
Philophthalmiasis
[Philophthalmus spp.]
Causal Agents
Pentatrichomonas hominis, a nonpathogenic flagellate.
Life Cycle
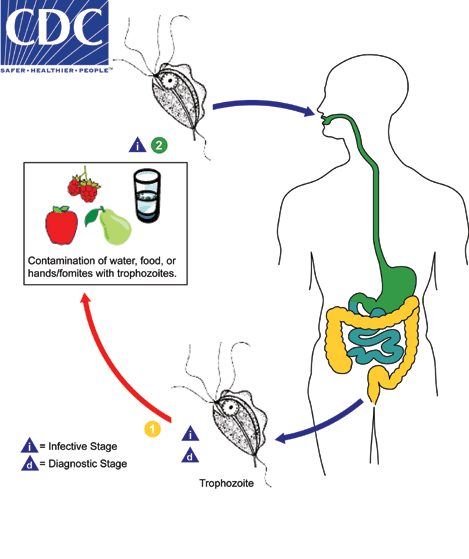
Only trophozoites of Pentatrichomonas hominis are shed in feces  , as there is no known cyst stage for this species. Infection occurs after the ingestion of trophozoites in fecal-contaminated food or water, or on fomites
, as there is no known cyst stage for this species. Infection occurs after the ingestion of trophozoites in fecal-contaminated food or water, or on fomites  . Pentatrichomonas resides in the large intestine, where it is regarded as a commensal and is not known to cause disease.
. Pentatrichomonas resides in the large intestine, where it is regarded as a commensal and is not known to cause disease.
Geographic Distribution
Worldwide
Clinical Presentation
Pentatrichomonas hominis is considered nonpathogenic. The presence of trophozoites in stool specimens can however be an indicator of fecal contamination of a food or water source, and thus does not rule-out other parasitic infections.
Pentatrichomonas hominis trophozoites.
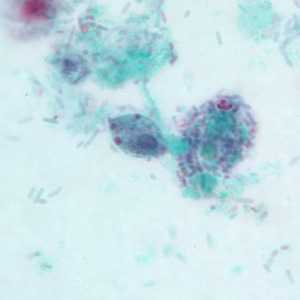
Figure A: Trophozoite of P. hominis in a stool specimen, stained with trichrome.
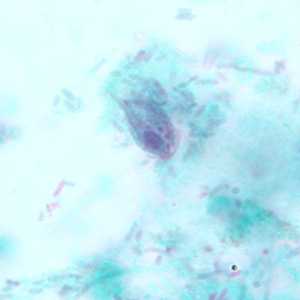
Figure B: Trophozoite of P. hominis in a stool specimen, stained with trichrome.
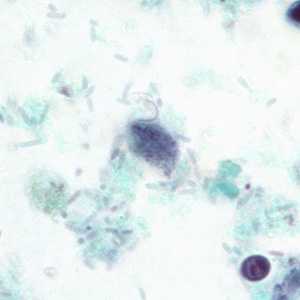
Figure C: Trophozoite of P. hominis in a stool specimen, stained with trichrome.
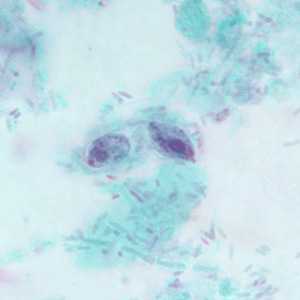
Figure D: Two trophozoites of P. hominis in a stool specimen, stained with trichrome.
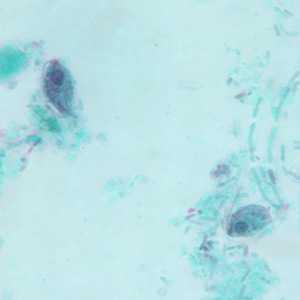
Figure E: Trophozoites of P. hominis in a stool specimen, stained with trichrome.

Figure F: Trophozoite of P. hominis in a stool specimen, stained with iron hematoxylin.
Laboratory Diagnosis
Pentatrichomonas hominis is identified through the detection of trophozoites in stool specimens. Identification is best accomplished by direct wet mounts that reveal the characteristic, jerky movement of the organisms. They may also be identified in permanent stained smears, although their affinities for stain are inconsistent and with their small size are often overlooked.
Treatment Information
As this species is considered nonpathogenic, there are no treatment recommendations for this organism.
DPDx is an education resource designed for health professionals and laboratory scientists. For an overview including prevention and control visit www.cdc.gov/parasites/.
- Page last reviewed: May 3, 2016
- Page last updated: May 3, 2016
- Content source:
- Global Health – Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria
- Notice: Linking to a non-federal site does not constitute an endorsement by HHS, CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the site.
- Maintained By:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir