
Echinococcosis
[Echinococcus granulosus] [Echinococcus multilocularis] [Echinococcus oligarthrus] [Echinococcus vogeli]
Causal Agent
Human echinococcosis (hydatidosis, or hydatid disease) is caused by the larval stages of cestodes (tapeworms) of the genus Echinococcus. Echinococcus granulosus causes cystic echinococcosis, the form most frequently encountered; E. multilocularis causes alveolar echinococcosis; E. vogeli causes polycystic echinococcosis; and E. oligarthrus is an extremely rare cause of human echinococcosis.
Life Cycle
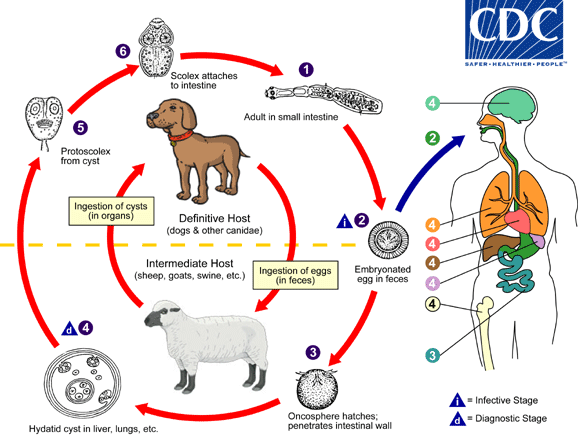
The adult Echinococcus granulosus (3 to 6 mm long)  resides in the small bowel of the definitive hosts, dogs or other canids. Gravid proglottids release eggs
resides in the small bowel of the definitive hosts, dogs or other canids. Gravid proglottids release eggs  that are passed in the feces. After ingestion by a suitable intermediate host (under natural conditions: sheep, goat, swine, cattle, horses, camel), the egg hatches in the small bowel and releases an oncosphere
that are passed in the feces. After ingestion by a suitable intermediate host (under natural conditions: sheep, goat, swine, cattle, horses, camel), the egg hatches in the small bowel and releases an oncosphere  that penetrates the intestinal wall and migrates through the circulatory system into various organs, especially the liver and lungs. In these organs, the oncosphere develops into a cyst
that penetrates the intestinal wall and migrates through the circulatory system into various organs, especially the liver and lungs. In these organs, the oncosphere develops into a cyst  that enlarges gradually, producing protoscolices and daughter cysts that fill the cyst interior. The definitive host becomes infected by ingesting the cyst-containing organs of the infected intermediate host. After ingestion, the protoscolices
that enlarges gradually, producing protoscolices and daughter cysts that fill the cyst interior. The definitive host becomes infected by ingesting the cyst-containing organs of the infected intermediate host. After ingestion, the protoscolices  evaginate, attach to the intestinal mucosa
evaginate, attach to the intestinal mucosa  , and develop into adult stages
, and develop into adult stages  in 32 to 80 days. The same life cycle occurs with E. multilocularis (1.2 to 3.7 mm), with the following differences: the definitive hosts are foxes, and to a lesser extent dogs, cats, coyotes and wolves; the intermediate host are small rodents; and larval growth (in the liver) remains indefinitely in the proliferative stage, resulting in invasion of the surrounding tissues. With E. vogeli (up to 5.6 mm long), the definitive hosts are bush dogs and dogs; the intermediate hosts are rodents; and the larval stage (in the liver, lungs and other organs) develops both externally and internally, resulting in multiple vesicles. E. oligarthrus (up to 2.9 mm long) has a life cycle that involves wild felids as definitive hosts and rodents as intermediate hosts. Humans become infected by ingesting eggs
in 32 to 80 days. The same life cycle occurs with E. multilocularis (1.2 to 3.7 mm), with the following differences: the definitive hosts are foxes, and to a lesser extent dogs, cats, coyotes and wolves; the intermediate host are small rodents; and larval growth (in the liver) remains indefinitely in the proliferative stage, resulting in invasion of the surrounding tissues. With E. vogeli (up to 5.6 mm long), the definitive hosts are bush dogs and dogs; the intermediate hosts are rodents; and the larval stage (in the liver, lungs and other organs) develops both externally and internally, resulting in multiple vesicles. E. oligarthrus (up to 2.9 mm long) has a life cycle that involves wild felids as definitive hosts and rodents as intermediate hosts. Humans become infected by ingesting eggs  , with resulting release of oncospheres
, with resulting release of oncospheres  in the intestine and the development of cysts
in the intestine and the development of cysts  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  in various organs.
in various organs.
Geographic Distribution
Echinococcus granulosus occurs practically worldwide, and more frequently in rural, grazing areas where dogs ingest organs from infected animals. Echinococcus multilocularis occurs in the northern hemisphere, including central Europe and the northern parts of Europe, Asia, and North America. Echinococcus vogeli and Echinococcus oligarthrus occur in Central and South America.
Clinical Presentation
Echinococcus granulosus infections remain silent for years before the enlarging cysts cause symptoms in the affected organs. Hepatic involvement can result in abdominal pain, a mass in the hepatic area, and biliary duct obstruction. Pulmonary involvement can produce chest pain, cough, and hemoptysis. Rupture of the cysts can produce fever, urticaria, eosinophilia, and anaphylactic shock, as well as cyst dissemination. In addition to the liver and lungs, other organs (brain, bone, heart) can also be involved, with resulting symptoms. Echinococcus multilocularis affects the liver as a slow growing, destructive tumor, with abdominal pain, biliary obstruction, and occasionally metastatic lesions into the lungs and brain. Echinococcus vogeli affects mainly the liver, where it acts as a slow growing tumor; secondary cystic development is common.
Echinococcus granulosus in tissue.
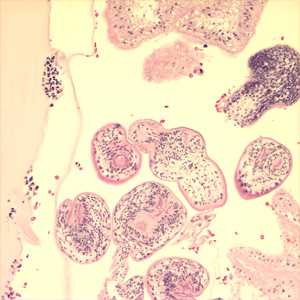
Figure A: Protoscoleces in a hydatid cyst removed from lung tissue, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Image taken at 200x magnification. Image courtesy of Phoenix Children's Hospital, Phoenix, AZ.

Figure A: Protoscoleces in a hydatid cyst removed from lung tissue, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Image taken at 200x magnification. Image courtesy of Phoenix Children's Hospital, Phoenix, AZ.
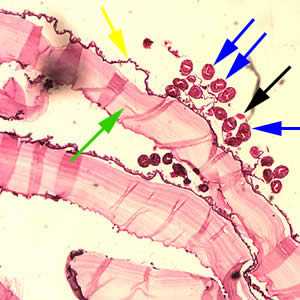
Figure C: Cross-section of an E. granulosus cyst, stained with H&E. The cyst wall is composed of an acellular laminated external layer (green arrow) and a thin, germinal (nucleated) inner layer (yellow arrow). Note the brood capsule (black arrow) with protoscoleces (blue arrows) inside. Image taken at 40x magnification.
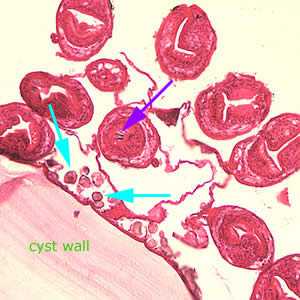
Figure D: Higher magnification (200x) of the cyst in Figure C, showing daughter cyst (brood capsule). Note the hooklets (purple arrow) inside one of the protoscoleces and the calcareous corpuscles (light blue arrows) along the germinal layer.
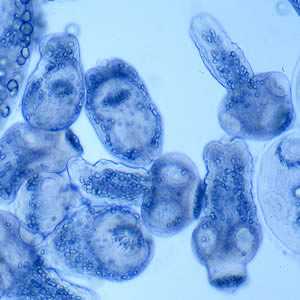
Figure E: Protoscoleces liberated from a hydatid cyst.
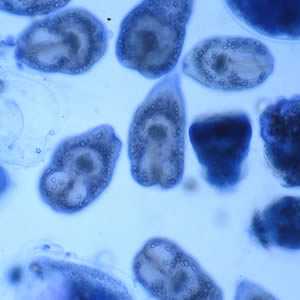
Figure F: Protoscoleces liberated from a hydatid cyst.
Echinococcus sp. from a liver cyst, stained with Papanicolaou (PAP) stain.
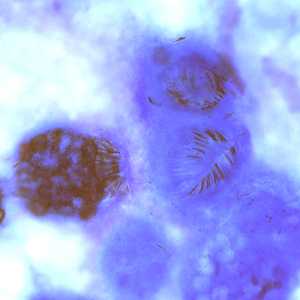
Figure A: Protoscoleces in a hydatid cyst removed a liver cyst, stained with PAP.
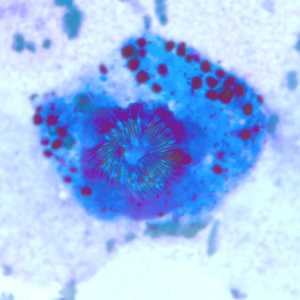
Figure B: Protoscoleces in a hydatid cyst removed a liver cyst, stained with PAP.
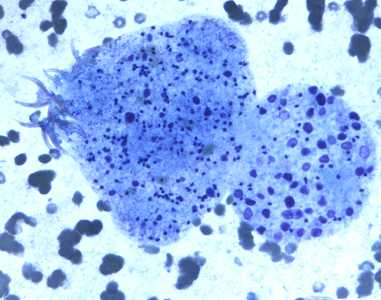
Figure C: Degenerating protoscolex from a liver cyst, stained with PAP.
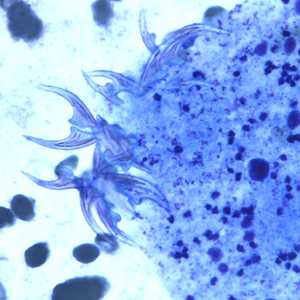
Figure D: Higher magnification of the image in Figure C, showing a close-up of the hooklets.
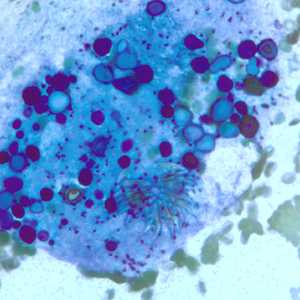
Figure E: Degenerating protoscolex from a liver cyst, stained with PAP. Notice the conspicuous calcareous corpuscles, characteristic of cestode infections.
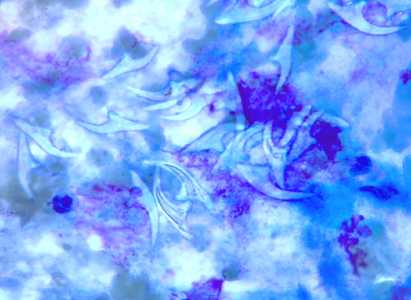
Figure F: Free hooklets in 'hydatid sand' from the aspirate of a liver cyst, stained with PAP.
Echinococcus multilocularis in tissue, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E).
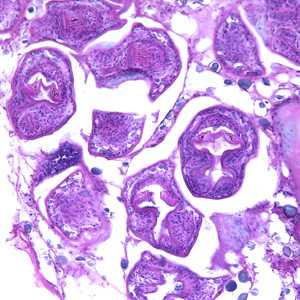
Figure A: Echinococcus multilocularis in liver tissue, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Magnification at 200x
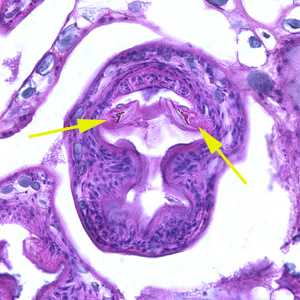
Figure B: Higher magnification (400x) of the specimen in Figure A. Notice a pair of refractile hooks (yellow arrows). Cestode hooks do not stain with H&E but may be visible with proper adjustment of the microscope.
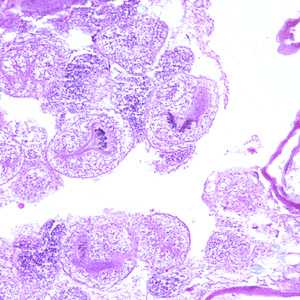
Figure C: Echinococcus multilocularis is tissue, stained with H&E. Magnification at 200x.
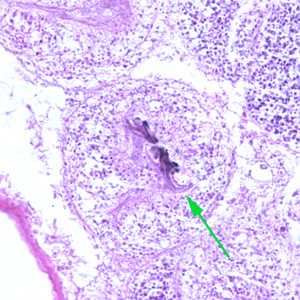
Figure D: Higher magnification (400x) of the specimen in Figure C. Notice the refractile hook (green arrow).
Echinococcus eggs in feces.

Figure A: Egg of Echinococcus sp. in an unstained wet mount of concentrated stool from a dog. Image taken at 400x magnification.
Echinococcus spp. adults.
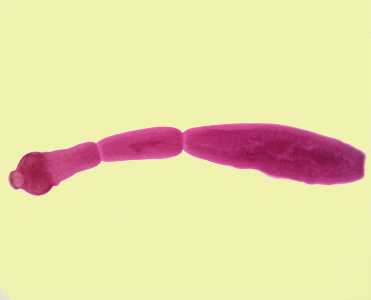
Figure A: Echinococcus granulosus adult, stained with carmine.
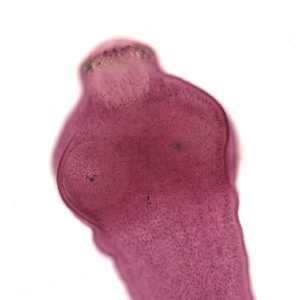
Figure B: Close-up of the scolex of E. granulosus in Figure A. In this focal plane, one of the suckers is clearly visible, as is the ring of rostellar hooks.
Diagnostic Findings
The diagnosis of echinococcosis relies mainly on findings by ultrasonography and/or other imaging techniques supported by positive serologic tests. In seronegative patients with hepatic image findings compatible with echinococcosis, ultrasound guided fine needle biopsy may be useful for confirmation of diagnosis; during such procedures precautions must be taken to control allergic reactions or prevent secondary recurrence in the event of leakage of hydatid fluid or protoscolices.
Antibody Detection
Immunodiagnostic tests can be very helpful in the diagnosis of echinococcal disease and should be used before invasive methods. However, the clinician must have some knowledge of the characteristics of the available tests and the patient and parasite factors associated with false results. False-positive reactions may occur in persons with other helminthic infections, cancer, and chronic immune disorders. Negative test results do not rule out echinococcosis because some cyst carriers do not have detectable antibodies. Whether the patient has detectable antibodies depends on the physical location, integrity, and vitality of the larval cyst. Cysts in the liver are more likely to elicit antibody response than cysts in the lungs, and, regardless of localization, antibody detection tests are least sensitive in patients with intact hyaline cysts. Cysts in the lungs, brain, and spleen are associated with lowered serodiagnostic reactivity, whereas those in bone appear to more regularly stimulate detectable antibody. Fissuration or rupture of a cyst is followed by an abrupt stimulation of antibodies. A patient with senescent, calcified, or dead cysts is generally found to be seronegative.
Cystic echinococcal disease (Echinococcus granulosus). Indirect hemagglutination (IHA), indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) tests, and enzyme immunoassays (EIA) are sensitive tests for detecting antibodies in serum of patients with cystic disease; sensitivity rates vary from 60% to 90%, depending on the characteristics of the cases. Crude hydatid cyst fluid is generally employed as antigen. At present, the best available serologic diagnosis is obtained by using combinations of tests. EIA or IHA is used to screen all specimens; a positive reaction is confirmed by immunoblot assay or any gel diffusion assay that demonstrates the echinococcal "Arc 5." Although these confirmatory assays give false-positive reactions with sera of 5% to 25% of persons with neurocysticercosis, the clinical and epidemiological presentation of neurocysticercosis patients should be rarely confused with that of cystic echinococcosis. A commercial EIA kit is available in the United States.
Antibody responses have also been monitored as a way of evaluating the results of treatment, but with mixed results. Following successful radical surgery, antibody titers decline and sometimes disappear; titers rise again if secondary cysts develop. Tests for Arc 5 or IgE antibodies appear to reflect antibody decline during the first 24 months postsurgery, whereas the IHA and other tests remain positive for at least 4 years. Chemotherapy has not been followed by consistent declines in antibody titers. Consequently, the usefulness of serology to monitor the course of disease is limited; imaging techniques provide a more accurate assessment of the patient's condition.
Alveolar echinococcal disease (Echinococcus multilocularis). Most patients with alveolar disease have detectable antibodies in serologic tests using heterologous E. granulosus or homologous Echinococcus multilocularis antigens. With crude Echinococcus antigens, nonspecific reactions create the same difficulties as described above, however, immunoaffinity-purified E. multilocularis antigens (Em2) used in EIA allow the detection of positive antibody reactions in more than 95% of alveolar cases. Comparing serologic reactivity to Em2 antigen with that to antigens containing components of both E. multilocularis and E. granulosus permits discrimination of patients with alveolar from those with cystic disease. Combining two purified E. multilocularis antigens (Em2 and recombinant antigen II/3-10) in a single immunoassay optimized sensitivity and specificity. These antigens are sold in a commercial EIA kit in Europe, but not in the United States. As in cystic echinococcosis, Em2 tests are more useful for postoperative follow-up than for monitoring the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Reference
Lightowlers MW, Gottstein B. Echinococcosis/hydatidosis: antigens, immunological and molecular diagnosis. In: Thompson RCA, Lymbery AJ, editors. Echinococcus and hydatid disease. Wallingford, UK: CAB International; 1995. p. 355-410.
Treatment Information
Cystic Echinococcosis
In the past, surgery was the only treatment for cystic echinococcal cysts. Chemotherapy, cyst puncture, and PAIR (percutaneous aspiration, injection of chemicals and reaspiration) have been used to replace surgery as effective treatments for cystic echinococcosis and, for some cases, no treatment but a conservative "watch and wait" approach is best. Treatment indications vary with cyst characteristics, including cyst type, location, size, and complications. Surgery may be the best treatment for liver cysts that are secondarily infected or cysts located in the brain, lungs, or kidney. Liver cysts larger than 7.5 cm are likely to have biliary communication; surgery may be the best option for these cysts. Many abdominal cysts can be treated by injection of protoscolicidal chemical solutions into the cyst, followed by evacuation, prior to further manipulations and extirpation of cysts.
For some patients, chemotherapy with benzimidazoles is the preferred treatment. Patients with small cysts or multiple cysts in several organs can be treated successfully with albendazole. Approximately one third of patients treated with chemotherapy with benzimidazole drugs have been cured of the disease and even higher proportions, between 30-50%, have responded with significant regression of the cyst size and alleviation of symptoms. Both albendazole 10 to 15 mg/kg body weight per day (max 800 mg orally in two doses) in several 1-month courses with treatment-free intervals of 14 days and, as a second choice for treatment, mebendazole 40-50 mg/kg body weight per day continuously have been highly effective. Additionally, chemotherapy can be very effective when used in conjunction with surgery. Albendazole has been administered to patients prior to surgery for the intended purpose of facilitating the safe surgical manipulation of the cysts by inactivating protoscolices, altering the integrity of the cysts membranes, and reducing the turgidity of the cysts. A third treatment option, PAIR (percutaneous aspiration, injection of chemicals and reaspiration), has been shown to be effective. This option is indicated for patients with relapse after surgery, failure of chemotherapy alone, or who refuse surgery.
| Drug* | Adult Dosage | Pediatric Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Albendazole | 400 mg orally twice a day for 1-6 months | 10-15 mg/kg/day (max 800 mg) orally in two doses for 1-6 months |
*Praziquantel may be useful preoperatively or in case of spillage of cyst contents during surgery (Bygott JM, Chiodini PL. Acta Tropica 2009; 111: 95-101).
Albendazole
Oral albendazole is available for human use in the United States.
Note on Treatment in Pregnancy
Mebendazole
Mebendazole is available in the United States only through compounding pharmacies.
Note on Treatment in Pregnancy
Alveolar Echinococcosis
Alveolar echinococcosis requires chemotherapy with or without surgery; radical surgery is the preferred approach in suitable cases. Effective treatment involves benzimidazoles administered continuously for at least 2 years and patient monitoring for 10 years or more since recurrence is possible. This has inhibited progression of alveolar echinococcosis and reduced lesion size in approximately half of treated cases. Intermittent treatment with albendazole is not recommended.
DPDx is an education resource designed for health professionals and laboratory scientists. For an overview including prevention and control visit www.cdc.gov/parasites/.
- Page last reviewed: May 3, 2016
- Page last updated: May 3, 2016
- Content source:
- Global Health – Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria
- Notice: Linking to a non-federal site does not constitute an endorsement by HHS, CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the site.
- Maintained By:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir