Acute prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is a serious bacterial infection of the prostate gland. This infection is a medical emergency. It should be distinguished from other forms of prostatitis such as chronic bacterial prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS).
| Acute Prostatitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Prostatitis - bacterial[1] |
 | |
| Specialty | Urology |
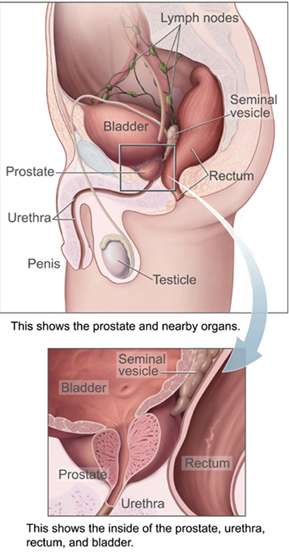
Signs and symptoms
Men with acute prostatitis often have chills, fever, pain in the lower back, perineum, or genital area, urinary frequency and urgency often at night, burning or painful urination, body aches, and a demonstrable infection of the urinary tract, as evidenced by white blood cells and bacteria in the urine. Acute prostatitis may be a complication of prostate biopsy.[2] Often, the prostate gland is very tender to palpation through the rectum.[3]
Diagnosis
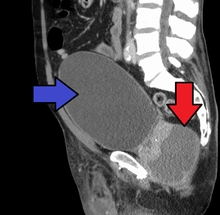
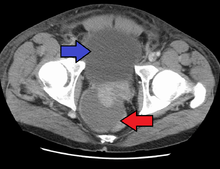
Acute prostatitis is relatively easy to diagnose due to its symptoms that suggest infection. The organism may be found in blood or urine, and sometimes in both.[2] Common bacteria are Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Enterobacter, Enterococcus, Serratia, and Staphylococcus aureus. This can be a medical emergency in some patients and hospitalization with intravenous antibiotics may be required. A complete blood count reveals increased white blood cells. Sepsis from prostatitis is very rare, but may occur in immunocompromised patients; high fever and malaise generally prompt blood cultures, which are often positive in sepsis. A prostate massage should never be done in a patient with suspected acute prostatitis, since it may induce sepsis. Since bacteria causing the prostatitis is easily recoverable from the urine, prostate massage is not required to make the diagnosis. Rectal palpation usually reveals an enlarged, exquisitely tender, swollen prostate gland, which is firm, warm, and, occasionally, irregular to the touch. C-reactive protein is elevated in most cases.[4]
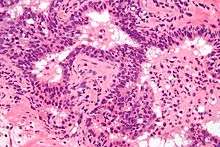
Prostate biopsies are not indicated as the (clinical) features (described above) are diagnostic. The histologic correlate of acute prostatitis is a neutrophilic infiltration of the prostate gland.
Acute prostatitis is associated with a transiently elevated PSA, i.e., the PSA is increased during an episode of acute prostatitis and then decreases again after it has resolved. PSA testing is not indicated in the context of uncomplicated acute prostatitis. Other diagnostic method is sonography
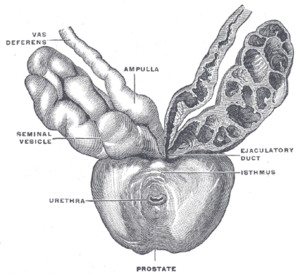 Prostate, urethra, and seminal vesicles.
Prostate, urethra, and seminal vesicles. The arteries of the pelvis.
The arteries of the pelvis. Male pelvic organs seen from right side.
Male pelvic organs seen from right side.
Treatment
Antibiotics are the first line of treatment in acute prostatitis. Antibiotics usually resolve acute prostatitis infections in a very short time, however a minimum of two to four weeks of therapy is recommended to eradicate the offending organism completely.[5] Appropriate antibiotics should be used, based on the microbe causing the infection. Some antibiotics have very poor penetration of the prostatic capsule, others, such as ciprofloxacin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, and tetracyclines such as doxycycline penetrate prostatic tissue well. In acute prostatitis, penetration of the prostate is not as important as for category II because the intense inflammation disrupts the prostate-blood barrier. It is more important to choose a bactericidal antibiotic (kills bacteria, e.g., a fluoroquinolone antibiotic) rather than a bacteriostatic antibiotic (slows bacterial growth, e.g. tetracycline) for acute potentially life-threatening infections.[6]
Severely ill patients may need hospitalization, while nontoxic patients can be treated at home with bed rest, analgesics, stool softeners, and hydration. Men with acute prostatitis complicated by urinary retention are best managed with a suprapubic catheter or intermittent catheterization. Lack of clinical response to antibiotics should raise the suspicion of an abscess and prompt an imaging study such as a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS).[7]
Prognosis
Full recovery without sequelae is usual.
References
- "Prostatitis - bacterial: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 20 July 2019.
- Stoica G, Cariou G, Colau A, et al. (2007). "[Epidemiology and treatment of acute prostatitis after prostatic biopsy]". Prog. Urol. (in French). 17 (5): 960–3. doi:10.1016/S1166-7087(07)92397-0. PMID 17969797.
- Goldman, Lee (2011). Goldman's Cecil Medicine (24th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. p. 808. ISBN 978-1437727883.
- Auzanneau C, Manunta A, Vincendeau S, Patard JJ, Guillé F, Lobel B (2005). "[Management of acute prostatitis, based on a series of 100 cases]". Prog. Urol. (in French). 15 (1): 40–4. PMID 15822390.
- Easley, Susan K.; Stevermer, James J. (2000-05-15). "Treatment of Prostatitis". American Family Physician. 61 (10): 3015–3022.AAFP Prostatitis Treatment Article
- Hua VN, Schaeffer AJ (2004). "Acute and chronic prostatitis". Med. Clin. North Am. 88 (2): 483–94. doi:10.1016/S0025-7125(03)00169-X. PMID 15049589.
- Göğüş C, Ozden E, Karaboğa R, Yağci C (2004). "The value of transrectal ultrasound guided needle aspiration in treatment of prostatic abscess". European Journal of Radiology. 52 (1): 94–8. doi:10.1016/S0720-048X(03)00231-6. PMID 15380852.