Informational Brief on CDC Hepatitis Funded Program: Strengthening Surveillance
Surveillance for viral hepatitis is the ongoing systematic collection and analysis of data that reflect the health status of a community or population. Active disease surveillance involves case ascertainment conducted through proactive, direct engagement with providers, laboratories, and patients that can facilitate collection of data necessary to support public health action. These data are used by CDC and state and local health departments to monitor trends in new hepatitis cases and the number of persons infected, identify sources of infection and changes in transmission patterns, and estimate burden of disease. Hepatitis surveillance also detects outbreaks; identifies persons in need of medical treatment after exposure to viruses; and, provides information on trends in new hepatitis cases and risks for recent infection – all of which are needed to develop and evaluate prevention and control strategies.
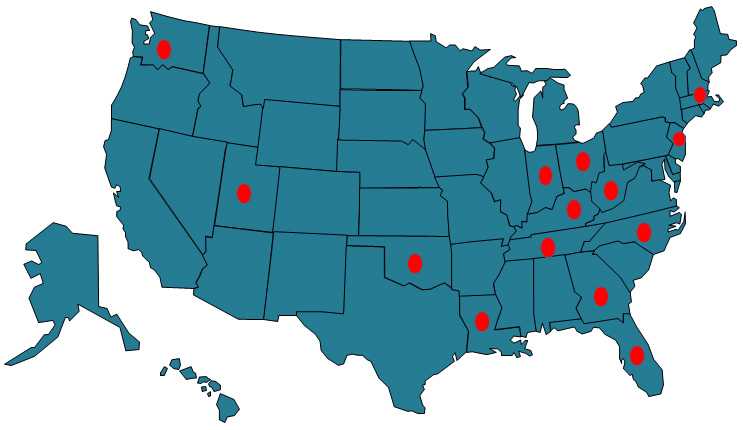
To improve active surveillance of hepatitis C virus and hepatitis B virus in statewide jurisdictions, CDC has awarded funding for fourteen grantees in:
- Florida
- Georgia
- Indiana
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Massachusetts
- New Jersey
- North Carolina
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Tennessee
- Utah
- Washington
- West Virginia
To enhance and strengthen viral hepatitis surveillance, the projects will:
- Work with local departments of health, traditional and non-traditional partner organizations, and CDC to produce reliable estimates of the incidence of hepatitis B and hepatitis C infections, document the current epidemiology of hepatitis B and hepatitis C infections, and support and evaluate prevention programs.
- Work with partners to implement and evaluate interventions to improve hepatitis B and hepatitis C testing, diagnosis, reporting, and linkage to care in areas with high rates of new cases of hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C.
- Integrate evidence-based hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention activities into existing public health, clinical care, and community settings.
Funding
Funding for the four-year project period is expected to be approximately $3.2M each year.
- Page last reviewed: May 3, 2017
- Page last updated: May 3, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir