
Case #288 - November, 2010
A 50-year-old man underwent a screening colonoscopy after complaints of constipation. A polyp measuring approximately 3 mm was observed during the procedure. A biopsy of the polyp was taken and sent to a pathology laboratory for sectioning and staining. Figures A-D show what was observed by the attending pathologist. The image in Figure A was captured at 40x magnification. The images in Figures B and C were captured at 100x magnification. The image in Figure D was captured at 400x magnification. What is your diagnosis? Based on what criteria?
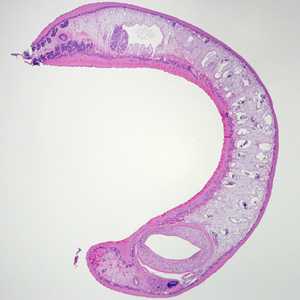
Figure A
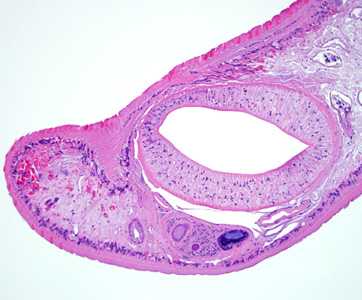
Figure B
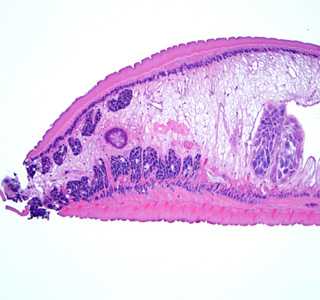
Figure C
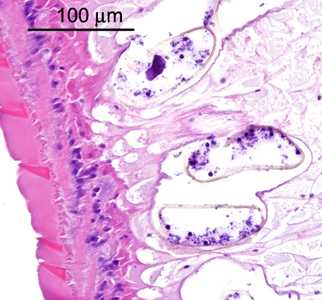
Figure D
Case Answer
This was a case of echinostomiasis caused by an intestinal fluke in the genus, Echinostoma. Diagnostic morphologic features included:
- an elongate habitus (Figure A).
- the presence of an oral sucker, or acetabulum (AC, Figure B), located near the anterior end of the fluke.
- the presence of vitelline glands along lateral margins (VT, Figure C).
- lobed testes located in the medial posterior region of the body (TE, Figure C).
- eggs (Figure D) within the uterus that are within the size range for the Echinostoma spp.
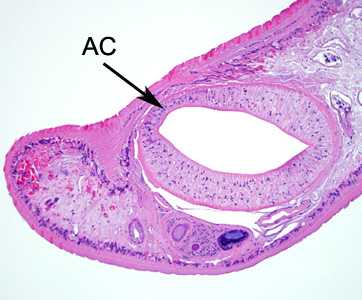
Figure B
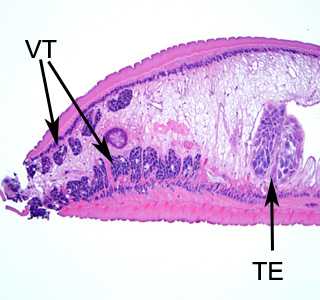
Figure C
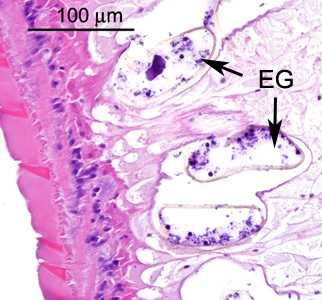
Figure D
More on: Echinostomiasis
Images presented in the monthly case studies are from specimens submitted for diagnosis or archiving. On rare occasions, clinical histories given may be partly fictitious.
DPDx is an education resource designed for health professionals and laboratory scientists. For an overview including prevention and control visit www.cdc.gov/parasites/.
- Page last reviewed: August 24, 2016
- Page last updated: August 24, 2016
- Content source:
- Global Health – Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria
- Notice: Linking to a non-federal site does not constitute an endorsement by HHS, CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the site.
- Maintained By:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir