Implementation Guidebook
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Intended Audience
- Purpose
- HL7 Case Notification Implementation: Quick Steps
- HL7 Case Notification Implementation: Detailed Guidance.
- HL7 Case Notification Implementation Technical Assistance
- Appendix
ACKNOWLEDGMENT: We gratefully acknowledge staff of the Association of Public Health Laboratories, Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists, and NNDSS Modernization Initiative pilot states for their contributions to this guidebook.
Introduction
As part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Surveillance Strategy, the National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS) Modernization Initiative (NMI) is enhancing NNDSS capabilities to provide more comprehensive, timely, and higher quality data than ever before for public health decision making.
Through this multi-year initiative, CDC seeks to increase the robustness of the NNDSS technological infrastructure so that it is based on interoperable, standardized data and exchange mechanisms.
NMI has three key components:
- developing prioritized message mapping guides (MMGs) for Health Level 7 (HL7) case notifications;
- developing, maintaining, and upgrading the Message Validation, Processing, and Provisioning System (MVPS), software that validates and processes nationally notifiable disease case notification messages sent by jurisdictions and provisions the data to CDC programs; and
- providing technical assistance (TA) for implementation of HL7 case notification messages in jurisdictions submitting case notifications to NNDSS.
One of the most important processes in the NMI effort is public health agencies (PHAs) successfully implementing HL7 case notification messages based upon each of the new NNDSS HL7 MMGs developed through NMI.
Intended Audience
This guide is intended for the following audiences in PHAs:
- surveillance system administrators,
- program subject matter experts (SMEs), and
- PHA information technology (IT) staff.
Please note: This resource is not intended for PHAs who use the National Electronic Disease Surveillance System (NEDSS) Base System (NBS) for disease surveillance. NBS PHAs can learn more about their technical assistance options by emailing the CDC Electronic Data Exchange Mailbox at edx@cdc.gov.
Purpose
This guidebook provides a high-level description of the NMI implementation process and serves as a guide for PHA teams that are going through this process. For PHA program SMEs, the guidebook describes how to prepare internally for sending HL7 messages and to address potential barriers. For PHA IT staff, this document provides guidance that they can use to design and set up the PHA’s infrastructure for messaging and validation.
CDC supports NMI Technical Assistance through the Association of Public Health Laboratories (APHL) to help PHAs through the implementation process. This guidebook summarizes the TA options available to PHAs and outlines the TA process. PHAs can request technical assistance at any point in the implementation process, from assessing readiness and infrastructure through validating HL7 test messages, by sending an email outlining support needs to edx@cdc.gov.
Please note: No solution is universal. Therefore, the guidance contained in this document is advisory only. PHAs should use the guidebook to inform their approach to implementation, adapting the process where appropriate.
HL7 Case Notification Implementation: Quick Steps
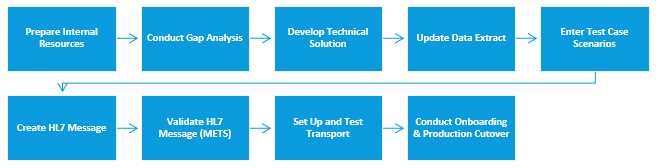
Figure 1: The steps in the HL7 case notification implementation process
This section lists the major steps involved in implementing HL7 case notification messages. See the following section(s) for further guidance on each step in this process.
- Prepare Internal Resources: Review materials and identify the technical and staffing resources to begin implementing HL7 messaging for case notification.
- Conduct Gap Analysis: Compare MMG data elements against PHA’s current surveillance system to identify available data elements needed to populate MMG fields.
- Identify and Develop Technical Solution: Review technical infrastructure and develop and document the system design for HL7 case notification messages.
- Update Data Extract/Surveillance System (if needed): If gaps exist, update the data extract so that it contains all MMG required elements and as many preferred and optional data elements as possible.
- Enter Test Case Scenarios: Enter test scenario data that CDC has developed for each MMG.
- Create HL7 Message: Transform and translate data as needed to generate valid HL7 test messages according to the test scenarios accompanying the MMG for a given condition.
- Validate HL7 Messages in METS: Validate HL7 test messages by using the Message Evaluation and Testing Service (METS) tool. The METS tool provides feedback on message structure and content. Make changes as necessary until all test messages successfully pass the METS tool without errors.
- Set Up and Test Transport: Use the PHIN Messaging System (PHINMS), or other transport services, to send case notification messages to CDC.
- Conduct MVPS Onboarding and Production Cutover: Proceed through the Message Validation, Processing, and Provisioning System onboarding and production cutover process. CDC considers a PHA ready for MPVS onboarding and cutover to production once their full suite of test messages for an MMG has passed METS validation and PHINMS has been set up and tested for connectivity.
HL7 Case Notification Implementation: Detailed Guidance
Prepare Internal resources
PHAs can take several steps to prepare for implementing HL7 messaging for case notification. Table 1 shows a preparation checklist that guides the PHA through their initial planning and helps ensure that the PHA has considered all elements of implementation:
- Collect and review NMI resources.
- Conduct readiness assessment.
- Assemble PHA implementation team.
- Gather technical documentation.
| | Readiness | Description |
| ☐ | Technical Infrastructure | The PHA’s infrastructure (i.e., the hardware, software, network resources, and related systems) should have the minimum requirements to create, generate, validate, and transport HL7 case notification messages. |
| ☐ | Test Environment | The PHA’s test environment should mimic the workflows of the production environment, and the relationship of the systems in the test environment should mirror those of the production environment. |
| ☐ | Transport | The PHIN Messaging System (PHINMS) (https://www.cdc.gov/phin/tools/PHINms/) is the preferred method of transport for HL7 case notification messages. PHAs sending HL7 messages though PHINMS will need to establish PHINMS connectivity and obtain the necessary certificates. PHAs that either cannot establish PHINMS connectivity or would like to identify alternative transport options can discuss further with CDC. |
| ☐ | Expertise/Resources | Table 2 below summarizes specific roles that are required at the PHA to implement HL7 messaging for case notifications. The level of effort for experts in each role will vary by PHA and likely by condition. In general, PHA program SMEs are primarily involved early in the process to reconcile condition-specific MMG fields with surveillance system data, while the PHA’s IT implementer is involved later to create and validate the HL7 message. |
Collect and review NMI Resources
Prior to beginning HL7 message implementation, PHAs should visit CDC’s NNDSS HL7 Case Notification Resource Center to learn more about MMG development and to confirm which MMGs are final and ready for PHAs to implement. From the resource center PHAs can download MMGs, associated artifacts, and other related documentation, including the latest PHIN Messaging Guide for Case Notification and FAQs for MMG Implementation.
Conduct Readiness Assessment
The list shown in Table 1 identifies the technical and staffing resources that each PHA should have in place to begin implementing HL7 messaging for case notification. The PHA should carefully review these resources and determine the agency’s readiness to implement case notifications. PHAs are encouraged to review and complete the NMI Infrastructure Questions to help assess internal readiness and identify needs prior to beginning implementation efforts.
Assemble PHA Implementation team
The PHA should identify the appropriate staff for each role listed below in Table 2, as well as designate an overall project champion. Project stakeholders should understand the roles and responsibilities associated with each step of implementation. The PHA should coordinate with existing staff resources to ensure resource availability and their understanding of and commitment to NMI’s project objectives and timeline.
Table 2 lists common implementation team members. Keep in mind that a PHA may need multiple contacts for each role, particularly if multiple surveillance systems are involved in the message mapping process. Individuals from the PHA also may be able to serve multiple roles on the PHA’s implementation team.
| Implementation Team Role | Name | Phone | |
| Project Lead/Champion | |||
| Lead for Integrated Surveillance System | |||
| Person Responsible for Gap Analysis | |||
| Person Responsible for Creating Electronic Messages | |||
| Person Responsible for Configuring Message Transport | |||
| Person Responsible for Data Administration of PHA Surveillance System for Conditions Covered by MMG |
Gather Technical Documentation
The technical documentation checklist in Error! Reference source not found. summarizes the artifacts that the PHA may find useful while preparing to implement HL7 case notifications. These artifacts help the PHA fully understand the current technical architecture within the agency, initiate a gap analysis, and design an appropriate technical solution.
| Technical Document | Description | |
| ☐ | Case Investigation Form(s) | Forms used by the PHA to collect case investigation information from the provider for the relevant condition(s). |
| ☐ | Example Electronic Laboratory Reporting (ELR) Message | ELR message specification used by the agency to receive ELR from laboratories; or example ELR messages. |
| ☐ | Data Extract | Example extract from the surveillance system that the PHA uses to generate the current case report for the National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (often an xml). |
| ☐ | Technical Architecture Diagrams/Workflows | Any diagrams, workflows, or other information that the PHA has outlining or describing the systems that comprise the PHA’s technical infrastructure and how these systems are integrated. |
Implementation Milestone Complete: PHA internal resource preparation completed.
Conduct Gap Analysis
During the gap analysis, the PHA compares MMG data elements (required, preferred, and optional) against the information contained in the PHA’s surveillance system and identifies the data elements needed to populate MMG fields, including:
- existing data elements,
- data elements that may be derived from script and logic creation, and
- data elements that may need to be created or added to the PHA surveillance system. (Note: Required data elements noted in the MMG must be sent as part of the HL7 case notification message. If a required data element is not present in the PHA surveillance system, it will need to be added prior to onboarding.)
The PHA may need to apply surveillance system changes to populate MMG required fields; MMG preferred and optional fields are populated if data are available.
The PHA can use the NMI Implementation Spreadsheet to help facilitate gap analysis. As Figure 2 demonstrates, this template merges information from the MMGs, NMI HL7 Message Specification, and the PHIN Vocabulary Access and Distribution System (PHINVADS). See the Implementation Spreadsheet Instructions for a detailed guide on how to use this tool.
Implementation Milestone Complete: Gap analysis template completed.
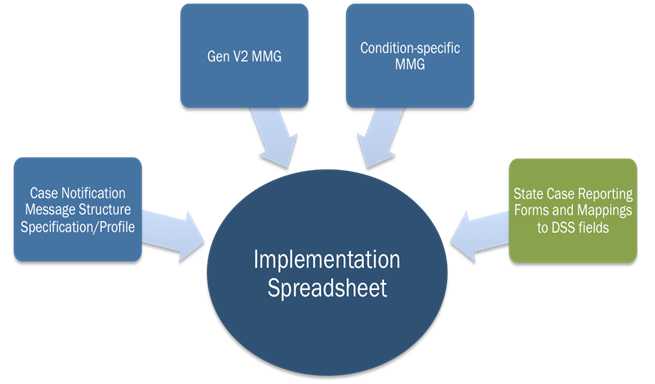
Figure 2: Sources for the National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System Modernization Initiative Implementation Spreadsheet
Identify and Develop Technical Solution
Next, the PHA will want to identify their technical solution. The technical solution will outline how the PHA system components (e.g., surveillance system, database, integration engine) will interact to build and send HL7 case notification messages to CDC. The solution will vary depending on the PHA’s existing technical architecture and messaging capabilities. The PHA may identify a need for new components, such as an additional database or data warehouse. The PHA is encouraged to document the technical architecture design for HL7 case notification messages and the process to identify new, updated, and deleted cases and to identify message actions for each case. Once the technical solution design has been identified, the PHA can develop the appropriate routes and components.
Through CDC support, APHL developed template Rhapsody and Mirth channels based on the MMG specifications that PHAs can use as a baseline to develop the route that will transform and translate data from the surveillance system to create valid HL7 messages; these routes and the associated user guides are available on the NMI Technical Assistance and Training Resource Center.
Implementation Milestone Complete: Technical solution identified and developed.
Update Data Extract/Surveillance System
The gap analysis may identify certain elements of the agency’s data extract that need to be modified to generate a valid case notification message. Once the PHA applies the required changes to its surveillance system and data extract, the updated data extract should contain all MMG elements, including required, preferred, and optional elements as available.
Implementation Milestone Complete: Data extract file updated, unit tested, and reviewed.
EnterTest Case Scenarios
CDC has developed test case scenarios for each MMG that the PHAs will use to create test HL7 messages in preparation for onboarding. Each PHA will need to enter test scenario data and generate the data extract per MMG. The test scenarios should be customized based on the agency’s local codes and information management system. The PHA uses the test scenario worksheet to record the specific data element entered in the test case scenarios. Depending on the surveillance system, the PHA may need to generate a data extract based on this test scenario document.
NOTE: The Test Scenario Worksheet is required documentation for completing the onboarding process and will be used by CDC programs to validate test messages sent through MVPS as part of the onboarding process.
Implementation Milestone Complete: Test scenarios created and test scenario worksheet completed.
Create HL7 Messages
Once the PHA has implemented the technical solution, the agency generates HL7 test messages per the test scenarios in accordance with the MMG and the Message Structure Specification for National Condition Reporting.
Implementation Milestone Complete: HL7 message produced through newly updated route.
Validate HL7 Messages in METS
The PHA generates a full suite of test messages, per the test scenarios accompanying the MMG for a given condition. At this stage, the PHA can validate generated HL7 messages by using the Message Evaluation and Testing Service (METS) Tool. The METS tool allows users to upload messages or copy and paste messages into text boxes and then provides feedback on message structure and content.
During this iterative process, the PHA will make changes as necessary to the PHA’s surveillance system, data extract, and generated HL7 test messages until all test messages successfully pass the METS tool without errors. The PHA should investigate all warnings, and, if a warning cannot be resolved (e.g., a warning for a missing optional data field that the PHA does not collect), then the PHA should document that warning and consider it expected throughout the validation process. Note that the minimum full suite of test messages will consist of the standard test messages provided by CDC.
Implementation Milestone Complete: HL7 message validation completed when the full test message suite is complete and all messages pass the METS validation tool with no errors and only expected warnings.
Set Up and Test Transport
MVPS uses the PHIN Messaging System to receive HL7 case notification messages at CDC. PHINMS is CDC-developed software that provides a secure messaging platform with a common approach to security requirements (such as encryption and authentication) and a standard method for addressing and routing content. PHAs can view specific PHINMS configuration and setup steps online at the PHINMS website.
Some PHAs are unable to use PHINMS to send case notification messages to CDC and may want to explore other transport services such as the APHL Informatics Messaging Services (AIMS) Platform. PHAs in this circumstance should contact CDC at edx@cdc.gov to discuss transport issues and determine a solution.
Implementation Milestone Complete: Transport service set up and tested.
Conduct MVPS Onboarding and Production Cutover
Onboarding Preparation:
CDC considers a PHA ready for Message Validation, Processing, and Provisioning System onboarding and production cutover once a PHA’s full suite of test messages for an MMG has passed METS validation and PHINMS has been set up and tested for connectivity. To initiate the onboarding process, the PHA sends an email to edx@cdc.gov that confirms that the PHA has completed the following steps and attaches the completed documentation listed below:
- Completed all required trainings (Secure Access Management Services [SAMS], MVPS), is able to access MVPS Dashboard, and has identified a Data Manager role in MVPS.
- Provided PHA stakeholder roles and contact information to CDC.
- Identified NNDSS diseases that are state reportable for the guide to be onboarded.
- Completed NMI Implementation Spreadsheet Condition Summary tab(s).
- Completed NMI Test Case Scenario Worksheet with jurisdiction-specific data.
- Validated that test messages have passed METS with no errors.
Onboarding Process
An NMI onboarding specialist will meet with the PHA and review the submitted onboarding readiness package (please refer to above list) and onboarding process in detail. For specific information on the onboarding process, please refer to the NMI Public Health Agency Onboarding Guidebook found at the NMI Technical Assistance and Training Resource Center.
HL7 Case Notification Implementation Technical Assistance
Technical Assistance Areas
CDC is supporting technical assistance through APHL to assist public health agencies in implementing electronic data exchange, including HL7 case notification protocols. The NMI TA Team provides services across all areas of data exchange implementation and is available for both onsite and virtual help. The TA teams work with PHA leadership, IT personnel, and epidemiology SMEs to assist in any of the following areas:
-
Project management and business analysis
- Help understand the short- and long-term goals, benefits, and challenges of HL7 case notification messaging.
- Help determine your path to completing this project, identify potential risk and needed resources, and develop a custom project plan.
- Transfer knowledge to enhance in-house capability on the use of integration engines and infrastructure management for case notifications to CDC based on MMGs.
- Provide hands-on assistance and training to build capacity to implement case notification messages and achieve production status.
-
Terminology expertise, data standards expertise, and workflow analysis
- Harmonize surveillance system terminology and incorporate nationally recognized electronic data standards into your workflow.
- Help map local vocabulary and disease surveillance system (DSS) data elements to data elements within the MMG and to PHINVADS value sets.
- Identify and explore solutions to gaps between available DSS data elements and MMG data elements.
- Help understand how, when, and why to use standard codes (e.g., LOINC, SNOMED, PHIN value sets).
-
Technical architecture and system integration expertise
- Extract data from surveillance information systems.
- Map codes in the data extract to vocabulary specified in the MMGs.
- Create HL7 messages based on the MMGs by using an integration engine (e.g., Rhapsody) or other tools.
- Facilitate secure transport of HL7 messages.
- Address security concerns.
- Provide detailed analysis of proposed solution(s).
- Use previous experience and reusable components from successful solutions in other organizations so that every implementation does not reinvent the wheel.
- Provide hands-on assistance with data exchange mechanisms and other technical architecture options.
Technical Assistance Approach
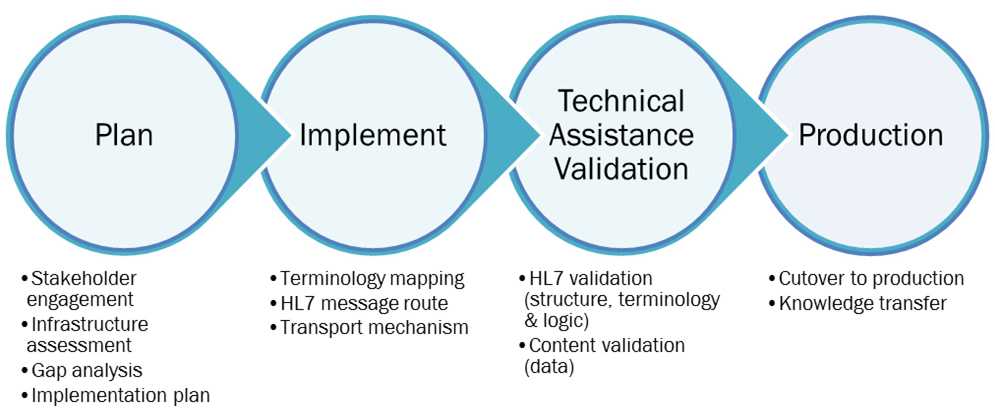
Figure 3: The HL7 case notification implementation technical assistance approach
The TA team provides customized assistance to meet the needs of each PHA. For example, some PHAs may have the internal resources and expertise to complete the implementation process independently but would appreciate a project planning consultation with the TA team, while another PHA with limited SME and/or IT resources may request hands-on assistance with the gap analysis or customizing an integration engine route. The TA team is available to guide PHAs through every step of the implementation process as described in the Detailed Guidance section above.
For PHAs that request assistance, the TA team will lead the agency’s team through the following planning exercises during the preparation step:
- Technical assistance initial call
- Readiness assessment conducted and reviewed with PHA
- Plan drafted for PHA, including proposed timeline, preliminary gap analysis, and technical solution
- Technical assistance kickoff call.
Technical Assistance Initial Call
The purpose of the initial call between the TA team and the PHA team is to collect and share baseline information about the agency’s systems and current case notification processes. Generally during this call, the TA team will discuss the agency’s responses to the Infrastructure Assessment Questionnaire to determine the resources and level of effort required for the implementation. The PHA will need to answer questions related to its technical architecture, security setup, disease surveillance system, and vocabulary (i.e., standard coding). The TA team will use the information collected to draft a plan for the PHA, including a proposed timeline, a preliminary gap analysis, and a technical solution.
Technical Assistance Milestone Complete: Initial call conducted.
Technical Assistance Kickoff Call
The second call between the TA team and the PHA team officially begins implementation work and finalizes the project plan. The kickoff call occurs when both the TA team and PHA are ready to begin work. During this call, the TA team and PHA will identify any remaining preparation to be done, develop a target implementation timeline, and establish weekly checkpoints.
Technical Assistance Milestone Complete: Kickoff call conducted.
After the kickoff call, the TA team will work with the PHA through all of the implementation steps described above in the Detailed Guidance section and provide support to meet specific needs.
How to Request Technical Assistance
PHAs may request NMI technical assistance for implementing HL7 messaging for case notifications by emailing the CDC Electronic Data Exchange mailbox at edx@cdc.gov with “NMI Technical Assistance Request” as the subject line.
Appendix
- Page last reviewed: February 3, 2017
- Page last updated: February 3, 2017
- Content source:



 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir