We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
ACLS: Bradycardia
From WikEM
(Redirected from Symptomatic Bradycardia)
This page is for bradycardia with a pulse; for bradycardia without a pulse (i.e. PEA) see Adult pulseless arrest
Contents
Background
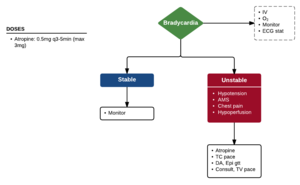
- HR < 60
- Intervention only necessary if patient is symptomatic (hypotension, altered mental status, chest pain, pulmonary edema)
Categories
- Sinus node dysfunction
- Sinus bradycardia
- Sinus arrest
- Tachy-Brady Syndrome (Sick Sinus)
- Chronotropic incompetence
- AV node dysfunction
- 1st degree AV block
- 2nd degree AV block Mobitz I/Wenckebach
- 2nd degree AV block Mobitz II
- 3rd degree AV block (complete heart block)
Differential Diagnosis
Symptomatic bradycardia
- Ischemia/Infarction
- Inferior MI (involving RCA)
- Neurocardiogenic/reflex-mediated
- Increased ICP
- Vasovagal reflex
- Hypersensitive carotid sinus syndrome
- Intra-abdominal hemorrhage (i.e. ruptured ectopic)
- Metabolic/endocrine/environmental
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypothermia (Osborn waves on ECG)
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypoglycemia (neonates)
- Toxicologic
- Infectious/Postinfectious
- Sick Sinus Syndrome
Management
- Atropine
- Can be used as temporizing measure (while awaiting pacing and/or chronotropes)
- Use cautiously in patients with ongoing ischemia (tachycardia may worsen ischemia)
- Avoid and/or do not rely on in wide complex bradycardia, especially in setting of ischemia[1]
- 0.5mg q3-5min (max 3mg or 6 doses)
- May not work in 2nd/3rd degree heart block, heart transplant
- Priority is to use external cardiac pacemaking[2]
- Block is below AV node so atropine will accelerate sinus rate, leading to worsening of block and increased fatigue of AV nodal cells
- Chronotropes
- Dopamine 2-10 mcg/kg/min, max 50 mcg/kg/min
- Dobutamine 2-20 mcg/kg/min, max 40 mcg/kg/min
- Epinephrine 2-10 mcg/min (~0.03-0.2 mcg/kg/min, max 1 mcg/kg/min)
- Isoproterenol 2-10 mcg/min
- Transcutaneous Pacing
- Transvenous Pacing
Antidotes for toxicologic causes
- Beta-Blocker Toxicity
- Glucagon 5mg IV Q10min (rpt up to 3 doses)
- Insulin 1U/kg bolus
- Intralipid (ILE)
- Calcium Channel Blocker Toxicity
- Calcium gluconate 3g
- Insulin 1U/kg bolus
- Intralipid (ILE)
- Digoxin Toxicity
- Dig immune Fab 10-20 vials
- Opioid Toxicity
- Naloxone 0.4mg IV
- Organophosphate Toxicity
- Atropine 2mg IV, double dose q5-30m until secretions controlled
- Pralidoxime 1-2g IV over 15-30min
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Neumar RW et al. Part 8: Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support. 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care.
- ↑ Burns, E. AV block: 3rd degree (complete heart block). http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/basics/complete-heart-block/