Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm
The lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve (or lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm) (branch of musculocutaneous nerve, also sometimes spelled "antebrachial") passes behind the cephalic vein, and divides, opposite the elbow-joint, into a volar and a dorsal branch.
| Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm | |
|---|---|
Diagram of segmental distribution of the cutaneous nerves of the right upper extremity. Anterior view. ("Lat. antebrach. cutan." visible in purple.) | |
| Details | |
| From | Musculocutaneous nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus cutaneus antebrachii lateralis |
| TA | A14.2.03.026 |
| FMA | 39080 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Volar branch
The volar branch (ramus volaris; anterior branch) descends along the radial border of the forearm to the wrist, and supplies the skin over the lateral half of its volar surface.
At the wrist-joint it is placed in front of the radial artery, and some filaments, piercing the deep fascia, accompany that vessel to the dorsal surface of the carpus.
The nerve then passes downward to the ball of the thumb, where it ends in cutaneous filaments.
It communicates with the superficial branch of the radial nerve, and with the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve.
Dorsal branch
The dorsal branch (ramus dorsalis; posterior branch) descends, along the dorsal surface of the radial side of the forearm to the wrist.
It supplies the skin of the lower two-thirds of the dorso-lateral surface of the forearm, communicating with the superficial branch of the radial nerve and the dorsal antebrachial cutaneous branch of the radial nerve.
See also
Additional images
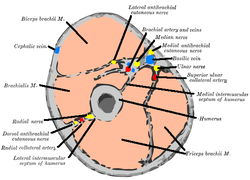 Cross-section through the middle of upper arm.
Cross-section through the middle of upper arm.- Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.
- Cutaneous nerves of right upper extremity. Anterior view.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 936 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Lateral_antebrachial_cutaneous_nerve at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
- lesson2superficveinsupperlimb at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University), lesson5nervesofpostforearm at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- EatonHand ner-097
- Anatomy figure: 06:03-08 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Cutaneous nerves of the upper extremity."
- Hand kinesiology at the University of Kansas Medical Center