RW, Selman WR. Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354(4):387–396.
- ↑ Douglas VC, Johnston CM, Elkins J, et al. Head computed tomography findings predict short-term stroke risk after transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2003;34:2894-2899.
- ↑ ACEP Clinical Policy: Suspected Transient Ischemic Attackfull text
- ↑ Nederkoorn PJ, Mali WP, Eikelboom BC, et al. Preoperative diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis. Accuracy of noninvasive testing. Stroke. 2002;33:2003-2008.