We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Acute cholecystitis
From WikEM
Contents
Background
Clinical Features
Local Signs
- RUQ pain
- Murphy Sign
- Highest positive LR of any clinical finding or lab value
Systemic signs
Differential Diagnosis
RUQ Pain
- Gallbladder disease
- Acute cholecystitis
- Cholangitis
- Symptomatic cholelithiasis
- Choledocholithiasis
- Acalculous cholecystitis
- Peptic ulcer disease with or without perforation
- Pancreatitis
- Acute hepatitis
- Pyelonephritis
- Pneumonia
- Kidney stone
- Pancreatitis
- GERD
- Appendicitis (retrocecal)
- Pyogenic liver abscess
- Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome
- Hepatomegaly due to CHF
- Herpes zoster
- Myocardial ischemia
- Bowel obstruction
- Pulmonary embolism
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Evaluation
Laboratory Findings
- Leukocytosis
- LFT abnormalities (obstructive picture)
Imaging
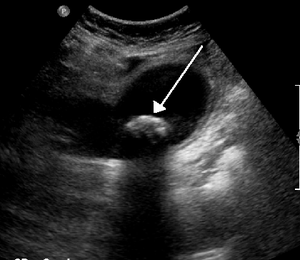
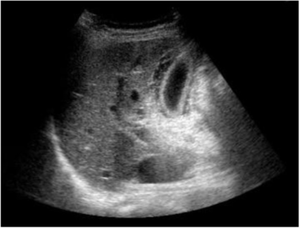
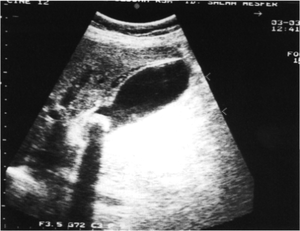
- Biliary ultrasound
- Gallstones
- Distinguish by characteristic "shadowing"
- Better seen with patient in left lateral decub
- GB wall thickening (>3mm)
- May also be seen with Pancreatitis, ascites, Congestive heart failure, alcoholic hepatitis
- Pericholecystic fluid
- Sonographic Murphy's Sign (PPV 92%)
- May be absent in patients with DM, gangrenous cholecystitis
- Gallstones
- CT
- Useful when ultrasound results are equivocal
Management
Antibiotics
Coverage is targeted at E. coli, Enterococcus, Bacteroides, and Clostridium (anerobic)
Uncomplicated Cholecystitis
- Ertapenem 1g IV once daily OR
- Metronidazole 500mg IV q8hrs PLUS
- Ciprofloxacin 400mg IV q12 hrs OR
- Levofloxacin 750mg IV q24hrs OR
- Ceftriaxone 1g IV q24hrs
Complicated
Complicated disease such as severe sepsis or hemodynamic instability
- Vancomycin 15-20mg/kg PLUS any of the following options
Options:
- Metronidazole 500mg IV q8hrs PLUS Ciprofloxacin 400mg IV q12hrs
- Piperacillin/Tazobactam 4.5g IV q8hrs
- Imipenem/Cilastin 500mg IV q6hrs
- Doripenem 500mg IV q8hrs
- Meropenem 1g IV q8hrs
Surgical consultation
- Definitive treatment involves surgical removal or decompression
Disposition
- Admit
Complications
- Gangrene
- Occurs in 20% if untreated (esp. diabetics, elderly, delay in seeking care)
- Consider if patient presents with sepsis in addition to cholecystitis
- Perforation
- Occurs in 2% after development of gangrene
- Usually localized, leading to pericholecystic abscess
- Gallstone Ileus
- Due to cholecystoenteric fistula
- Emphysematous cholecystitis
- Due to secondary infection of GB by gas-forming organisms (C. perfringens)
- Presents like cholecystitis but often progresses to sepsis and gangrene
- IV antibiotic and cholecystectomy are essential
- Ultrasound report may mistake GB wall gas for bowel gas
- Mortality as high as 15% due to gangrene or perforation
- Mirizzi Syndrome
- Partial obstruction of common hepatic duct due to stone impaction / chronic inflammation
- Symptoms of acute cholecystitis + dilated intrahepatic ducts + jaundice
- Inflammation can cause erosive fistula from Hartmann pouch into common hepatic duct
- US and CT can usually delineate the fistula
- Treatment = open cholecystectomy
- Gallstone Ileus
- Bowel obstruction due to impaction of gallstone at terminal ileum
- Gallstone enters small bowel through biliary-duodenal fistula
- Diagnosis suggested by pneumobilia, bowel obstruction, ectopic gallstone
- Bowel obstruction due to impaction of gallstone at terminal ileum