We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Tinea pedis
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- The most common dermatophyte infection
- Most commonly in young men
- Caused by T. rubrum, T. interdigitale, and E. floccosum
- Spread through direct contact (locker rooms, near swimming pools)
- Manifests as interdigital, hyperkeratotic, or vesiculobulbous eruption, rarely ulcerative
- Often accompanied by other forms of tinea
Tinea Types
- Tinea capitis (head)
- Tinea corporis (body)
- Tinea pedis (foot)
- Tinea cruris (groin)
Clinical Features
- Interdigital tinea pedis: pruritic, erythematous erosions between the toes, can be associated with painful fissures (most common type)
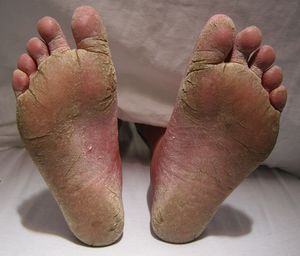
- Hyperkeratotic tinea pedis (mocasin-type): A mocasin distribusion of hyperkeratosis on the soles and side of the feet
- Vesiculobullous tinea pedis (inflammatory): Pruritic or painful vessicles or bullae with underlying erythema often affecting the medial foot
- Ulcerative tinea pedis: Interdigital erosions or ulcers (uncommon and usually associated with secondary bacterial infection)
Differential Diagnosis
- Interdigital tinea pedis
- Erythrasma
- Interdigital Candida infection
- Hyperkeratotic tinea pedis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Chronic contact dermatitis
- Acute palmoplantar eczema
- Palmoplantar psoriasis
- Pitted keratolysis
- Juvenile plantar dermatosis
- Keratolysis exfoliativa
- Keratodermas
- Vesiculobullous tinea pedis
- Acute palmoplantar eczema
- Acute contact dermatitis
- Palmoplantar pustulosis
Foot diagnoses
Acute
- Foot and toe fractures
- Subtalar dislocation
- Metatarsophalangeal sprain (turf toe)
- Acute arterial ischemia
- Calcaneal bursitis
Subacute/Chronic
- Diabetic foot infection
- Peripheral artery disease
- Plantar fasciitis
- Trench foot
- Ingrown toenail
- Tinea pedis
Evaluation
- Generally a clinical diagnosis
- Diagnosis can by confirmed by detecting segmented in hyphae in skin scrapings when put in KOH prep
Management
- Topical antifungals: Clotrimazole, terbinafine
- treatment to reduce symptoms, prevent secondary bacterial infection, and limit spread
- Systemic antifungals reserved for patients who fail topical therapy
- Systemic antifungals that can be used include: terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole
Disposition
- Outpatient treatment
See Also
References
<UpToDate>