Bucillamine
Bucillamine is an antirheumatic agent developed from tiopronin. It is mainly used in Japan and Korea. Activity is mediated by the two thiol groups that the molecule contains. Research done in USA showed positive transplant preservation properties.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
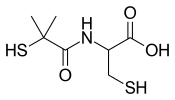
| IUPAC name
2-[(2-Methyl-2-sulfanylpropanoyl)amino]-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | bucillamine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C7H13NO3S2 |
| Molar mass | 223.31 g·mol−1 |
| log P | 1.032 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.012 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 10.985 |
| Pharmacology | |
| M01CC02 (WHO) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related Alkanoic acids |
|
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Amersi, F.; Nelson, S. K.; Shen, X. D.; Kato, H.; Melinek, J.; Kupiec-Weglinski, J. W.; Horwitz, L. D.; Busuttil, R. W.; Horwitz, M. A. (2002). "Bucillamine, a Thiol Antioxidant, Prevents Transplantation-Associated Reperfusion Injury" (pdf). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 99 (13): 8915–8920. doi:10.1073/pnas.132026099. PMC 124398. PMID 12084933.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.