Lymphoepithelioma
Lymphoepithelioma is a type of poorly differentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma characterized by prominent infiltration of lymphocytes in the area involved by tumor. Lymphoepithelioma is also known as "class III nasopharyngeal carcinoma" in the WHO classification system. It has a high tendency to metastasize and is responsive to radiotherapy. Most cases are associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection.[1]
| Lymphoepithelioma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Schmincke-Regaud tumor |
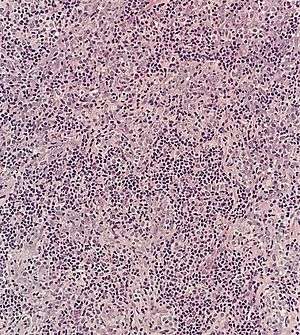 | |
| Nasopharyngeal lymphoepithelioma in a lymph node. Note the small, blue lymphocytes between the larger cancer cells. | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinomas are carcinomas that arise outside of the nasopharynx, but resemble a lymphoepithelioma histologically. Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinomas may be found in almost any epithelial organ, including the lung, thymus, breast, colon, endometrium, prostate, and skin,[1] as well as urinary bladder, trachea, esophagus, stomach, salivary glands, vulva.[2]
History
Lymphoepithelioma may also be referred to as Schmincke-Regaud tumor, after the German pathologist Alexander Schminke and French radiologist Claude Regaud.
References
- Richard Cote, Saul Suster, Lawrence Weiss, Noel Weidner (Editor). Modern Surgical Pathology (2 Volume Set). London: W B Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-7253-1.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- Juan Rosai. Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology. 9th edition