We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Headache
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Headache accounts for ~2.2% of all ED visits[1]
- The majority of these have a benign cause, but serious causes can be devastating, and a thorough H&P with an eye toward "red flag" symptoms is important in ED evaluation.
Headache Red Flags
Features
- Sudden onset or accelerating pattern
- No similar headache in past
- Age >50 yr or <5 yr
- Occipitonuchal HA
- Visual disturbances
- Exertional or postcoital
- Family history of SAH or cerebral aneurysm
- Focal neurologic signs
- Diastolic BP >120
- Papilledema
- Jaw claudication
Clinical Context
Headache in setting of:
- Infection
- Cancer
- Immunosuppression
- Syncope
- Trauma
- Altered mental status
- Systemic illness (fever, stiff neck, rash)
- Nausea/vomiting
- Patient on anticoagulation, steroids, NSAIDs
Clinical Features
History
- Time to maximal onset
- Location
- Occipital - Cerebellar lesion, muscle spasm, cervical radiculopathy
- Orbital - Optic neuritis, cavernous sinus thrombosis
- Facial - Sinusitis, carotid artery dissection
- Prior headache history
Physical Exam
- Scalp and temporal artery palpation
- Sinus tap / transillumination
- EBQ: Jolt Test
- Neuro exam
Jolt Test
- Horizontal rotation of the head at frequency of 2 rotations/second - exacerbation of pre-existing headache is positive test.
- Although a 1991 study[2] showed high sensitivity with this test, multiple newer studies have cast doubt on its sensitivity[3][4]. Although it may be clinically useful in the right subset of patients, it should not be considered to be 100% Sn
Differential Diagnosis
Headache
Common
Killers
- Meningitis/encephalitis
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Intracranial Hemorrhage (ICH)
- SAH / sentinel bleed
- Acute obstructive hydrocephalus
- Space occupying lesions
- CVA
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Basilar artery dissection
- Preeclampsia
- Cerebral venous thrombosis
- Hypertensive emergency
- Depression
Maimers
- Temporal arteritis
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (aka Pseudotumor Cerebri)
- Acute Glaucoma
- Acute sinusitis
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis or cerebral sinus thrombosis
Others
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- TMJ pain
- Post-lumbar puncture headache
- Dehydration
- Analgesia abuse
- Various ocular and dental problems
- Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
- Herpes zoster oticus
- Cryptococcosis
- Febrile headache (e.g. pyelonephritis, nonspecific viral infection)
- Ophthalmoplegic migraine
- Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
Aseptic Meningitis
- Viral
- Varicella
- Herpes
- Enterovirus
- West Nile
- Tuberculosis
- Lyme disease
- Syphilis
- Drug induced aseptic meningitis
- Fungal (AIDS, transplant, chemotherapy, chronic steroid use)
- Noninfectious
- Sarcoidosis
- Vasculitis
- Connective tissues disease
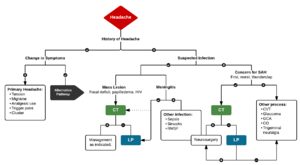
Evaluation
Laboratory Tests
- If suspect temporal arteritis → ESR
- If suspect meningitis → CSF studies
- Cannot use CBC to rule-out meningitis
- Add India Ink, cryptococcal antigen if suspect AIDS-related infection
- If suspect CO poisoning → carboxyhemoglobin level
- If concern for ICH → non-contrast CT Brain ± Lumbar puncture
Imaging
- Consider non-contrast head CT in patients with:
- Thunderclap headache
- Worst headache of life
- Different headache from usual
- Meningeal signs
- Headache + intractable vomiting
- New-onset headache in patients with:
- Age > 50yrs
- Malignancy
- HIV
- Neurological deficits (other than migraine with aura)
- Consider CXR
- 50% of patients with pneumococcal meningitis have evidence of pneumonia on CXR
Management
Non-specific Headache
Treat specific headache type, if known
- 1st line: prochlorperazine (compazine) 10 mg IV (+/- diphenhydramine 25-50 mg IV) + 1 L normal saline IV bolus
- Place prochlorperazine in IV bag to reduce chances of side effects from rapid administration
- Alternative metoclopramide 10 mg IV[5] (diphenhydramine addition shows no clinical benifit[6])
- Acetaminophen IV or PO, 325-1000 mg
- Ketorolac 30 mg IV
- Lower doses are shown to be just as effective[7]
- Consider dexamethasone 10 mg IV single dose to prevent recurrence 48-72 hrs post-ED discharge, if history of recurrent headaches[8]
- Avoid opioid medications if possible
Other 2nd and 3rd Line Medications
- Magnesium 1 g IV over 30-60 minutes, low side effect profile, in treatment of acute migraine attacks[9]
- Valproate sodium 500-1000 mg IV in 50 mL of NS over 20 minutes (alternatively 10 mg/kg IV, pediatrics, max 500 mg)[10]
- Droperidol IV/IM 1.25-2.75 mg, plus or minus diphenhydramine for extrapyramidal symptoms[11]
- Perform EKG monitoring for patients at risk of QTc prolongation
- Do not give to patients who take already multiple QT prolonging drugs
- Consider haloperidol IV 5 mg in IVF bolus with diphenhydramine to prevent need for rescue medications[12]
- Consider 5-10 mg PO olanzapine (Zyprexa, Zydis) for prochlorperazine allergy[13][14]
- While less extrapyramidal symptoms than typical antipsychotics, beware QT prolongation
- Particularly useful in psych patients with mania, BPD, psychosis
- IV olanzapine may be as safe or safer than IM, with faster onset[15]
- Ketamine IM/IV at subdissociative dosages, with risk stratification for potential ICP increase, though now widely considered a myth[16]
- Cervical spine injection with IM injection of 1.5 mL of 0.5% bupivacaine (plus or minus methylprednisolone acetate) bilaterally to the sixth or seventh spinous process[17]
- Severe, intractable status migrainosus may benefit from off-label IV propofol[18][19][20]
- Requires procedural sedation monitoring and possible IV fluid resuscitation, respiratory decompensation intervention
- Propofol 0.5 mg/kg bolus, then 0.25 mg/kg every 10 minutes for 1 hour
- Less aggressive regimens include propofol 10 mg q5-10 min to ma of 80 mg[21]
- Consider using 1 mL 2% lidocaine added to every 10 mL of 10 mg/mL concentration propofol
- Average dosage required ~100-125 mg
Disposition
- Outpatient referral to primary care or neurology for recurrent, recalcitrant headaches
- Admission for status migranosus
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Edlow JA, Panagos PD, Godwin SA, Thomas TL, Decker WW; American College of Emergency Physicians. Clinical policy: critical issues in the evaluation and management of adult patients presenting to the emergency department with acute headache. Ann Emerg Med. 2008 Oct;52(4):407-36. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2008.07.001.
- ↑ Jolt accentuation of headache: the most sensitive sign of CSF pleocytosis. Headache. 1991 Mar;31(3):167-71.
- ↑ Absence of jolt accentuation of headache cannot accurately rule out meningitis in adults. Am J Emerg Med. 2013 Nov;31(11):1601-4
- ↑ Jolt accentuation of headache and other clinical signs: poor predictors of meningitis in adults. Am J Emerg Med. 2014 Jan;32(1):24-8
- ↑ Metoclopramide for Pain and Nausea in Patients with Migraine. Am Fam Physician. 2005 May 1;71(9):1770.
- ↑ Friedman BW, et al. Diphenhydramine as Adjuvant Therapy for Acute Migraine: An Emergency Department-Based Randomized Clinical Trial. Annals of EM. January 2016. 67(1):32-39.
- ↑ Brown CR, Moodie JE, Wild VM, Bynum LJ. Comparison of intravenous ketorolac tromethamine and morphine sulfate in the treatment of postoperative pain. Pharmacotherapy. 1990;10(6Patient 2):116S-121S.
- ↑ Colman et al Paraenteral dexamethasone for acute severe migraine headache: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials for preventing recurrence. BMJ 2008 Jun.;336(7657):1359–1361
- ↑ Demirkaya S et al. Efficacy of intravenous magnesium sulfate in the treatment of acute migraine attacks. Headache. 2001 Feb;41(2):171-7.
- ↑ Shahien R et al. Intravenous sodium valproate aborts migraine headaches rapidly. Acta Neurol Scand. 2011 Apr;123(4):257-65.
- ↑ Thomas MC et al. Droperidol for the treatment of acute migraine headaches. Ann Pharmacother. 2015 Feb;49(2):233-40.
- ↑ Gaffigan ME et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Intravenous Haloperidol vs. Intravenous Metoclopramide for Acute Migraine Therapy in the Emergency Department. J Emerg Med. 2015 Sep;49(3):326-34.
- ↑ Silberstein SD et al. Olanzapine in the treatment of refractory migraine and chronic daily headache. Headache. 2002 Jun;42(6):515-8.
- ↑ Rozen TD. Olanzapine as an abortive agent for cluster headache. Headache. 2001;41(8):813-816.
- ↑ Farkas J. PulmCrit. PulmCrit- Intravenous olanzapine: Faster than IM olanzapine, safer than IV haloperidol? Feb 1, 2016. http://emcrit.org/pulmcrit/intravenous-olanzapine-haloperidol/
- ↑ Sin B et al. The use of subdissociative-dose ketamine for acute pain in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2015 Mar;22(3):251-7.
- ↑ Mellick LB et al. Treatment of headaches in the ED with lower cervical intramuscular bupivacaine injections: a 1-year retrospective review of 417 patients. Headache. 2006 Oct;46(9):1441-9.
- ↑ The Efficacy of Propofol vs. Subcutaneous Sumatriptan for Treatment of Acute Migraine Headaches in the Emergency Department: A DBCT. Pain Prac. 2014 Jul 12.
- ↑ Fortuitous Finding – IV Propofol: Unique Effectiveness in Treating Intractable Migraine. Krusz, John C. Headache 2000;40:224-230.
- ↑ Simmonds MK. The effect of single-dose porpofol injection on pain and quality of life in chronic daily headaches: a RDBCT. Anesth Analg. 2009 3Dec;109(6):1972-80.
- ↑ Soleimanpour et al. BMC Neurology 2012. 12:114. 90 pts in ED w/ Migraine.