Mucinous cystadenoma
Mucinous cystadenoma is a benign cystic tumor lined by a mucinous epithelium. It is a type of cystic adenoma (cystadenoma).
| Mucinous cystadenoma | |
|---|---|
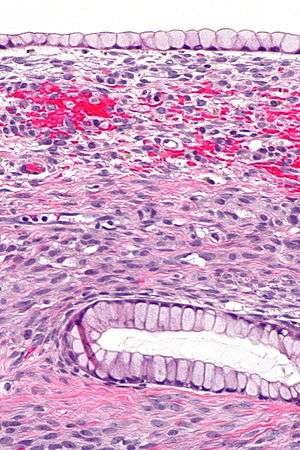 | |
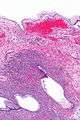
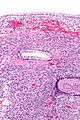
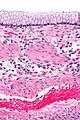
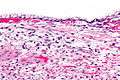
| Micrograph showing a mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
Mucinous cystadenomata may arise in a number of locations; however, mucinous cystadenoma at different locations are not generally considered to be related to one another.
Overview
Mucinous cystadenomas may be found in the:
- Ovary—ovarian mucinous cystadenoma
- Pancreas—pancreatic mucinous cystadenoma
- Peritoneum—peritoneal mucinous cystadenoma
- Liver—mucinous cystadenoma of the liver[1]
- Vermiform appendix—appendiceal mucinous cystadenoma (see cystadenoma)
Ovarian mucinous cystadenoma
Mucinous cystadenomas make up 15–20% of all ovarian tumors. They often become very large and can extend up into the abdomen.
These tumors are usually evaluated using ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. Findings on imaging studies are nonspecific. These ovarian tumors are usually multi-septated, cystic masses with thin walls. They also contain varying amounts of solid tissue which consists of proliferating stromal tissue, papillae, or malignant tumor cells.
Benign mucinous cystadenomas compose 80% of mucinous ovarian tumors[2] and 20–25% of benign ovarian tumors overall. The peak incidence occurs between 30 and 50 years of age. Benign tumors are bilateral in 5–10% of cases.
Macroscopy
Microscopy
Pancreatic Mucinous Cystadenoma
Pancreatic Mucinous Cystadenoma or Mucinous Cystadenoma of the pancreas (MCN) are a type of mucinous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas.[3] The cure rate is very high in cases on benign cystic lesions, but the case changes if malignant changes ensue.[4] Benign cystadenomas are the most common cystic tumors of the pancreas accounting for 75% of the cases. On an average, mucinous accounts for 40%-50% of cystic tumors, and serous cytadenoma accounts for 30% of it. Mucinous cystadenomas are in the dital pancreas in about 80% of the cases and distal pancreatectomy is needed for resection.[4] In 20% of the cases it is in the head of the pancreas.[3]
Primary Retroperitoneal Mucinous Cystadenoma
Cases of primary retroperitoneal mucinous cystadenom (PRMC) are extremely rare. However, they are observed more frequently in women, with only 4 cases having been found in men.[6] Even though mucinous cystadenoma are common ovarian tumor, what makes PRMC so rare is their retroperitoneal location.
PRMC and benign mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary are microscopically similar. Both are multiloculated cystic neoplasms and are lined by a single layer of tall columnar cells with a clear basal nucleus and cytoplasm. Both of them have identical histochemical and ultrastructural features.[7] Flat to low cuboidal cells, resembling mesothelial cells, in the lining interspersed between columnar cells in the same area is the only histological difference between the two tumors.[7]
Mucinous Cystadenoma Of The Liver
A rare neoplasm, 95% cases occur in women, especially at the mean age of 45.[8] Biliary cystadenoma and cystadenocarcinoma constitute less than 5% of intrahepatic cysts originating from the bile duct.[8]
Cystadenomas in liver are often confused with hydatid cyst as their appearance on various imaging techniques is nearly same.[9] Treating cystadenomas as hydatid cyst has resulted in recurrence of the cyst.[9]
See also
References
- Grubor, NM.; Colovic, RB.; Atkinson, HD.; Micev, MT. (2013). "Giant biliary mucinous cystadenoma of the liver". Ann Hepatol. 12 (6): 979–83. doi:10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31306-7. PMID 24114831.
- Hart WR (January 2005). "Mucinous tumors of the ovary: a review". Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 24 (1): 4–25. PMID 15626914.
- Weerakkody, Yuranga. "Mucinous cystadenoma of the pancreas | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2019-09-21.
- Weledji, Elroy P.; Eyongetah, Divine; Nana, Theophile C.; Ngowe, Marcelin N. (February 2018). "Excision of mucinous cystadenoma of pancreas is safe and effective: a case report". IJS Oncology. 3 (2): e47. doi:10.1097/IJ9.0000000000000047. ISSN 2471-3864.
- "Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)". www.pathologyoutlines.com. Retrieved 2019-09-21.
- Lee, Seok Youn; Han, Weon Cheol (February 2016). "Primary Retroperitoneal Mucinous Cystadenoma". Annals of Coloproctology. 32 (1): 33–37. doi:10.3393/ac.2016.32.1.33. ISSN 2287-9714. PMC 4783510. PMID 26962534.
- Subramon, Habibpour, Hashimoto, Charu, Saied, Louis A (2001). "Retroperitoneal Mucinous Cystadenoma". https://www.archivesofpathology.org/. 125: 691. doi:10.1043/0003-9985(2001)125<0691:RMC>2.0.CO;2 (inactive 2019-12-04). ISSN 0003-9985. External link in
|website=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Biliary cystadenoma". www.pathologyoutlines.com. Retrieved 2019-09-21.
- Ahmad, Zubair; Uddin, Nasir; Memon, Wasim; Abdul-Ghafar, Jamshid; Ahmed, Arsalan (2017-11-10). "Intrahepatic biliary cystadenoma mimicking hydatid cyst of liver: a clinicopathologic study of six cases". Journal of Medical Case Reports. 11 (1): 317. doi:10.1186/s13256-017-1481-2. ISSN 1752-1947. PMC 5680786. PMID 29121977.

.jpg)