What We Know About Indoor Tanning Among Minors
Indoor tanning increases skin cancer risk. The risk of skin cancer increases with each indoor tanning session and is highest among those who start tanning at a younger age.11, 12
Indoor tanning begins during youth. Indoor tanning often begins during adolescence and increases with age until the late teens or early- to mid-20s.23 Nearly one out of every three white high school girls tans indoors each year. Some start tanning as early as age 14, or even younger, as shown below.
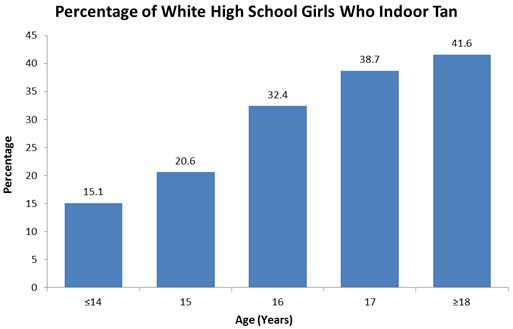
Many white high school girls tan indoors frequently. Girls are more likely to tan indoors than boys, and non-Hispanic whites are more likely to tan indoors than members of other racial and ethnic groups.24 Most indoor tanners report tanning frequently (10 or more times per year).25
Parents influence indoor tanning. Adolescents whose parents tan indoors or allow them to tan indoors are more likely to report indoor tanning themselves.26 Girls who first tan indoors with their mothers tend to start at a younger age and are more likely to become habitual indoor tanners than girls who initially tan indoors alone or with a friend.27
For indoor tanners, the short-term cosmetic effects of tanning may be more apparent than the many long-term health risks:
Malignant Melanoma
Basal and Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Wrinkles and Age Spots
Cataracts, Macular Degeneration, and Other Eye Damage
- Page last reviewed: April 26, 2017
- Page last updated: January 13, 2015
- Content source:
- Maintained By:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir