Medical Uses of Water Figure Showing Hemodialysis Process
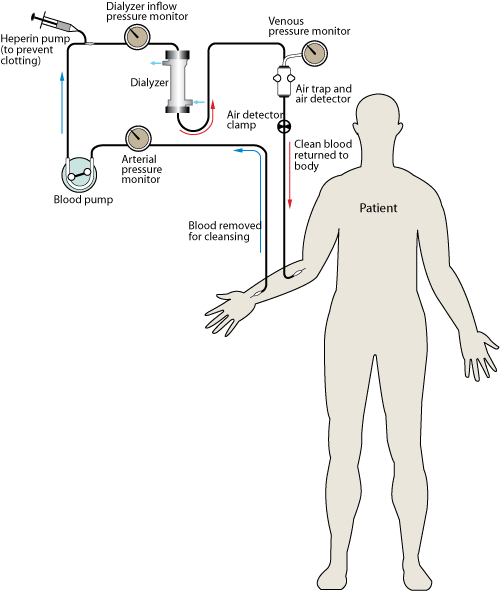
Figure description: During hemodialysis, blood flows out of the body and by one side of a semi-permeable membrane. Dialysate, the fluid in a dialysis machine, flows by the opposite side of the membrane. Undesired waste in the blood flows into the dialysate, while bicarbonate (a needed solute that helps in pH balance) flows from the dialysate into the blood. The clean blood is then returned to your body. Removing the harmful waste and extra salt and fluids helps control blood pressure, pH balance, and plasma volume, similar to the results of a functioning kidney.
- Page last reviewed: October 11, 2016
- Page last updated: October 11, 2016
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir