Prescription Painkiller Overdoses
Use and Abuse of Methadone as a Painkiller
July 2012


 1 in 3
1 in 3
Methadone contributed to nearly 1 in 3 prescription painkiller deaths in 2009.
 5,000
5,000
About 5,000 people die every year of overdoses related to methadone.
 6x
6x
Six times as many people died of methadone overdoses in 2009 than a decade before.
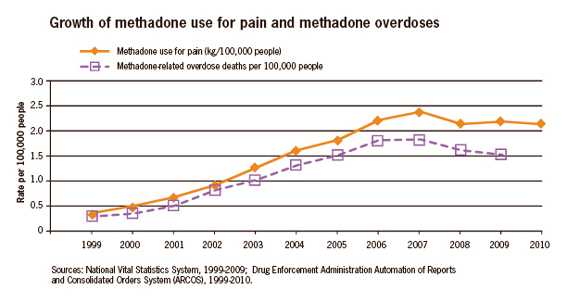
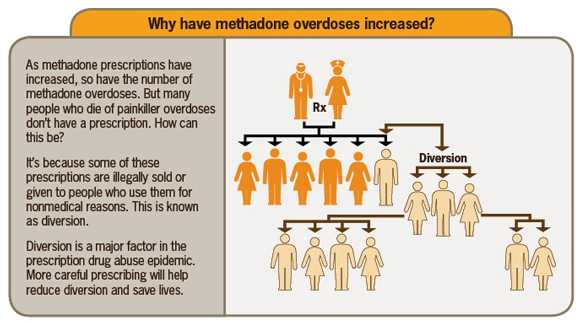
Prescription painkiller overdoses* were responsible for more than 15,500 deaths in 2009. While all prescription painkillers have contributed to an increase in overdose deaths over the last decade, methadone has played a central role in the epidemic. More than 30% of prescription painkiller deaths involve methadone, even though only 2% of painkiller prescriptions are for this drug. Six times as many people died of methadone overdoses in 2009 than a decade before.
Methadone has been used safely and effectively to treat drug addiction for decades. It has been prescribed increasingly as a painkiller because it is a generic drug that can provide long-lasting pain relief. But as methadone’s use for pain has increased, so has nonmedical use of the drug and the number of overdoses.
* "Prescription painkiller overdoses" refers to deaths from using harmful amounts of opioid or narcotic pain relievers, including drugs such as Vicodin (hydrocodone), OxyContin (oxycodone), Opana (oxymorphone), and methadone.
Problem
Methadone use poses risks
Methadone is frequently prescribed for pain.
- Methadone, like other painkillers, is commonly prescribed for chronic problems like back pain even though it might not help these problems in the long run.
- More than 4 million methadone prescriptions were written for pain in 2009, despite US Food and Drug Administration warnings about the risks associated with methadone.
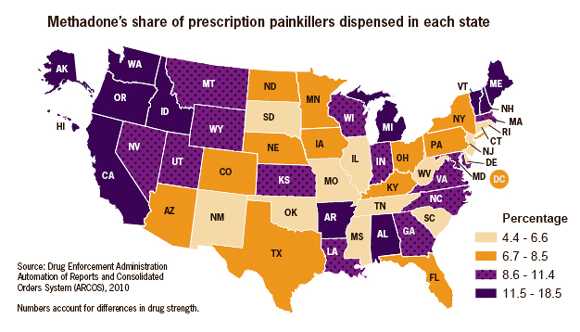
- Methadone is available as a low-cost generic drug. It is often listed as a preferred drug by insurance companies.
Methadone's risks include:
- The difference between appropriate prescribed doses and dangerous doses of methadone is small.
- Methadone has special risks as a painkiller. For example, taking it more than 3 times a day can cause the drug to build up in a person’s body, leading to dangerously slowed breathing.
- Methadone can seriously disrupt the heart’s rhythm.
- Methadone can be particularly risky when used with tranquilizers or other prescription painkillers.
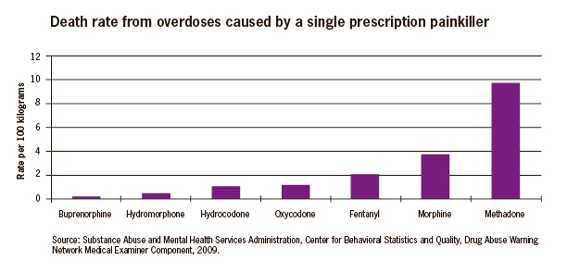
- In one study, four in ten overdose deaths involving single prescription painkillers involved methadone, twice as many as any other prescription painkiller.
Who's At Risk
What Can Be Done
The US government is
- Enforcing federal laws to prevent nonmedical use of methadone.
- Educating health care providers and consumers about the correct use of methadone.
- Tracking prescription drug overdose trends and the impact of efforts to stop overdoses.
States can
- Develop and promote the use of safe prescribing guidelines for methadone.
- Support the use of methadone as a treatment for opioid dependence in opioid treatment programs.
- Use prescription drug monitoring programs to identify patients who are using methadone or other prescription painkillers for nonmedical purposes.
Health care providers can
- Follow guidelines for prescribing methadone and other prescription painkillers correctly, including
- Screening and monitoring for substance abuse and mental health problems.
- Prescribing only the quantity needed based on the expected length of pain.
- Using prescription drug monitoring programs to identify patients who are misusing or abusing methadone or other prescription painkillers.
- Monitor patients on high doses for heart rhythm problems.
- Educating patients on how to safely use, store, and dispose of methadone and how to prevent and recognize overdoses.
Health insurers can
- Evaluate methadone’s place on preferred drug lists.
- Consider strategies to ensure that pain treatment with any dose higher than 30 mg of methadone a day (the recommended maximum daily starting dose) is appropriate.
Individuals can
- Use methadone only as directed by a health care provider.
- Make sure they are the only ones to use their methadone and never sell or share it with others.
- Store methadone in a secure place and dispose of it properly. See www.cdc.gov/HomeandRecreationalSafety/Poisoning/preventiontips.htm for correct storage and disposal of medications.
- Get help for substance abuse problems (1-800-662-HELP or www.samhsa.gov/treatment/).
Science Behind the Issue
Related Pages
- Vital Signs Issue details: Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR): Vital Signs: Risk for Overdose from methadone Used for Pain Relief–United States, 1999-2010
- Vital Signs: Prescription Painkiller Overdoses in the United States
- Policy Impact: Prescription Painkiller Overdoses
- Unintentional Poisoning
- Home and Recreational Safety
- Methadone [PODCAST – 1:15 minutes]
- Methadone [PSA – 0:60 seconds]
- Winnable Battles
On Other Web Sites
- MedlinePlus – Prescription Drug Abuse
- MedlinePlus – Pain Relievers
- The White House – Office of National Drug Control Policy
- SAMSHA – Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
- Drug Enforcement Administration – Office of Diversion Control
- National Institute on Drug Abuse – Prescription Medications
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration - Drugs Information
- Page last reviewed: July 3, 2012
- Page last updated: July 3, 2012
- Content source:
- National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Division of Unintentional Injury Prevention
- Page maintained by: Office of the Associate Director for Communications (OADC)


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir