Accomplishments
DGMQ strives to keep Americans safe by preventing the introduction and spread of infectious disease into and within the United States. Read the accomplishment fact sheets below to learn more about how DGMQ saves lives and protects the health of our communities in a globally mobile world.
Fiscal Year 2016
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Division of Global Migration and Quarantine (DGMQ) focuses on improving the health of globally mobile populations by preventing the introduction and spread of communicable disease. From October 2015 through September 2016, DGMQ responded to public health emergencies; applied innovative technology and collaboration; modernized and maintained regulations, policy, and guidance; provided support to international and domestic partners; and conducted communication, education, and training activities to protect the public’s health. To learn more about how DGMQ impacts the health of our communities, visit: www.cdc.gov/migrationhealth.
DGMQ Responds to Public Health Emergencies
Zika Virus
- DGMQ’s Travelers’ Health Branch posted 57 Zika travel notices (Alert Level 2, “Practice Enhanced Precautions”) between October 1, 2015, and September 30, 2016, for people traveling to international destinations and US territories where Zika virus is spreading.
- DGMQ developed an interactive risk assessment tool to provide Zika messages tailored to users’ travel history and personal risk factors.
- DGMQ developed an opt-in Zika text message system to inform travelers about the status of Zika outbreaks and appropriate travel precautions. Travelers received Zika information for their destination as well as Zika prevention messages to help travelers stay healthy before, during, and after their trip.
- DGMQ conducted a risk analysis to predict countries at risk for Zika virus importation exclusively attributable to the 2016 Olympic and Paralympic Games in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The analysis was published in the MMWR: Projected Zika Virus Importation and Subsequent Transmission after Travel to the 2015 Olympic and Paralympic Games – Country Specific Assessment.
DGMQ Applies Innovative Technology and Collaboration

The interactive exhibit on refugee health highlighted clinical and public health aspects of the refugee experience from displacement to resettlement.
- The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH), DGMQ, and other partners created an interactive exhibit on refugee health, highlighting DGMQ’s role in ensuring US-bound refugees arrive healthy to the United States. The exhibit debuted at the ASTMH Annual Conference in Atlanta in November 2016.
- DGMQ collaborated with other CDC partners to release the “Mystery at the Border” outbreak scenario in CDC’s Solve the Outbreak app. This fictitious scenario is based on a binational Guillain-Barré syndrome outbreak in 2011.
- DGMQ piloted an innovative travel health awareness program, HealthTalker: Destination India, to improve acceptance of pre-travel vaccines, medicines, and preventive behaviors among high-risk travelers to India living in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut. The program relies on volunteers (HealthTalkers) to share Travelers’ Health-approved messages and resources with their social networks by word of mouth.
DGMQ Maintains Regulations, Policy, and Guidance
- On January 26, 2016, DGMQ posted a Final Rule in the Federal Register for Medical Examination of Aliens (CFR- Part 34), which became effective March 28, 2016. These regulations govern the required medical examination for US-bound immigrants and refugees.
- DGMQ published a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking on August 15, 2016, to update the current domestic (interstate) and foreign quarantine regulations for the control of communicable diseases. Amendments to the rule improve CDC’s ability to protect the public health of the United States from the introduction, transmission, and spread of communicable diseases into the United States and interstate. The Final Rule for Control of Communicable Diseases: Interstate and Foreign was published on January 19, 2017.
DGMQ Provides Support to International and Domestic Partners

Intergovernmental Panel Physicians Training Summit in Prague, Czech Republic drew a record high of more than 300 participants from around the world, from Afghanistan to Vietnam.
- DGMQ partnered with the International Panel Physicians Association and the Immigration and Refugee Health Working Group to deliver training and education to more than 300 panel physicians at the Intergovernmental Training Summit in Prague, Czech Republic.
- DGMQ and partners instituted an overseas presumptive parasite treatment and vaccination program for US-bound refugees in 2013. As of December 2016, vaccination project activities have been established in 18 countries, with 11 locations having implemented the program, including Pakistan and Indonesia in Asia; Tanzania, Burundi, Chad, and Rwanda in Africa; former Soviet Union countries, and emergency transit centers in Europe.
- DGMQ finalized an “Operational Protocol for US-Mexico Binational Communication and Coordination on Disease Notifications and Outbreaks.” This collaboration of local, state, and federal partners provided guidance for implementing standardized communication and follow-up of binational cases, as well as identification of, and response to, binational outbreaks.
DGMQ Offers Communication, Education, and Training to Protect the Public’s Health

- Through a partnership with the United States Olympic Committee, DGMQ identified top concerns for athletes, staff, and family and tailored the complex Zika guidance for these audiences. DGMQ developed customized communication materials for the Team USA Zika Prevention Playbook.
- DGMQ rolled out a new CDC course – “NPI 101: An Introduction to Nonpharmaceutical Interventions (NPIs) for Pandemic Influenza.” The web-based training assists state, tribal, local, and territorial public health professionals in preparing for, and responding to, flu pandemics through the use of NPIs.
- DGMQ developed six plain-language, pre-pandemic NPI Planning Guides for various audiences and community settings to enhance implementation of NPIs.
Fiscal Year 2014-2015
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Division of Global Migration and Quarantine (DGMQ) focuses on improving the health of globally mobile populations by preventing the introduction and spread of communicable disease. From October 2013 through September 2015, DGMQ responded to public health emergencies; modernized regulations, policy, and guidance; conducted communication, education, and training activities; provided support to state and local health departments and partners; and began outbreak response and surveillance activities. To learn more about how DGMQ saves lives and protects the health of our communities in a globally mobile world, visit: www.cdc.gov/migrationhealth.
DGMQ Responds to Public Health Emergencies
Ebola in West Africa
The Road to Zero: CDC’s Response to the West African Ebola Epidecmic 2014-2015
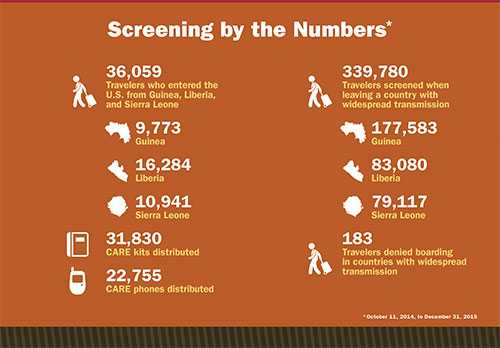
Statistics on travelers screened when leaving Ebola-affected countries in West Africa (right column), and when entering the United States (left column), between October 11, 2014, and December 31, 2015.
- DGMQ provided guidance on monitoring and movement of persons who might have been exposed to the Ebola virus. The purpose was to clarify recommendations for those considered at some risk and prevent the unneeded use of healthcare services for those with very low risk of exposure.
- DGMQ developed the CARE program (Check and Report Ebola) to help travelers monitor and report health concerns for the first 21 days upon arrival from countries with Ebola outbreaks. Team members distributed CARE Kits to travelers entering the United States through five international airports.
- DGMQ collaborated with officials in West Africa to provide assistance for exit screenings and travel restrictions in countries with Ebola outbreaks.
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) in Arabian Peninsula and South Korea

- DGMQ communication teams developed materials to educate travelers on how to protect themselves and prevent further introduction of MERS into the United States.
- DGMQ collaborated with partners to displayed electronic monitors in English and Arabic for travelers arriving from MERS-affected countries on U.S. Customs and Border Protection and CDC monitors at 13 international airports.
- DGMQ’s Travelers’ Health team provided MERS travel health notices on the CDC Travelers’ Health website specifically for persons making the Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca.
Chikungunya and Dengue in the United States-Mexico
- DGMQ created a chikungunya awareness campaign and coordinated surveillance and communication strategies with state health departments.
- DGMQ developed culturally appropriate print materials to help border residents and border crossers take precautions to avoid the mosquito-borne disease.
Unaccompanied Children from Central America Crossing into the United States

- DGMQ provided consultation in collaboration with other CDC partners on medical screenings, disease surveillance, vaccinations, and other public health issues.
- DGMQ communication teams developed health screening posters in Spanish to help children follow health and hygiene practices.
DGMQ Applies Innovative Outbreak Response and Surveillance
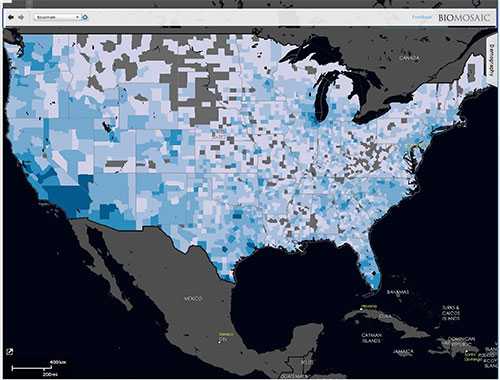
Map of the U.S. displaying travel disease patterns in BioMosaic.
- DGMQ developed BioMosaic, a web application using epidemiologic and aviation data to help forecast the next cases of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome and Ebola. The tool combines information about travel, disease patterns, and where groups of people from other countries settle in the United States, to help public health agencies direct information and services where they are needed most.
DGMQ Maintains Regulations, Policy, and Guidance
- DGMQ updated the Tuberculosis Screening and Treatment Technical Instructions using Cultures and Directly Observed Therapy for Panel Physicians (CDOT TB TIs) in 2014, to require digital images for any applicant having a chest X-ray overseas. These include persons applying for U.S. immigration status and nonimmigrants who are required to have an overseas medical examination. The requirements help physicians overseas identify more than 600 additional cases of TB each year. Research has shown a decrease in TB diagnoses after U.S. arrival.
- DGMQ staff made three visits to Cuba in 2014 and 2015 to assess required medical screenings for 20,000 U.S.-bound immigrants, refugees, and parolees a year. Re-established relations between DGMQ and the Cuban Ministry of Public Health, which oversees the panel physician program.

Director Dr. Martin Cetron provided insight about the article.
- DGMQ published Tuberculosis Incidence in Immigrants and Refugees in Annals of Internal Medicine showing the positive effect of improved diagnostic procedures on reducing the number of U.S. immigrants with tuberculosis (TB). With the new TB screening requirements issued in 2007, there was a 1/3 decrease in TB cases among foreign-born persons during their first year in the United States. Also, physicians overseas identified 629 additional cases of TB in 2012 among immigrants and refugees bound for the United States.
- DGMQ published an interim final rule in the federal register revising medical examination of aliens, including the removal of three sexually transmitted infections, and an update to reflect current medical standards and terms commonly used by public health partners.
- DGMQ published a federal register notice recommending federal travel restrictions for public health purposes. The notice describes the federal government’s tools to ensure that people with serious contagious diseases don’t board commercial flights or enter the United States without a public health evaluation.
DGMQ Offers Communication, Education, and Training to Protect the Public’s Health

Apps assist travelers in planning a healthy and safe international trip.

- The DGMQ teams expanded electronic communication at U.S. points of entry to capture the attention of 51 million travelers arriving annually. Posted health messages visible to 139,000 international travelers per day.
- DGMQ posted 96 travel notices on the Travelers’ Health website, with 65.5 million page views and 25.4 million visits from October 1, 2013 through September 30, 2015.
- DGMQ launched two mobile apps to help travelers plan safe and healthy international trips.
- DGMQ published the 2016 edition of CDC Health Information for International Travel: The Yellow Book, featuring the latest health recommendations for international travel.
- DGMQ won the ClearMark Awards of Distinction from the Center for Plain Language for Health Advisory: Ebola Outbreak.
- DGMQ co-sponsored Intergovernmental Panel Physicians Training Summits in Cape Town, South Africa (2014) and Hong Kong SAR, China (2015), which attracted 146 and 260 attendees, respectively, and presented multiple opportunities to increase the panel physicians’ knowledge of the Technical Instructions that govern the overseas medical examination.
DGMQ Provides Support to International and Domestic Partners
- DGMQ conducted a large contact investigation related to a U.S. healthcare worker diagnosed with Ebola who traveled domestically on two commercial flights from Dallas to Cleveland and back. Interviewed all 268 contacts (passengers, flight crew, and cleaning crew) to determine their risk. No secondary cases were identified.
- DGMQ conducted two large contact investigations involving four international and domestic flights and one commercial bus for travelers possibly exposed to Middle East Respiratory Syndrome. No evidence of transmission was identified among the 655 passengers and crew members.
- DGMQ founded the Zoonoses Education Coalition with the American Veterinary Medical Association, U.S. Food and Drug Administration, National Association of State Public Health Veterinarians, Pet Industry Joint Advisory Council, and other representatives from the pet industry. The Coalition develops evidence-based recommendations for safe pet handling to prevent human illness.
- DGMQ developed U.S. guidance on Ebola for airport and airlines personnel, businesses, families, healthcare workers, humanitarian aid workers, K-12 schools, laboratory workers, law enforcement professionals, responders and their loved ones, ship crew members, travelers, U.S. and other countries’ port-of-entry partners, and West African audiences.
- DGMQ researched the causes, frequency, and characteristics of unplanned school closures during a flu epidemic. This study helps communities, educators, and public health officials prepare for similar emergencies.
- DGMQ updated the Nonpharmaceutical Interventions (NPI) website with materials such as fact sheets and checklists to assist in planning for pandemic flu.
- DGMQ strengthened collaborations with Mexico City through a binational meeting to discuss binational issues such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever, dengue, and Ebola.
- DGMQ collaborated with states receiving refugees from countries with Ebola outbreaks to assure culturally appropriate follow-up upon arrival.
Fiscal Year 2013
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Division of Global Migration and Quarantine (DGMQ) puts science into action – working 24/7 to protect the health of U.S. communities.
In today’s globally connected world, one infected person can carry a disease from any place in the world to another within 24 hours. DGMQ’s initiatives support CDC’s commitment to save lives and protect people through global health security.
Detection
DGMQ surveillance initiatives serve as critical early warning systems for the emergence of biological threats, preventing the spread of disease into the United States.
- Cholera can be life-threatening. DGMQ’s laboratory surveillance in Dadaab refugee camp identified cases of infection with Vibrio cholerae O1, the bacterium that causes cholera, before any clinical cases were reported by physicians. The discovery of these cases enabled DGMQ and its partners to take preventive action and avert a large-scale outbreak.
- DGMQ began a surveillance program for diarrheal diseases along the Kenya/Somalia border (and within southern Somalia) which gives public health responders the opportunity to collect information, study data, and prevent the possible spread of disease.
- DGMQ completed evaluations for communicable disease surveillance systems for the Federated States of Micronesia and the Republic of the Marshall Islands, which helped to further develop health information systems and surveillance in the Western Pacific.
- DGMQ worked with partners to identify illness and notify nearly 2,000 airline passengers that they had been exposed to contagious diseases on flights, directing travelers to their providers for care, treatment, and vaccination.
Response
DGMQ’s response initiatives involve rapid and targeted interventions to prevent the spread of disease.

Women carrying water in Dadaab refugee camp
- Polio was eliminated in the United States in 1979, but outbreaks have been occurring among displaced mobile populations in the Middle East and the Horn of Africa where the disease has not been seen in years. This rise in polio cases poses a global threat and increases the possibility that the disease may be brought into the United States. DGMQ joined partners to conduct mass vaccinations in Kenya’s Dadaab refugee camp, and DGMQ led the implementation of a program to vaccinate all U.S.-bound Kenyan refugees. These programs prevent the spread of disease and protect Americans at home and abroad.
- DGMQ delivered 110 life-saving medications for malaria and botulism to critically ill U.S. patients, saving precious hours in the treatment of these life-threatening conditions.
- DGMQ mobilized to lead border and travel health preparedness initiatives to safeguard public health for a new strain of bird flu (H7N9) and a new virus in the same family as SARS coronavirus (MERS-CoV). DGMQ staff developed the following:

Arriving international travelers read a MERS-CoV health advisory on a TravAlert monitor.
- guidance and communication materials for international travelers and U.S. citizens living in regions of the world affected by H7N9 and MERS-CoV;
- protocols to investigate possible disease transmission on airplanes;
- guidance and training for airport partners to heighten awareness about sick travelers and to facilitate reporting to CDC.
Prevention
DGMQ’s prevention activities save lives by preventing disease from coming into the United States and by protecting travelers abroad.
- A pilot overseas vaccination and parasitic treatment program conducted in Thailand, Malaysia, Nepal, and Kenya prevents incoming refugees from acquiring vaccine-preventable diseases and cures them of intestinal parasites and malaria before their arrival in the United States. This DGMQ initiative also prevents the introduction of disease into the United States, reducing the burden on state and local health departments.
- More than 36,000 refugees in the Mae La refugee camp on the Thailand/Burma border were vaccinated against cholera by DGMQ and international partners. Vaccinating refugees reduces the likelihood that disease will be introduced and spread into the United States.
- DGMQ research, conducted with partners through Global TravEpiNet, a network of travel clinics, demonstrated that insurance providers can save substantial costs by focusing on malaria prevention rather than treatment.
- DGMQ published the 2014 CDC Health Information for International Travel (the Yellow Book) in print, ebook, app, and web formats. The Yellow Book is the definitive guide for travel-medicine providers seeking information about health risks around the globe and how to prevent them.
- DGMQ’s new and improved Travelers’ Health website (www.cdc.gov/travel) provides comprehensive, targeted content for travelers, clinicians, and high-risk groups.
- Awareness is a key component of prevention. DGMQ expanded CDC’s electronic messaging capability by equipping selected high-traffic airports and ports of entry with TravAlert monitors. These monitors provide up-to-date, disease-specific alerts to arriving international travelers. Monitors located at airports where quarantine stations are staffed can reach up to 139,000 international travelers each day and nearly 51 million a year.
- Information, resources, and guidelines about U.S.-Mexico public health are at the forefront of DGMQ’s comprehensive new website, www.cdc.gov/USMexicoHealth.
Fiscal Year 2012
Protecting the health of our communities in a globally mobile world

Refugee receiving a single-dose presumptive treatment for Strongyloides infection.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Division of Global Migration and Quarantine (DGMQ) works 24/7 to keep Americans safe by preventing the introduction and spread of infectious disease into and within the United States. From October 2011 through September 2012, DGMQ saved lives and protected Americans by putting science into action, keeping communities safe through health security and preparedness, and strengthening communities through partnerships with state and local health departments.
DGMQ Puts Science into Action
- DGMQ strengthened overseas tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis and treatment by expanding the use of the 2007 Culture and Directly Observed Therapy (CDOT) TB Technical Instructions to 62 countries. In 2012, use of the CDOT TB Technical Instructions for screening immigrants and refugees resulted in a 200% increase in diagnosis and treatment for TB cases and an annual cost savings of more than $30 million in U.S. health care costs.
- DGMQ completed a one-year trial treatment program to prevent Strongyloides infection for more than 6,000 Burmese refugees resettling to the United States from Thailand. Strongyloides is a parasitic infection causing gastrointestinal illness and in severe cases can lead to death. The results of the trial program will lead to expanding this effort to cover other U.S.-bound refugees.
- DGMQ vaccinated over 10,000 U.S.-bound Burmese refugees for measles, mumps, and rubella, because of their exposure to an outbreak of measles while living in Kuala Lumpur.
- Following evaluations conducted in 2010-2011, DGMQ modified protocols for communicable disease contact investigations on airplanes to improve cost-effectiveness. Changes in the TB investigation protocol resulted in an estimated 50% decrease in work burden to state and local health departments without increasing health risks to travelers.
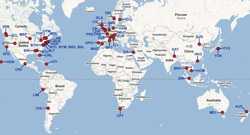
GeoSentinel surveillance sites, which helped to identify the largest recorded Sarcocystis infection outbreak in humans.
- DGMQ’s partnership with GeoSentinel, a worldwide network for monitoring travel-related illnesses, led to the discovery of the largest recorded Sarcocystis infection outbreak in travelers returning from Tioman Island, Malaysia. This disease is typically found in animals, and little is known about how it affects humans. The partnership with GeoSentinel is providing clinicians with new information to help protect the health of overseas travelers.
DGMQ Keeps You Safe through Health Security and Preparedness
- DGMQ coordinated the development of The Technical Guidelines for United States-Mexico Coordination on Public Health Events of Mutual Concern, endorsed by the U.S. Health and Human Services Secretary and the Mexico Secretary of Health. The guidelines call for the two neighboring countries to work together on shared public health events and emergencies, such as outbreaks of disease that cross borders.
- By training over 3,300 Customs and Border Protection officers, DGMQ enhanced its ability to detect communicable diseases in people and CDC- regulated animals and animal products entering the United States, resulting in responses to 1,020 illness reports. DGMQ also partnered with state and local health departments to conduct over 40 training exercises and provide upgraded plans to respond to reports of infectious diseases at the 329 ports of entry into the United States.

A girl covers her nose and mouth with a tissue while sneezing, practicing one of several nonpharmaceutical interventions highlighted on www.cdc.gov/npi.
- DGMQ developed a health profile for Bhutanese refugees resettling in the United States. With close to 65,000 Bhutanese refugees arriving in 2012 and an estimated 12,000 in 2013, this profile provides key health and cultural information that assists resettlement agencies, clinicians, and public health providers in facilitating appropriate medical screening and treatment for Bhutanese refugees.
- DGMQ launched the Nonpharmaceutical Interventions (NPIs) website, which provides information on preventive actions people and communities can take to avoid getting sick from illnesses like influenza (flu) and to limit the spread of flu during a pandemic.
- DGMQ launched a CDC Travel Health Twitter channel @CDCtravel providing information to protect the health of U.S. residents traveling and living abroad. To date it has about 2200 followers.
DGMQ Strengthens Your Community
- DGMQ awarded approximately $900,000 to state and county health departments, universities, and nonprofit organizations to conduct disease surveillance in refugee populations and evaluate health programs to support the detection, prevention, and control of diseases affecting refugees. The findings will be used by state and local health departments to determine policy changes for refugee health.
- DGMQ staff in Hawaii helped coordinate the rapid on-the-ground response to dengue outbreaks in the Federated States of Micronesia and the Republic of the Marshall Islands, facilitating a unified outbreak response by U.S. federal agencies and the governments of these island nations.
- DGMQ provided technical assistance to agencies serving Iraqi refugees and conducted an investigation of suicides in Bhutanese refugees to understand suicide risk factors and improve the mental health status of Iraqi and Bhutanese refugees in the United States. The recommendations were used to enhance access to care, help communities where the suicides occurred create a standardized suicide reporting system, provide suicide prevention and awareness trainings, encourage nonmedical interventions, and conduct outreach to refugee communities.
Fiscal Year 2011
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Division of Global Migration and Quarantine (DGMQ) focuses on improving the health of globally mobile populations to prevent the introduction, transmission, and spread of communicable diseases. From October 2010 through September 2011, DGMQ responded to emergencies, modernized regulations and policy, conducted communication and training, provided support to state and local partners, and implemented outbreak response and surveillance.
Responded to Public Health Emergencies
Cholera in Haiti
-

Measles Health Advisory on an electronic monitor at O'Hare International Airport.
Distributed approximately 73,000 Travel Health Alert Notices (T-HANs) in four languages to travelers arriving from Haiti at four U.S. airports.
- Conducted an evaluation of the cholera T-HAN and found that reading the T-HAN can influence travelers to seek medical attention after they arrive in the United States.
- Investigated the risk of cholera spread through seafood by water released from ships, resulting in cholera prevention recommendations to the International Maritime Organization for cargo ships departing from Haiti.
Earthquake in Japan
- Responded to the Japan earthquake, tsunami, and radiation disaster by developing health information and guidance documents for travelers and U.S. citizens living in Japan.
- Developed enhanced radiation screening and decontamination protocols for travelers arriving from Japan, which resulted in U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) screening nearly 550,000 travelers.
Measles around the World
- Developed health messages in response to the increase in measles around the world, which were posted on electronic monitors by CBP at 18 U.S. international airports, providing a measles advisory to over 2.7 million arriving international travelers each month.
- Demonstrated that electronic messaging is less expensive, $1,050 compared with $180,000 to print SARS T-HANs in 2003, more environmentally friendly, and a faster method of reaching more travelers than traditional print methods.
Modernized Regulations, Policy, and Guidance
- Developed “Guidance for School Administrators to Help Reduce the Spread of Seasonal Influenza in K-12 Schools during the 2010-11 School Year” and “How to Clean and Disinfect Schools to Help Slow the Spread of Flu Guide” in English and Spanish.
- Developed 5 new guidelines for U.S. Domestic Medical Examination for Newly Arriving Refugees, which are available on a new website, Guidelines for the U.S. Domestic Medical Examination for Newly Arriving Refugees.
- Implemented the Technical Instructions for Tuberculosis Screening and Treatment using Cultures and Directly Observed Therapy in eight additional countries, resulting in improved screening of 68% of all refugees and immigrants coming to the United States and leading to an increased rate of TB diagnosis.
Conducted Communication, Education, and Training Activities
-

Cover of 2012 Yellow Book
Published the 2012 version of the CDC Health Information for International Travel: The Yellow Book, regarded as the gold standard travel medicine reference for health care providers.
- Posted 42 travel notices on the Travelers’ Health website, which was ranked 6th among all CDC sites, with over 23 million page-views and 5.6 million visits.
- Conducted training summits in Thailand and Peru and launched a Panel Physician Portal, to provide information for panel physicians who implement the required medical screening for U.S. immigration applicants.
- Posted flu materials for refugee populations in 11 languages on Immigrant and Refugee Resources.
- Launched an International Adoption website to provide guidance on health-related immigration processes for adopting a child from other countries.
- Expanded the infectious disease surveillance system network and developed a training package for refugee camp medics to provide primary health care, hygiene, and sanitation in nine refugee camps along the Thailand-Myanmar border.
Provided Support to State and Local Health Departments
- Conducted 135 contact investigations, involving 190 flights, for travelers exposed to infectious diseases.
- Sent out 1,216 notifications to state and local public health partners for 4,641 people who were exposed to communicable diseases during air travel.
- Evaluated the Chicago Quarantine Station’s referral program for arriving immigrants with TB, demonstrating a 400% increase in starting their medical follow-up and timeliness in getting to a local health department.
- Completed a review of communicable disease response plans for all CDC Quarantine Stations, and conducted seven communicable disease response exercises with port, state health, and local health partners.
Implemented Outbreak Response and Surveillance Activities
-

The Dadaab lab in Kenya contains state-of-the-art equipment to better diagnose common pathogens.
From October 2010 to September 2011, the GeoSentinel network, a worldwide surveillance system for travel-related illness, surpassed 150,000 records, with 196,000 final diagnoses covering traveler exposures in over 237 countries.
- Conducted surveillance of respiratory diseases, diarrhea, fever, and dengue in refugee camps in Kenya.
- Responded and provided technical assistance to over a dozen disease outbreaks (including cholera, dengue, diphtheria, malaria, measles, meningitis, mumps, rubella, and varicella) in refugee camps and migrant populations throughout Africa and Asia.
- Responded to rabies exposures among travelers exposed to a rabid zebra at a safari lodge in Kenya.
- Conducted an investigation of dengue cases in travelers returning from missionary work in Haiti.
- Responded to and investigated binational US-Mexico outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease and Guillain-Barre syndrome.
- Launched the Bio-Mosaic Project, designed to map the demographic and migration health data of foreign-born populations in the United States for 105 countries of birth and to assess the risk of international spread of infectious diseases.
- Opened a clinical laboratory in the Dadaab refugee camp in Kenya; the new lab allows swifter lab confirmation of potential outbreaks and detection of new pathogens in the camp, and minimizes importation of infections to the United States.
- Coordinated a multistate and international outbreak investigation for imported measles cases in refugees, leading to recommendations and implementation of measles vaccinations for all refugees from Malaysia.
Fiscal Year 2010
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Division of Global Migration and Quarantine (DGMQ) focuses on improving the health of globally mobile populations to prevent the introduction, transmission, and spread of communicable diseases.
From October 2009 through September 2010, DGMQ achieved accomplishments in the areas of emergency response, regulations and policy, communication, education, training, state and local public health support, international partnerships, outbreak response, surveillance, and preparedness.
Responded to 2009 H1N1 Flu

Poster from the national campaign for 2009 H1N1 flu.
- Initiated 16 studies throughout the United States and internationally, collaborating with state and international partners on community measures.
- Conducted surveys at binational ports of entry and with travelers to the Hajj, an investigation of a flu outbreak on a cruise ship and a contact investigation of air travelers, and an international multisectoral survey of public health border measures, in collaboration with the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Implemented a national communications campaign to raise awareness of ways to prevent the spread of flu during travel, covered in more than 50 newspaper outlets, 68 television broadcasts, and 80 websites.
- Identified key improvements to guidance for community settings (schools, universities, childcare programs, and businesses) through needs assessment and evaluation.
- Developed train-the-trainer workshops in Guatemala and Peru for governmental, nonprofit, and media representatives from 11 Latin American nations.
Responded to Earthquake in Haiti
- Posted a Travel Warning and guidance documents for health-care providers, relief workers, and adoptive parents that received over 100,000 web page views.
- Provided active response operations through extended deployments of staff to Haiti.
- Obtained arrival information about flights from Haiti to enable support and response.
- Provided direct support to repatriation activities in airports across the United States.
- Distributed Travel Health Alert Notices in English, French, and Creole for people arriving from Haiti at various airports throughout the country.
- Conducted survey of adoptive parents and health-care providers to determine the influence of recent CDC recommendations for medical screening of Haitian parolees.
Modernized Regulations and Policy
- In December 2009, instituted new vaccination criteria for immigrants to the United States, based on public health impact.
- In January 2010, published a final rule removing HIV infection from the list of diseases that can keep people who are not U.S. citizens from entering the United States.
- On June 1, 2010, published the Technical Instructions for Physical or Mental Disorders to clarify that diagnosis must be based on current medical standards.
Conducted Communication, Education, and Training Activities

Group picture at the FOTC kick-off in Miami, Florida. Image courtesy of David Hunter.
- The Division’s Travelers’ Health website, where 45 new or updated travel notices were posted, was ranked 5th among all CDC sites, with 24.9 million page-views and over 7 million visits during FY 2010.
- Launched the Field Operations Training Center (FOTC) in Miami to deliver standardized training to improve operations at all 20 CDC Quarantine Stations and outreach to federal, state, and local partners.
- Implemented training summits for physicians who conduct required medical screening for US immigration applicants, in India, Ghana, and the Dominican Republic, attended by 109 physicians from 33 countries and 26 consular officers from 14 countries.
Provided Support to State and Local Health Departments
- Exceeded the goal of notifying state health departments within 21 days of an immigrant’s or refugee’s arrival into the country, using the Electronic Disease Notification system to transmit more than 100,000 notifications.
- Conducted 104 contact investigations, involving 145 flights, for travelers exposed to infectious diseases.
- Of 48 people who were removed from federal travel restrictions, 42 either started or continued TB treatment.
- Amending the tuberculosis (TB) Technical Instructions in 2007 to require culture testing, which increased diagnoses of TB in refugees and immigrants to approximately 1,000 cases, and provided greater than $30 million in savings to state and local health departments.
Implemented Outbreak Response, Surveillance, and Preparedness Activities

Kakuma refugee camp in Kenya. Image courtesy of Terry Comans.
- Developed risk assessment reports for the January 2010 Haiti earthquake response, the 2010 South Africa World Cup, and the 2010 World Expo in Shanghai.
- Provided the World Health Organization and countries in Europe with technical assistance to support emergency risk assessment and surveillance planning for the 2010 polio outbreak in Tajikistan.
- From October 2009 to August 2010, the GeoSentinel network, a worldwide surveillance system for travel-related illness, surpassed 130,000 records with 167,532 final diagnoses covering traveler exposures in over 237 countries.
- Conducted respiratory surveillance in 2 refugee camps in Kenya, enrolling over 4,000 people and detecting 2009 H1N1 in this population.
- Responded to 9 disease outbreaks (including cholera, dengue, H1N1, malaria, measles, meningitis, mumps, and varicella) in refugee camps.
- Completed entry screening and communicable disease preparedness plans for all CDC Quarantine Stations, and conducted 10 exercises for port of entry response with port and state and local health partners.
- Page last reviewed: March 16, 2017
- Page last updated: March 16, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir


