We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Tinea
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Fungal infection caused by dermatophytes that feed on keratin
Tinea Types
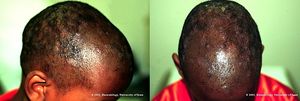
- Tinea capitis (head)
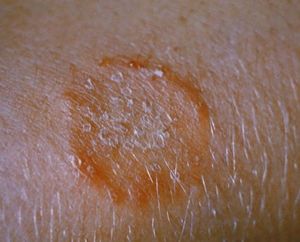
- Tinea corporis (body)
- Tinea pedis (foot)
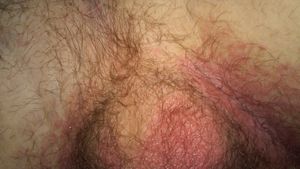
- Tinea cruris (groin)
Clinical Features
- Scaly, with variable pruritus
- Corporis: ring appearance with central clearing
- Capitis: patchy alopecia
Differential Diagnosis
- Pityriasis rosea
- Lichen planus
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
- Contact dermatitis
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis with Wood's lamp
- Kerion
- Painful, itchy, eczematous
- Hair loss
- Fever, malaise
- Lymphadenopathy
Management
- Topical antifungal treatment for all except tinea capitis
- Clotrimazole 1% BID x2-3wk
- Must use for 7-10d beyond resolution of lesions
- Capitis
- Griseofulvin 20-25mg/kg/d or BID
- Usually requires 8wk of treatment
- Selenium or ketoconazole shampoos are adjunct treatment
- Okay for child to go to school
- Griseofulvin 20-25mg/kg/d or BID
- Kerion[1]
- Oral griseofulvin, itraconazole, or terbinafine for 6-8 wks
- Cephalexin 40mg/kg/d in 4 divided doses in addition to systemic antifungal treatment if there is evidence or high risk of bacterial secondary infection
- Ketoconazole shampoo, isolated towels decrease spread to household members
Disposition
- Discharge
See Also
References
- ↑ Gnanasegaram M. Kerion. DermNet NZ. 2012. http://www.dermnetnz.org/fungal/kerion.html