Causes & Transmission
Español: Transmisión de la enfermedad de manos, pies y boca
Causes
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by viruses that belong to the Enterovirus genus (group), including polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, and enteroviruses.
- Coxsackievirus A16 is the most common cause of hand, foot, and mouth disease in the United States, but other coxsackieviruses can also cause the illness.
- Enterovirus 71 has also been associated with cases and outbreaks of hand, foot, and mouth disease. Less often, enterovirus 71 has been associated with severe disease, such as encephalitis.
- Several types of enteroviruses may be identified in outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease, however most of the time, one or two enteroviruses are identified more frequently.
Transmission
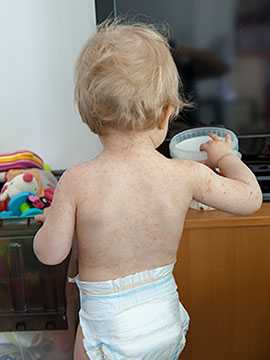
The viruses that cause hand, foot, and mouth disease can be found in an infected person’s:
- nose and throat secretions (such as saliva, sputum, or nasal mucus),
- blister fluid, and
- feces (stool).
An infected person may spread the viruses that cause hand, foot, and mouth disease to another person through:
- close personal contact,
- the air (through coughing or sneezing),
- contact with feces,
- contact with contaminated objects and surfaces.
For example, you might get infected by kissing someone who has hand, foot, and mouth disease or by touching a doorknob that has viruses on it then touching your eyes, mouth or nose.
It is possible to get infected with the viruses that cause hand, foot, and mouth disease if you swallow recreational water, such as water in swimming pools. However, this is not very common. This is more likely to happen if the water becomes contaminated with feces from a person who has hand, foot, and mouth disease and is not properly treated with chlorine.
Generally, a person with hand, foot, and mouth disease is most contagious during the first week of illness. People can sometimes be contagious for days or weeks after symptoms go away. Some people, especially adults, may not develop any symptoms, but they can still spread the virus to others. This is why people should always try to maintain good hygiene (e.g. handwashing) so they can minimize their chance of spreading or getting infections.
You should stay home while you are sick with hand, foot, and mouth disease. Talk with your healthcare provider if you are not sure when you should return to work or school. The same applies to children returning to daycare.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is not transmitted to or from pets or other animals.
Top of Page- Page last reviewed: January 6, 2017
- Page last updated: January 6, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir