Signs and Symptoms
On This Page
Español: Signos y síntomas
Pertussis (whooping cough) can cause serious illness in babies, children, teens, and adults. Symptoms of pertussis usually develop within 5 to 10 days after you are exposed. Sometimes pertussis symptoms do not develop for as long as 3 weeks.
Early Symptoms
The disease usually starts with cold-like symptoms and maybe a mild cough or fever. In babies, the cough can be minimal or not even there. Babies may have a symptom known as “apnea.” Apnea is a pause in the child’s breathing pattern. Pertussis is most dangerous for babies. About half of babies younger than 1 year who get the disease need care in the hospital. Learn more about pertussis complications.
In those who have gotten the pertussis vaccine:
- In most cases, the cough won’t last as many days
- Coughing fits, whooping, and vomiting after coughing fits occur less often
- The percentage of children with apnea (long pause in breathing), cyanosis (blue/purplish skin coloration due to lack of oxygen) and vomiting is less
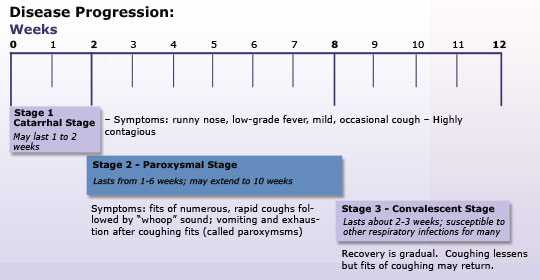
Early symptoms can last for 1 to 2 weeks and usually include:
- Runny nose
- Low-grade fever (generally minimal throughout the course of the disease)
- Mild, occasional cough
- Apnea – a pause in breathing (in babies)
Pertussis in its early stages appears to be nothing more than the common cold. Therefore, healthcare professionals often do not suspect or diagnose it until the more severe symptoms appear.
Later-stage Symptoms
After 1 to 2 weeks and as the disease progresses, the traditional symptoms of pertussis may appear and include:
- Paroxysms (fits) of many, rapid coughs followed by a high-pitched “whoop” sound
- Vomiting (throwing up) during or after coughing fits
- Exhaustion (very tired) after coughing fits
Pertussis in Babies
It is important to know that many babies with pertussis don’t cough at all. Instead it causes them to stop breathing and turn blue.
Pertussis can cause violent and rapid coughing, over and over, until the air is gone from your lungs. When there is no more air in the lungs, you are forced to inhale with a loud “whooping” sound. This extreme coughing can cause you to throw up and be very tired. Although you are often exhausted after a coughing fit, you usually appear fairly well in-between. Coughing fits generally become more common and bad as the illness continues, and can occur more often at night. The coughing fits can go on for up to 10 weeks or more. In China, pertussis is known as the “100 day cough.”
The “whoop” is often not there if you have milder (less serious) disease. The infection is generally milder in teens and adults, especially those who have gotten the pertussis vaccine.
Recovery
Recovery from pertussis can happen slowly. The cough becomes milder and less common. However, coughing fits can return with other respiratory infections for many months after the pertussis infection started.
References
- McNamara LA, Skoff T, Faulkner A, et al. Reduced severity of pertussis in person with age-appropriate pertussis vaccination — United States, 2010–2012. Clin Infect Dis. Epub ahead of print. 2017.
- Barlow RS, Reynolds LE, Cieslak PR, et al. Vaccinated children and adolescents with pertussis infections have decreased illness severity and duration, Oregon 2010-2012. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;58(11):1523–9.
- Stehr K, Cherry JD, Heininger U, et al. A comparative effectiveness trial in Germany in infants who received either the Lederle/Takeda acellular pertussis component DTP (DTaP) vaccine, the Ledele whole-cell component DTP vaccine, or DT vaccine. Pediatrics. 1998;101(1 Pt 1):1–11.
- Tozzi AE, Ravá L, Ciofi ML, et al. Clinical presentation of pertussis in unvaccinated and vaccinated children in the first six years of life. Pediatrics. 2003;112(5):1069–75.
- Ward JI, Cherry JD, Swei-Ju C, et al. Bordetella pertussis infections in vaccinated and unvaccinated adolescents and adults, as assessed in a national prospective randomized acellular pertussis vaccine trial (APERT). Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:151–7.
Related Page
- Page last reviewed: August 7, 2017
- Page last updated: August 7, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir