Informational Brief on CDC Hepatitis Funded Program: Community-Based Hepatitis B Program
As many as 2.2 million people in the U.S. are living with hepatitis B. Hepatitis B disproportionately affects persons born in countries with intermediate to high (> 2%) prevalence of hepatitis B infection; areas mostly in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. Hepatitis B is very common in these areas, making it easy for many people to come into contact with the virus. Most people in these areas become infected through maternal to child transmission of hepatitis B due to low hepatitis B vaccine.
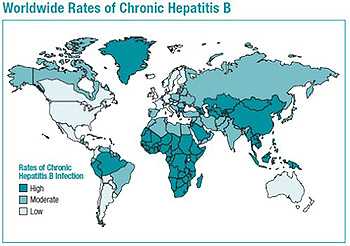
To decrease the burden of hepatitis B infections in communities with large foreign-born populations, there is a need to:
- Improve hepatitis B vaccination coverage among high risk adults, and improve universal birth dose coverage in all countries.
- Implement strategies to increase testing in hard-to-reach populations.
- Support and evaluate efforts to reduce infections and provide best practices that can be applied nationwide.
- Develop strategies to improve linkage to HBV-directed medical care.
CDC has awarded funding for three grantees in:
- Chicago, IL – Asian Health Coalition
- Northern New Jersey and New York City, NY – Saint Barnabas Medical Center in partnership with Charles B. Wang Community Health Center
- Sacramento, CA – The University of California at Davis
To Increase the identification of persons with hepatitis B and link them to high-quality hepatitis B directed care, each of these sites:
- Develop partnerships (which include primary health-care providers, medical specialists experienced in the treatment of hepatitis B, community-based organizations, and health departments) serving foreign-born persons from countries where hepatitis B occurs at an intermediate to high rate.
- Test > 2,000 persons born in countries where hepatitis B occurs at an intermediate to high rate.
- Identify persons with chronic hepatitis B infection, and get them into ongoing hepatitis B-specific medical care.
- Reduce morbidity and mortality associated with chronic hepatitis B infection.
Recent activities:
- To strengthen healthcare providers’ knowledge, grantees have:
- Developed a patient navigation training manual to improve lifesaving care and treatment.
- Established a clinician advisory board consisting of specialists to guide community providers in hepatitis B care.
- Providing ongoing continuing medical education on the prevention of hepatitis B to primary care providers.
- To increase hepatitis B testing, grantees have:
- Distributed “Hepatitis B Screening Coupons” for individuals to utilize at any testing laboratory.
- Utilized alerts for testing foreign-born persons in the electronic medical record.
- Leveraged partnerships with multiple community-based organizations to coordinate community screening events.
- To improve linkage to hepatitis B-directed care, grantees have:
- Launched alert reminders in EMR
- Assigned patient navigators to each HBsAg-positive person
- Conducting CME for providers
Funding
Funding for the four-year project period is expected to be approximately $4.5M each year.
- Page last reviewed: June 8, 2016
- Page last updated: June 8, 2016
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir