What Is Skin Cancer?
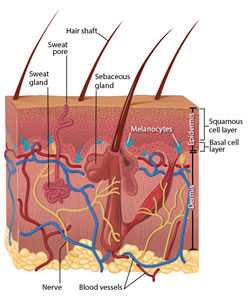
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Click to see a larger diagram.
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. The two most common types of skin cancer—basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas—are highly curable, but can be disfiguring and costly to treat. Melanoma, the third most common skin cancer, is more dangerous and causes the most deaths. The majority of these three types of skin cancer are caused by overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) light.
Ultraviolet (UV) Light
Ultraviolet (UV) rays are an invisible kind of radiation that comes from the sun, tanning beds, and sunlamps. UV rays can penetrate and change skin cells.
The three types of UV rays are ultraviolet A (UVA), ultraviolet B (UVB), and ultraviolet C (UVC)—
- More UVA rays reach the earth’s surface than the other types of UV rays. UVA rays can reach deep into human skin, UVA rays can damaging connective tissue and the skin’s DNA.
- Most UVB rays are absorbed by the ozone layer, so fewer of them reach the earth’s surface compared to UVA rays. UVB rays, which help produce vitamin D in the skin, don’t reach as far into the skin as UVA rays, but they can still cause sunburn and damage DNA.
- UVC rays are very dangerous, but they are absorbed completely by the ozone layer and do not reach the earth’s surface.
In addition to causing sunburn, too much exposure to UV rays can change skin texture, cause the skin to age prematurely, and can lead to skin cancer. UV rays also have been linked to eye conditions such as cataracts.
The National Weather Service and the Environmental Protection Agency developed the UV Index to forecast the risk of overexposure to UV rays. It lets you know how much caution you should take when spending time outdoors.
The UV Index predicts exposure levels on a 0 to 15 scale; higher levels indicate a higher risk of overexposure. Calculated on a next-day basis for dozens of cities across the United States, the UV Index takes into account clouds and other local conditions that affect the amount of UV rays reaching the ground.
More Information
- Skin Cancer (National Cancer Institute)
- NCI Video: Minorities and Skin Cancer Awareness
- Page last reviewed: April 25, 2017
- Page last updated: April 25, 2017
- Content source:
- Maintained By:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir