Resources
Some Foodborne Pathogens Commonly Found in Raw Milk
Educational Materials
Video Series: Real Stories of the Dangers of Raw Milk
Podcast: Raw or Nonpasteurized Products Can Make You Sick
Dr. Adam Langer, CDC epidemiologist, discusses the dangers of consuming raw or nonpasteurized dairy products in this CDC podcast, “Raw or Nonpasteurized Products Can Make You Sick.” (includes transcript).
Other Materials
- CDC Feature: Raw (Unpasteurized) Milk
- CDC Letter to Epidemiologists and Veterinarians: The Ongoing Public Health Hazards of Consuming Raw Milk
Foodborne Outbreak Data

The Foodborne Outbreak Online Database (FOOD Tool) provides information on foodborne disease outbreaks reported to CDC since 1998. You can use it to search outbreak data by state, food, or germ and see results displayed on interactive maps, graphs, and charts.
Partner Resources
FDA
- The Dangers of Raw Milk: Unpasteurized Milk Can Pose a Serious Health Risk (Español)
- Video: The Dangers of Unpasteurized Milk
- Questions & Answers: Raw Milk
- Consumer Update: Raw Milk May Pose Health Risk
- Raw Milk Misconceptions and the Danger of Raw Milk Consumption
- Preventing Listeriosis in Pregnant Hispanic Women in the United States (Español)
- Video: Food Safety for Moms-to-Be (English and Español)
- Food Safety for Moms-to-Be: Once Baby Arrives(Español)
Foodsafety.gov
Other
- Medscape Commentary: Got Milk? Don’t Get Raw Milk! A Cautionary Tale. CDC expert Dr. Rob Tauxe discusses the dangers of raw milk.
- Real Raw Milk Facts
Publications
2000–Present
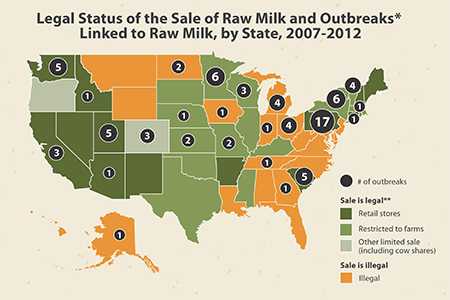
- Mungai EA, Behravesh CB, Gould LH. Increased outbreaks associated with nonpasteurized milk, United States, 2007–2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015 Jan; 21(1):119–22. DOI
- Gould LH, Mungai E, Behravesh CB. Outbreaks attributed to cheese: differences between outbreaks caused by unpasteurized and pasteurized dairy products, United States, 1998–2011. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2014 Jul; 11(7):545–51. DOI PubMed
- Buzby JC, Gould LH, Kendall ME, Jones TF, Robinson T, Blayney DP. Characteristics of consumers of unpasteurized milk in the United States. J Consum Aff. 2013 Jan 7; 47(1):153–66. DOI
- Langer AJ, Ayers T, Grass J, Lynch M, Angulo FJ, Mahon BE. Nonpasteurized dairy products, disease outbreaks, and state laws—United States, 1993–2006. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012 Mar; 18(3):385–91. DOI PubMed
- Hall JM, Rolfs RT, Herlihy RK, Dimond MPS, Holbrook J, Smith LH, et al. Notes from the field: Salmonella Newport infections associated with consumption of unpasteurized milk—Utah, April–June 2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2010 Jul 9; 59(26):817–8. MMWR
- Hunt DC, Banez Ocfemia MC, Neises D, Hansen G, Aghoghovbia ST. Campylobacter jejuni infection associated with unpasteurized milk and cheese—Kansas, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009 Jan 2; 57(51):1377–9. MMWR PubMed
- Cumming M, Kludt P, Matyas B, DeMaria A, Stiles T, Han L, et al. Outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes infections associated with pasteurized milk from a local dairy—Massachusetts, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008 Oct 10; 57(40):1097–100. MMWR PubMed
- Schneider J, Mohle-Boetani J, Vugia D, Menon M. Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections in children associated with raw milk and raw colostrum from cows—California, 2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008 Jun 13; 57(23):625–8. MMWR PubMed
- Austin C, Saathoff-Huber L, Bordson M, Dobbins C, Gross C, Marishta K, et al. Outbreak of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Newport infections associated with consumption of unpasteurized Mexican-style aged cheese—Illinois, March 2006–April 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008 Apr 25; 57(16):432–5. MMWR PubMed
- Lind L, Reeser J, Stayman K, Deasy M, Moll M, Weltman A, et al. Salmonella Typhimurium infection associated with raw milk and cheese consumption—Pennsylvania, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007 Nov 9; 56(44):1161–4. MMWR PubMed
- Bhat M, Denny J, MacDonald K, Hofmann J, Jain S, Lynch M, et al. Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection associated with drinking raw milk—Washington and Oregon, November–December 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007 Mar 2; 56(8):165–7. MMWR PubMed
- Honish L, Predy G, Hislop N, Chui L, Kowalewska-Grochowska K, Trottier L, et al. An outbreak of E. coli O157:H7 hemorrhagic colitis associated with unpasteurized gouda cheese. Can J Public Health. 2005 May–Jun; 96(3):182–4. PubMed
- Holt J, Propes D, Patterson C, Bannerman T, Nicholson L, Bundesen M, et al. Multistate outbreak of Salmonella serotype Typhimurium infections associated with drinking unpasteurized milk—Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, and Tennessee, 2002–2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2003 Jul 4; 52(26):613–5. MMWR PubMed
- Harrington P, Archer J, Davis JP, Croft DR, Varma JK. Outbreak of Campylobacter jejuni infections associated with drinking unpasteurized milk procured through a cow-leasing program—Wisconsin, 2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2002 Jun 28; 51(25):548–9. MMWR PubMed
- Boggs JD, Whitwam RE, Hale LM, Briscoe RP, Kahn SE, MacCormack JN, et al. Outbreak of listeriosis associated with homemade Mexican-style cheese—North Carolina, October 2000–January 2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001 Jul 6; 50(26):560–2. MMWR PubMed
- Durch J, Ringhand T, Manner K, Barnett M, Proctor M, Ahrabi-Fard S, et al. Outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection associated with eating fresh cheese curds—Wisconsin, June 1998. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2000 Oct 13; 49(40):911–3. MMWR PubMed
1979–1999
- Cody SH, Abbott SL, Marfin AA, Schulz B, Wagner P, Robbins K, et al. Two outbreaks of multidrug-resistant Salmonella serotype Typhimurium DT104 infections linked to raw-milk cheese in Northern California. JAMA. 1999 May 19; 281(19):1805–10. PubMed
- Villar RG, Macek MD, Simons S, Hayes PS, Goldoft MJ, Lewis JH, et al. Investigation of multidrug-resistant Salmonella serotype Typhimurium DT104 infections linked to raw-milk cheese in Washington State. JAMA. 1999 May 19; 281(19):1822–6. PubMed
- Altekruse SF, Timbo BB, Mowbray JC, Bean NH, Potter ME. Cheese-associated outbreaks of human illness in the United States, 1973 to 1992: sanitary manufacturing practices protect consumers. J Food Prot. 1998 Oct; 61(10):1405–7. PubMed
- Headrick ML, Korangy S, Bean NH, Angulo FJ, Altekruse SF, Potter ME, et al. The epidemiology of raw milk-associated foodborne disease outbreaks reported in the United States, 1973 through 1992. Am J Public Health. 1998 Aug; 88(8):1219–21. PubMed
- Keene WE, Hedberg K, Herriott DE, Hancock DD, McKay RW, Barrett TJ, et al. A prolonged outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections caused by commercially distributed raw milk. J Infect Dis. 1997 Sep; 176(3):815–8. PubMed
- Fishbein DB, Raoult D. A cluster of Coxiella burnetii infections associated with exposure to vaccinated goats and their unpasteurized dairy products. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Jul; 47(1):35–40. PubMed
- Taylor JP, Perdue JN. The changing epidemiology of human brucellosis in Texas, 1977–1986. Am J Epidemiol. 1989 Jul; 130(1):160–5. PubMed
- Schmid GP, Schaefer RE, Plikaytis BD, Schaefer JR, Bryner JH, Wintermeyer LA, et al. A one-year study of endemic campylobacteriosis in a midwestern city: association with consumption of raw milk. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul; 156(1):218–22. PubMed
- Osterholm MT, MacDonald KL, White KE, Wells JG, Spika JS, Potter ME, et al. An outbreak of a newly recognized chronic diarrhea syndrome associated with raw milk consumption. JAMA. 1986 Jul 25; 256(4):484–90. PubMed
- Warner DP, Bryner JH, Beran GW. Epidemiologic study of campylobacteriosis in Iowa and the possible role of unpasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Feb; 47(2):254–8. PubMed
- Blaser MJ. Brainerd diarrhea: a newly recognized raw milk-associated enteropathy. JAMA. 1986 Jul 25; 256(4):510–1. PubMed
- Klein BS, Vergeront JM, Blaser MJ, Edmonds P, Brenner DJ, Janssen D, et al. Campylobacter infection associated with raw milk: an outbreak of gastroenteritis due to Campylobacter jejuni and thermotolerant Campylobacter fetus subsp fetus. JAMA. 1986 Jan 17; 255(3):361–4. PubMed
- Kornblatt AN, Barrett T, Morris GK, Tosh FE. Epidemiologic and laboratory investigation of an outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis associated with raw milk. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Nov; 122(5):844–9. PubMed
- Potter ME, Kaufmann AF, Blake PA, Feldman RA. Unpasteurized milk. The hazards of a health fetish. JAMA. 1984 Oct 19; 252(15):2048–52. PubMed
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Epidemiologic notes and reports Campylobacter outbreak associated with certified raw milk products—California. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1984 Oct 5; 33(39):562. MMWR
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Campylobacteriosis associated with raw milk consumption—Pennsylvania. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1983 Jul 8; 32(26):337–8, 344. MMWR
- Potter ME, Blaser MJ, Sikes RK, Kaufmann AF, Wells JG. Human Campylobacter infection associated with certified raw milk. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Apr; 117(4):475–83. PubMed
- Taylor DN, Porter BW, Williams CA, Miller HG, Bopp CA, Blake PA. Campylobacter enteritis: a large outbreak traced to commercial raw milk. West J Med. 1982 Nov; 137(5):365–9. PubMed
- Doyle MP, Roman DJ. Prevalence and survival of Campylobacter jejuni in unpasteurized milk. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov; 44(5):1154–8. PubMed
- Chin J. Raw milk: a continuing vehicle for the transmission of infectious disease agents in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep; 146(3):440–1. PubMed
- Taylor DN, Bied JM, Munro JS, Feldman RA. Salmonella dublin infections in the United States, 1979–1980. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep; 146(3):322–7. PubMed
- Blaser MJ, Cravens J, Powers BW, Laforce FM, Wang WL. Campylobacter enteritis associated with unpasteurized milk. Am J Med. 1979 Oct; 67(4):715–8. PubMed
- Page last reviewed: June 15, 2017
- Page last updated: September 1, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir