OCCUPATIONAL HEARING LOSS (OHL) SURVEILLANCE
Overall Statistics – All U.S. Industries
Noise Exposure and Hearing Protection
- About 17% of all workers are exposed to hazardous noise (about 22 million workers).1
- 34% of noise-exposed workers report not wearing hearing protection.1
Hearing Loss and Tinnitus
- Approximately 11% of all workers have hearing difficulty.2
- About 8% of all workers have tinnitus.2
- About 19% of noise-exposed tested workers have a material hearing impairment.3 Hearing impairment is hearing loss that impacts day-to-day activities.
- 13% of noise-exposed tested workers have hearing impairment in both ears.4
Trends in Hearing Loss Among Noise-Exposed Tested Workers (1981-2010)3
- The prevalence for all industries combined decreased less than 1% over 30 years (1981-2010).
- The incidence for all industries combined decreased 2% over 25 years (1986-2010).
- The adjusted risk for all industries combined decreased 46% over 25 years (1986-2010).
Prevalence of Hearing Loss by Time Period and Industry Sector, 1981 – 2010, for 1,816,812 Workers
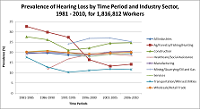
Adapted from Figure 1, Masterson et al. 2015

Adapted from Figure 1, Masterson et al. 2015
Incidence of Hearing Loss by Time Period and Industry Sector, 1986 – 2010, for 560,320 Workers
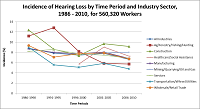
Adapted from Figure 2, Masterson et al. 2015

Adapted from Figure 2, Masterson et al. 2015
Risk of Incident Hearing Loss Compared to the 1986-1990 Time Period, by Industry Sector, for 560,320 Workers

Adapted from Figure 3, Masterson et al. 2015

Adapted from Figure 3, Masterson et al. 2015
Sources:
- Tak S, Davis RR, Calvert GM. (2009). Exposure to hazardous workplace noise and use of hearing protection devices among US workers — NHANES, 1999-2004. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 52(5):358-371.
- Masterson EA, Themann CL, Luckhaupt SE, Li J. & Calvert GM. (2016). Hearing difficulty and tinnitus among U.S. workers and non-workers in 2007. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 59, 290-300.
- Masterson EA, Deddens JA, Themann CL, Bertke S. & Calvert GM. (2015). Trends in worker hearing loss by industry sector, 1981-2010. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 58, 392-401.
- Masterson EA, Bushnell PT, Themann CL, & Morata TC. (2016). Hearing impairment among noise-exposed workers — United States, 2003–2012. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 65(15), 389-394.
- Page last reviewed: May 16, 2017
- Page last updated: May 16, 2017
- Content source:
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Division of Surveillance, Hazard Evaluations, and Field Studies


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir