Metildigoxin
Metildigoxin (INN, or medigoxin BAN, or methyldigoxin) is a cardiac glycoside,[1] a type of drug that can be used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat). The substance is closely related to digoxin; it differs from the latter only by an O-methyl group on the terminal monosaccharide.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
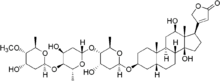
| Other names | 4-[(3S,5R,8R,9S,10S,12R,13S,14S)-12,14-Dihydroxy-3-[(2R,4S,5S,6R)-4-hydroxy-5-[(2S,4S,5S,6R)-4-hydroxy-5-[(2S,4S,5S,6R)-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-6-methyl-oxan-2-yl]oxy-6-methyl-oxan-2-yl]oxy-6-methyl-oxan-2-yl]oxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,15,16,17-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.045.705 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C42H66O14 |
| Molar mass | 794.965 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Hayward, R.; Greenwood, H.; Stephens, J.; Hamer, J. (1983). "Relationship between myocardial uptake and actions in heart failure of methyldigoxin". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 15 (1): 41–48. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01461.x. PMC 1427830. PMID 6849743.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.