We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Impetigo
From WikEM
Contents
Background
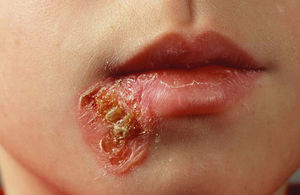
- Superficial epidermal infection characterized by amber crusts (nonbullous) or vesicles (bullous)
- May be super-infection or primary infection
- Typical causative organisms are Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes
- Fever and systemic signs are uncommon
- Post-streptococcal glomerular nephritis is a possible complication
Clinical Features
- Nonbullous
- Erythematous macules/papules develop into vesicles which become pustular and rupture
- As rupture release yellow fluid which dries to form stratified golden crust
- Erythematous macules/papules develop into vesicles which become pustular and rupture
- Bullous
- Bullae form as result of staph toxin
- Some cases caused by MRSA
Differential Diagnosis
Rash
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
- Allergic reaction
- Aphthous stomatitis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Cellulitis
- Chickenpox
- Chikungunya
- Coxsackie
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
- Drug rash
- DRESS syndrome
- Erysipelas
- Erythema multiforme
- Exfoliative erythroderma
- Henoch-schonlein purpura
- Hives
- Impetigo
- Measles
- Miliaria (Heat Rash)
- Necrotizing fasciitis
- Pellagra
- Petechiae & Purpura
- Poison Oak, Ivy, Sumac
- Psoriasis
- Pityriasis rosea
- Scabies
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Serum Sickness
- Smallpox
- Shingles
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Tinea capitus
- Tinea corporis
- Vitiligo
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis
Management
Antibiotics
Coverage for MSSA, MRSA, Group A Strep
Topical therapy
- Mupirocin 2% ointment q8hrs x 5 days
- For nonbullous impetigo, topic antibiotics are as effective as oral antibiotics
Oral Therapy
- Cephalexin 500mg (6.25mg/kg) PO q6hrs for 10 days OR
- Amoxicillin/Clavulanate 875mg (12.5mg/kg) PO q12hrs daily x 10 days OR
- Clindamycin 450mg PO q8hrs daily (or 10mg/kg PO q6hrs) for 10 days OR
- Dicloxacillin 500mg (3mg/kg) PO q6hrs daily x 10 days
Disposition
- Outpatient