We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Pediatric rashes
From WikEM
This page is for pediatric patients; for other age groups see general approach to rashes and neonatal rashes
Contents
Background
Dermatology Nomenclature
Small lesions (<0.5cm)
- Macule – flat, cirumscribed, colored, non palpable
- Papule – raised, solid and palpable
- Vesicle – raised, palpable, clear fluid-filled
- Pustule – raised, palpable, pus filled (leukocytes or keratin)
Large lesions (>0.5cm)
- Patch – large macule (flat non-palpable colored area)
- Plaque – superficially raised, circumscribed solid area
- Nodule – distinct large papule
- Bulla - large vesicle (blisters if epidermal layer completely sloughed off)
- Wheal – firm and edematous plaque (edema of the dermis)
Other
- Plaque/scaley papule
- Eschar
- Erosion/ulcer
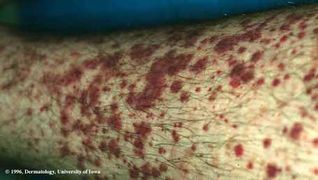
- Purpura/petechia
- Plaque/smooth papule
Rash Red Flags[1]
- Fever
- Toxic appearance
- Hypotension
- Mucosal lesions
- Severe pain
- Very old or young age
- Immunosuppressed
- New medication
Clinical Features
Differential Diagnosis
Pediatric Rash
- Drug rash
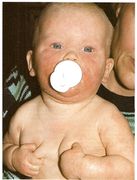
- Erythema Infectiosum (Fifth disease)
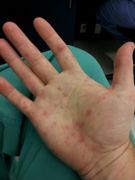
- Hand-foot-and-mouth disease
- Henoch-Schonlein Purpura (HSP)
- Herpangina
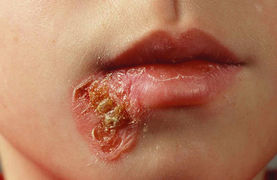
- Herpes simplex virus
- Infectious Mononucleosis
- Meningitis
- Measles
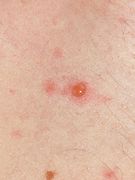
- Molluscum contagiosum
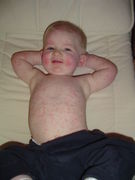
- Roseola infantum
- Rubella German measles)
- Scarlet fever
- Smallpox
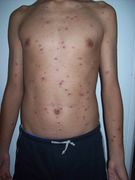
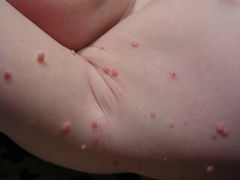
- Varicella (Chickenpox)
Evaluation
Pediatric rashes visual diagnosis
Management
Disposition
See Also
References
- ↑ Nguyen T and Freedman J. Dermatologic Emergencies: Diagnosing and Managing Life-Threatening Rashes. Emergency Medicine Practice. September 2002 volume 4 no 9.
Authors
Ross Donaldson, Jordan Swartz, Neil Young, Claire, Daniel Ostermayer