Celebrating 15 Years of CDC in Rwanda
-
2000
- U.S. Congress enacts Global AIDS and Tuberculosis Relief Act of 2000.
- U.S. and UN Security Councils each declare HIV/AIDS a security threat.
- CDC establishes its Global AIDS Program (CDC/GAP).
-
2002
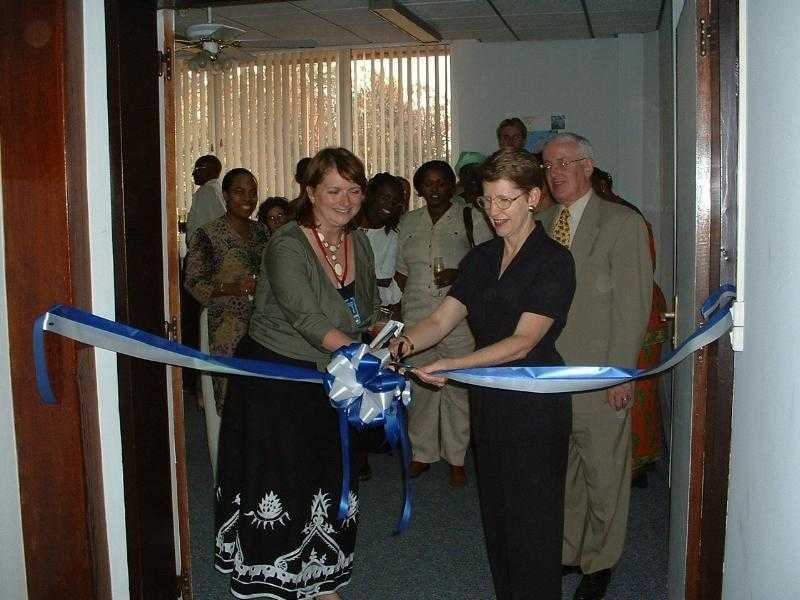

Valerie Koscelnik, CDC Rwanda’s first Chief of Party at the official opening ceremony.
- CDC/GAP officially opens in Rwanda in September 2002.
- Rwanda becomes one of the 25 countries in which CDC/GAP supports national governments with their fight against HIV/AIDS.
- In 2002 Rwanda’s HIV prevalence is estimated at 8%.The CDC/GAP Rwanda County Program begins working in the following strategic areas:
- PMTCT
- Laboratory
- Surveillance
- Monitoring and Evaluation
- In 2002 the CDC Rwanda office is housed on the 2ND floor of the Development Bank of Rwanda (BRD) building, on KN3 Avenue, in Kigali.
-
2003

FHI Surveillance Officer, seconded at TRAC, Dr. Eugenie Kayirangwa reviewing surveillance materials with ANC providers at a health center in Rwanda.
- CDC signs first Cooperating Agreement (CoAg) with the Rwandan Ministry of Health. The National Capacity-building through CDC-TRAC CoAg.
- This CoAg focuses on improving HIV/AIDS service Delivery through improved HIV Surveillance, Ante-Natal Care Sentinel Surveillance and National Capacity for quality HIV care and treatment expansion
- President Bush announces the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR).
- CDC signs first Cooperating Agreement (CoAg) with the Rwandan Ministry of Health. The National Capacity-building through CDC-TRAC CoAg.
-
2004

PEPFAR in Rwanda logo
- PEPFAR funding for Rwanda begins.
- CDC has a key role in PEPFAR implementation in Rwanda.
-
Track 1.0 begins.
Track 1.0 is a 5-year (2004-2009) central funding mechanism established to support rapid scale-up of care and treatment HIV programs in Rwanda.
Specific areas of support include:- Care and treatment HIV Clinical Services;
- PEPFAR funding for Rwanda begins.
-
2005

Monitoring and evaluation training
- The TRACnet initiative begins.
- TRACnet uses cell phones in the field to gather data on AIDS patients and their drug treatments.
- TRACnet is implemented by Voxiva Inc. a U.S. based information systems company, in collaboration with Rwanda’s Center for Treatment and Research AIDS Center (TRAC) through funding and support from PEPFAR/CDC Rwanda.
- TRACnet become one of Rwanda’s largest and most widely used e-Health platforms.
- Frist Demographic Health survey conducted in Rwanda including the HIV prevalence module. Rwanda’s national HIV prevalence shown to be at 3%.
- Malaria is the leading cause of death and disease among children and adults in Rwanda.
- Launch of the Healthy Schools Initiative (2005 – 2009).
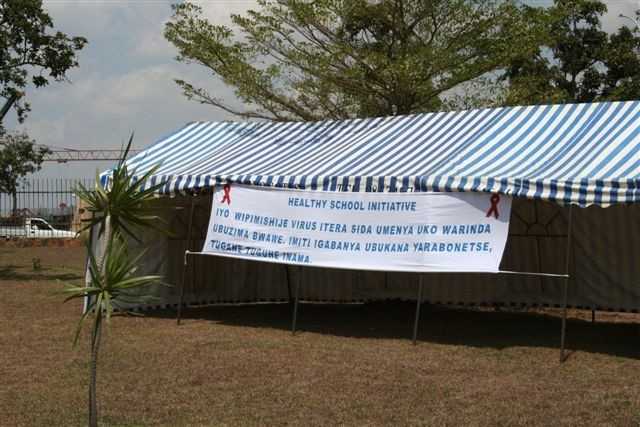 Official launch of the Healthy Schools Initiative
Official launch of the Healthy Schools Initiative -
2006

Dr. Eugenie Kayirangwa of CDC Rwanda.
- The U.S. Presidents Malaria Initiative supporting the Ministry of Health implement its Malaria Control and Prevention initiatives is introduced in Rwanda.
- Dr. Eugenie Kayirangwa joins CDC Rwanda as the first locally employed technical staff. Dr. Kayirangwa is employed as the Health specialist.
- CDC’s Avian Influenza Program begins in Rwanda.
- Through PEPFAR/CDC support the national scale-up of HIV treatment in Rwanda moves from about 900 PLHIV out of thousands on ART in 2002 to 32,000 PLHIV on ART in 2006.
- PEPFAR/CDC pilots the use of dried blood spot PCR tests at Rwanda’s National Reference Laboratory (NRL), to enable early infant diagnosis and faster response to the epidemic.
- PEPFAR/CDC launches the Mobile VCT initiative.
- The main goal of the MVCT initiative is to pilot the ‘Finger Prick’ HIV testing method in Rwanda.
- This is the first time the roll-out of the ‘Finger Prick Method’ for rapid HIV testing has been piloted in Rwanda.
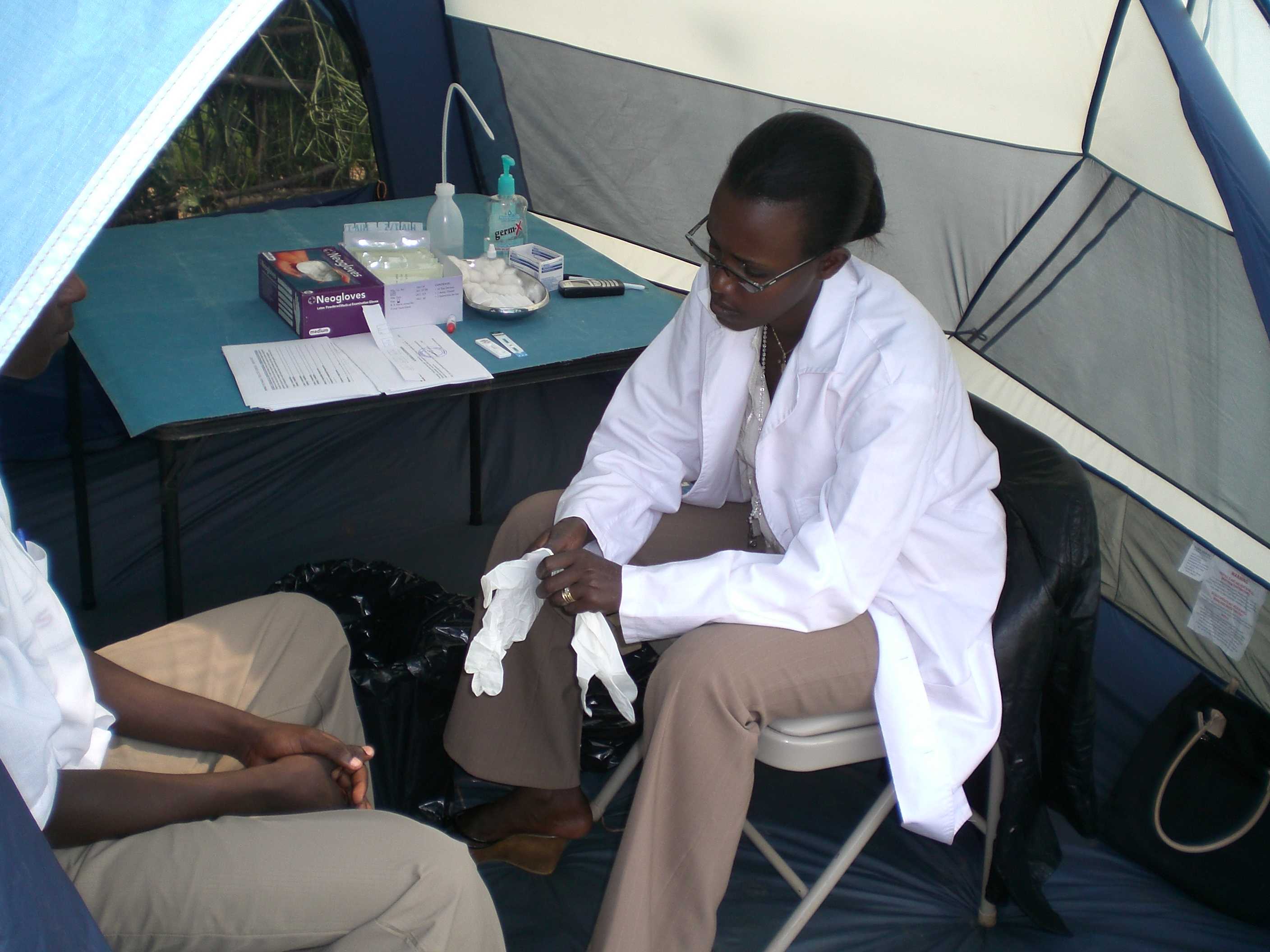

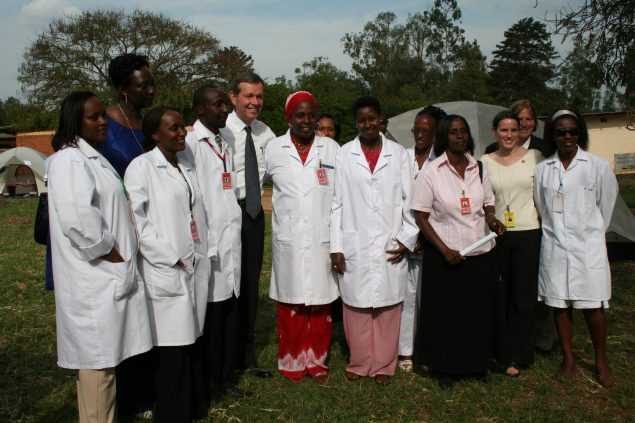
MVCT staffer preparing to give an HIV test using the finger prick method in a mobile VCT unit.
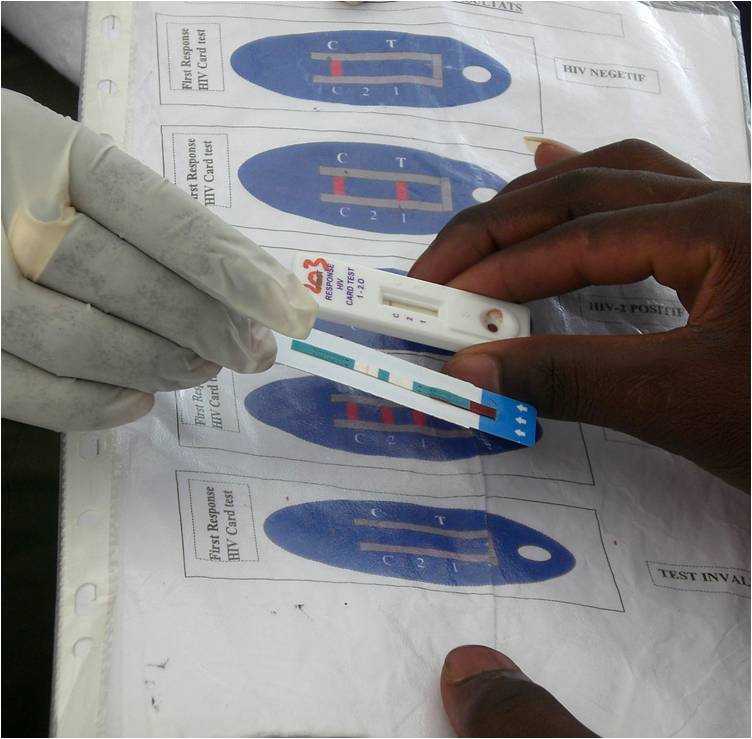
MVCT staffer assists a client to interpret the results of an HIV test.
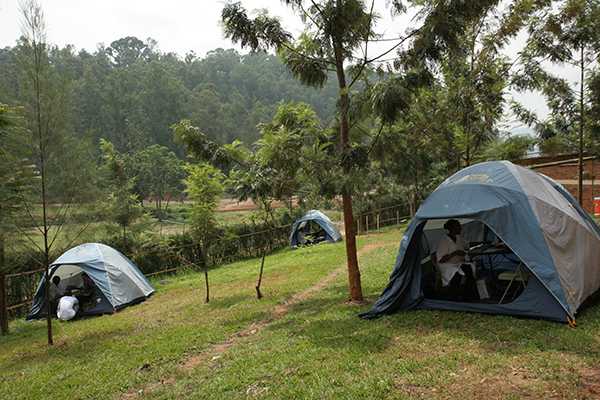

MVCT staffers conducting HIV tests using ‘finger prick method’ in mobile VCT tents.
-
2007
Secretary Leavitt poses for a photo with MVCT project staff.
- 4 year CoAg signed with Ministry of Health for “Preparedness and Response to Avian and Pandemic Influenza in Rwanda”.
- U.S. Secretary of Health, Michael Leavitt makes a special visit to Rwanda to witness firsthand the progress made with the Mobile VCT and Healthy Schools initiatives.
- Management of the ‘Mobile VCT initiative transitioned to the Ministry of Health.
- MOH considers adopting of the ‘Finger Prick’ testing method as national policy.
- PEPFAR/CDC through ICAP improve infrastructure and equipment at all Rwanda’s National Reference Laboratory (NRL) NRL/ICAP supported sites across the country.
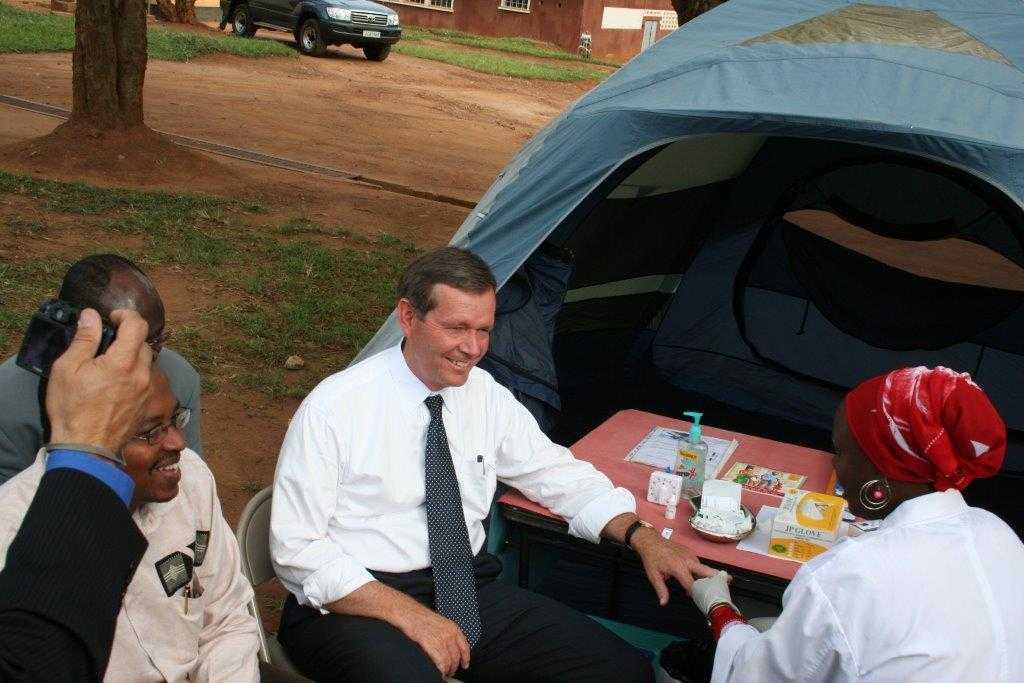

Secretary Leavitt gets a rapid HIV test done using the finger prick method by a MVCT staffer. Dr. Innocent Nyaruhirira, Rwanda’s State Minister for Health, looks on.

Reequipped and renovated HIV molecular section at NRL.

Reequipped and renovated TB unit at NRL -
2008

President Bush and Rwanda Minister of Health watch a skit by Lycee de Kigali High School’s ‘Anti-AIDS Club’
- President George Bush visits Rwanda.
- President Bush and President Kagame officially open the new U.S. Embassy building in Kigali Rwanda.
- CDC Rwanda Country Program moves office from the Development Bank of Rwanda (BPD) building, on KN3 Avenue to the new U.S. Embassy building on 2657 Avenue de la Gendarmerie, Kacyiru, Kigali.
- Pilot conducted for national biological specimen transportation system to support the scale up of EID and MDR TB Program.
- The Rwandan Ministry of Health with support from CDC and in collaboration with Partners in Health deploys Rwanda’s first electronic medical record system (EMR) to improve patient data management.
- CDC works with PSI to develop and air youth protection programs including the Sinigurisha mass media campaign aimed at empowering youth to say no to cross generational sex.
- Launch of the Field Epidemiological Training Program (FETP) in Rwanda with short courses in applied epidemiology for government employees.
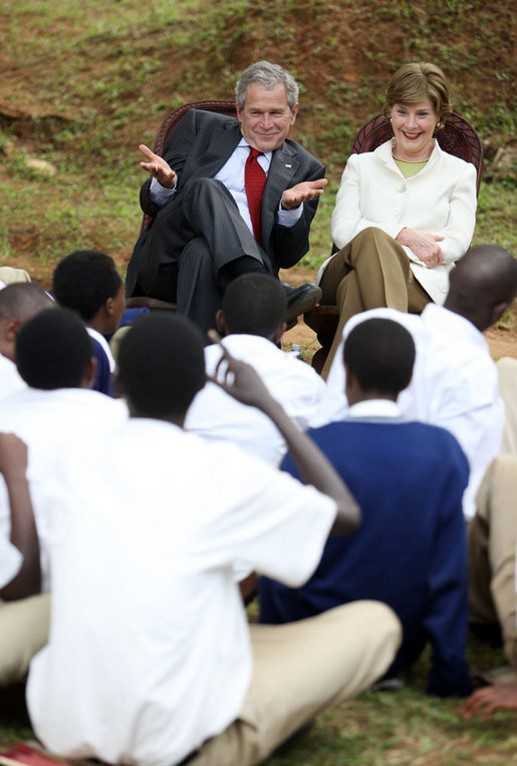

Photo of President Bush and the first lady as they talk with students of Lycee de Kigali High School’s ‘Anti-AIDS Club’

Photo of former U.S. President Bush and Rwanda’s President Kagame at the official opening of the new U.S. Embassy building in Kigali, Rwanda

New U.S. Embassy building in Kigali, Rwanda

EMR deployment and training in Rwanda

The Sinigurisha Mass Media Campaign aimed at ending cross generational sex
-
2009

HIPPP supported health information exchange to support maternal and child health.
- Pandemic Influenza H1N1 outbreak in Rwanda.
- H1N1 outbreak is investigated and responded to successfully with support from CDC Rwanda.
- HIPP supported health information exchange program to support maternal and child health begins.
- Health Informatics Private-Public Partnership (HIPPP) a collaboration between the International Development Research Centre, Rockefeller Foundation, PEPFAR/CDC’s, Rwanda’s MOH and Jembi begins.
- Pandemic Influenza H1N1 outbreak in Rwanda.
-
2010

Cohort 1 FELTP trainees posing for a picture with the Rwanda Minister for Health, Agnes Binagwaho, 2010
- CDC/WHO-AFRO establish an accreditation process to build African Laboratory capacity.
- First cohort of 15 FELTP residents are enrolled in the program.
- CDC supports RBC/MOH to conduct Rwanda’s 2010 national HIV/Syphilis survey among pregnant women.
-
2011
- eIDSR – the electronic Disease Surveillance and Response System is set up under TRACnet II and used to monitor 23 diseases under surveillance in Rwanda.
- The Partnership for Advanced Clinical Mentorship (PACME) CoAg with the University of Maryland, School of Medicine begins.
- Goal is to ensure maintenance of quality clinical services at supported facilities in the country that were previously supported by Track 1.0 partners.
- President Obama announces accelerated U.S. goals for “the beginning of the end of AIDS.”
- Cases of malaria in Rwanda drop from 8% in 2010 to 3% in 2011 and account for 6% of total deaths in 2011 as compared to 13% in 2010.
-
2012
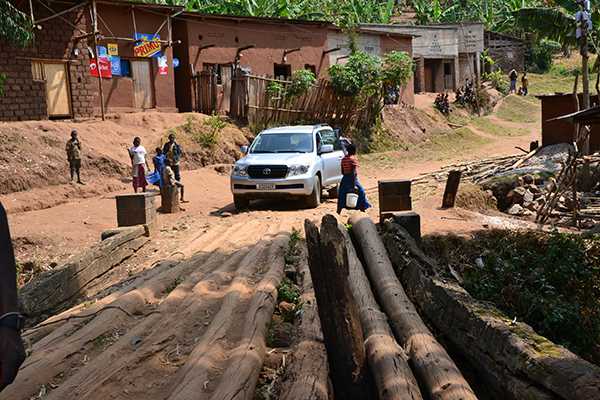

CDC Rwanda staff traveling out of Kigali for a SIMS visit.
- Site Improvement through Monitoring System (SIMS) of PEPFAR/CDC sites begins in Rwanda.
- Transition of the management of Rwanda’s Track 1.0 sites from International Non-Governmental Organizations (INGO) management to Government of Rwanda management begins.
- First cohort of FETP trainees graduate upon successful completion of the training.
- FETP trainees participate in the national yellow fever risk assessment. The results from this assessment inform WHO’s reclassification of Rwanda’s yellow fever risk status.
- CDC supports RBC/MOH to conduct the national 2012, HIV Behavioral Surveillance Survey for Female Sex workers.
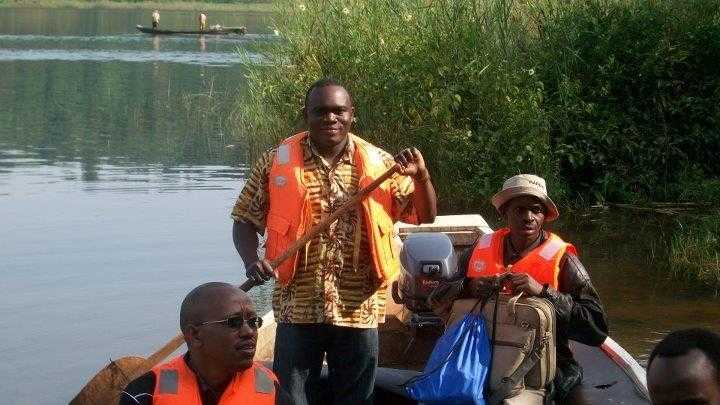

FETP trainees and supervisor riding on a boat on their way to Nkombo island, Rusizi district during an outbreak investigation.
-
2013
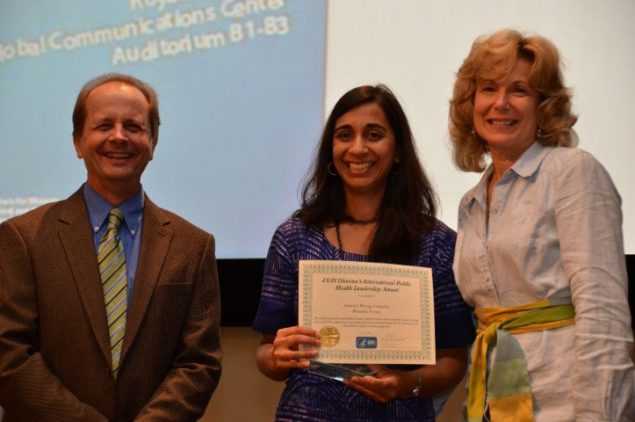

Dr. Pratima Raghanthan (Center) receives the 2013 CGH Honor Award on behalf of CDC Rwanda. The award was presented by Dr. Thomas Kenyon (Left), the former Director of the Center for Global Health and Dr. Debbie Birx (Right), the former Director of the DGHA.
- First Rwanda Field Epidemiology conference held in Kigali.
- Thierry Nyatanyi (cohort 2; Rwanda FELP) adjudged the Best Oral Presenter during the 5th African Field Epidemiology Network Conference held in Addis Ababa from Nov 17th-22nd 2013. His presentation was titled; ‘e-IDSR Rwanda: National Electronic System for Disease Surveillance, 2013’
- Four FETP graduates and three trainees are nominated as members of the National Rapid Response teams.
- Laboratory Master Trainers and Mentors are acquired to support and continue country led SLMTA trainings and laboratory accreditation process towards meeting international standards (ISO 15189) using the WHO/AFRO-SLIPTA checklist with support from ASCP.
- CDC Rwanda receives 2013 Center for Global Health Honor Award.

Four Cohort 1 Rwanda FELP residents (Left to Right: Claude Rutanga, Marie Aimee Muhimpundu, Jean Felix Kinani, Hinda Ruton posing with Dr. Douglas Shaffer CDC Rwanda Country Director, after receiving their completion certificates during the University of Rwanda, School of Public Health’s 2013 Scientific Day held on Dec 3rd 2013).
-
2014
- Two graduates of Rwanda FELTP are deployed to West Africa to support the Ebola response.
- Over 10 FELTP graduates and trainees are involved in the Rwanda National Ebola Preparedness and Response planning.
- Piloted the use of Dried tube specimen (DTS) for proficiency testing (PT) as EQA for HIV Rapid Testing with support from CDC
- PEPFAR commemorates 10 years of working on HIV/AIDS in Rwanda.
- NRL acquires 5-stars in East African Public Health Laboratory Network assessment with support from CDC.
- Start of SIMS Version 1.0
- CDC supports RBC/MOH to conduct Rwanda’s first ever National HIV Behavioral Surveillance Survey for Men who have sex with Men.
-
2015

Dr Rukelibuga of CDC Rwanda meeting with community leaders in Katongor, Guinea as part of the Ebola outbreak investigations.
- With support from CDC through PEPFAR Rwanda’s National Reference Laboratories establishes 6 additional laboratories through training and mentorship to support scale up of Viral Load testing.
- Dr Joseph Rukelibuga of CDC Rwanda supports the International Ebola Response team in Guinea for a period of 45 days.
- Rwanda becomes among the first countries to bring its PMTCT rates below 2% per annum, showing that it is possible to eliminate Mother to Child Transmission of HIV in Rwanda.
-
2016
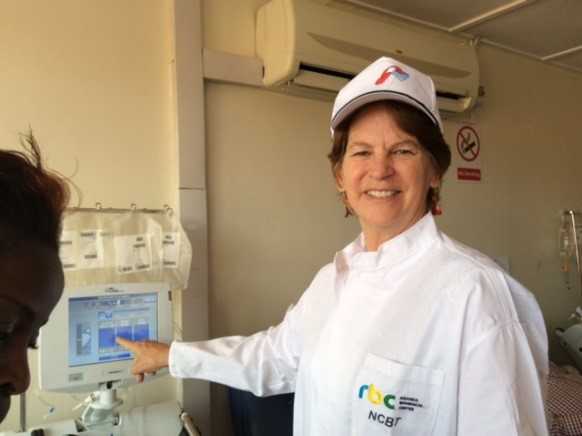

Dr. Gene MacDonald, CDC Rwanda’s Country Director during a site visit at Rwanda’s National Center for Blood Transfusion (NCBT). Dr. MacDonald is pointing at one of several Apheresis machines at NCBT which were bought using funds from CDC Rwanda.
- As of December 2016, CDC Rwanda, through PEPFAR funding, is supporting approximately 52% of all the adults and children receiving Anti-Retroviral drug Treatment (ART) in Rwanda.
- In Rwanda the occurrence of TB among PLHIW is reduced to 25% from 48% in 2005.
- Fourth cohort of the advanced Rwanda FETP trainees enrolled resulting in a total of 59 trainees enrolled into the program to date.
- 10th field epidemiology short course training conducted resulting in 456 mid-level public health managers trained in disease surveillance and outbreak investigations and response.
- Samuel Rwunganira, one of the advanced FELTP third cohort trainees undergoes one-on-one speed mentoring by CDC Director, Dr Tom Frieden. Samuel’s project was to identify risk factors for diabetes in Rwanda
- National Center for Blood Transfusion (NCBT) receives international standards accreditation from the Africa Society of Blood Transfusion.
- Rwanda hosts the 5th African Network for Influenza Surveillance and Epidemiology (ANISE) Meeting.
-
2017
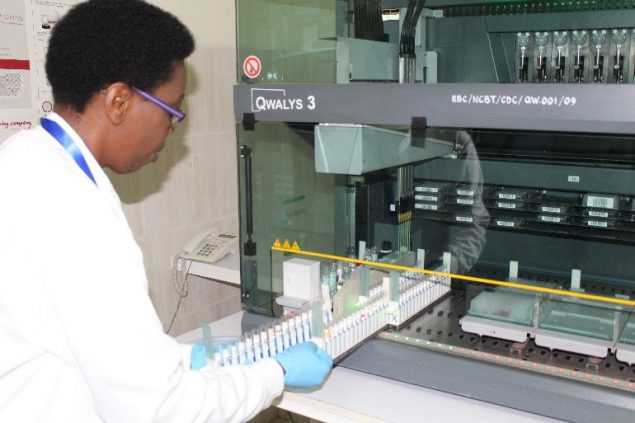

Picture of a Rwanda National Center for Blood Transfusion (NCBT) staffer using a QWALYS 3 – Blood grouping and cross matching machine bought with support from CDC Rwanda.
- The National Centers for Blood Transfusion (NCBT) is recognized as a regional center of excellence in Blood Transfusion Practice and is awarded the highest – level 3 – international standards accreditation by the Africa Society
for Blood Transfusion.- Dr Swaibu of NCBT says “We could not have achieved this without technical support from CDC through PEPFAR funding”.
- Since 2002, CDC and its implementing partners have published more than 30 scientific articles in journals with high public health impact, with scientific studies covering many diseases and areas of interest in public health. These publications have helped drive health program improvements in Rwanda and beyond.
- CDC celebrates 15 years of working in Rwanda.

- The National Centers for Blood Transfusion (NCBT) is recognized as a regional center of excellence in Blood Transfusion Practice and is awarded the highest – level 3 – international standards accreditation by the Africa Society
- Page last reviewed: October 16, 2017
- Page last updated: October 16, 2017
- Content source:
Global Health
Notice: Linking to a non-federal site does not constitute an endorsement by HHS, CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the site.


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir
