
Acanthocephaliasis
[Bolbosoma spp.] [Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceous] [Moniliformis moniliformis]
Causal Agents
The principle agents of acanthocephaliasis in humans are the thorny-headed worms, Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceous and Moniliformis moniliformis. Bolbosoma species have also been known to infect humans.
Life Cycle
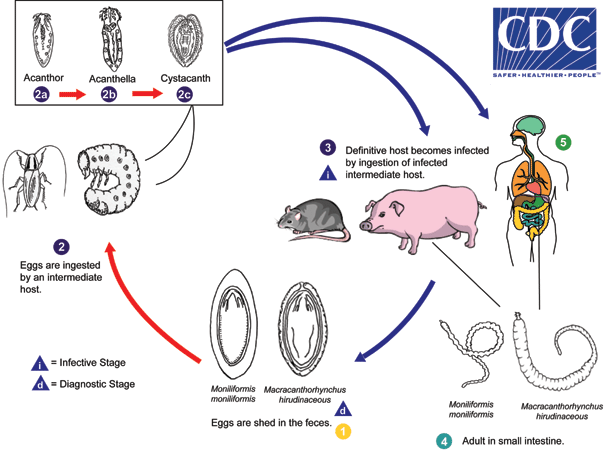
Eggs are shed in the feces of the definitive hosts  , which are usually rats for M. moniliformis and swine for M. hirudinaceous, although carnivores and primates, including humans, may serve as accidental hosts. The eggs contain a fully-developed acanthor when shed in feces. The eggs are ingested by an intermediate host
, which are usually rats for M. moniliformis and swine for M. hirudinaceous, although carnivores and primates, including humans, may serve as accidental hosts. The eggs contain a fully-developed acanthor when shed in feces. The eggs are ingested by an intermediate host  , which is an insect (usually scarabaeoid or hydrophilid beetles for M. hirudinaceous and beetles or cockroaches for M. moniliformis). Within the hemocoelom of the insect, the acanthor
, which is an insect (usually scarabaeoid or hydrophilid beetles for M. hirudinaceous and beetles or cockroaches for M. moniliformis). Within the hemocoelom of the insect, the acanthor  molts into a second larval stage, called an acanthella
molts into a second larval stage, called an acanthella  . After 6-12 weeks, the worm reaches the infective stage called a cystacanth
. After 6-12 weeks, the worm reaches the infective stage called a cystacanth  . The definitive host becomes infected upon ingestion of intermediate hosts containing infective cystacanths
. The definitive host becomes infected upon ingestion of intermediate hosts containing infective cystacanths ![]() . In the definitive host, liberated juveniles attach to the wall of the small intestine, where they mature
. In the definitive host, liberated juveniles attach to the wall of the small intestine, where they mature and mate in about 8-12 weeks. In humans
and mate in about 8-12 weeks. In humans  the worms seldom mature, or mature but will rarely produce eggs.
the worms seldom mature, or mature but will rarely produce eggs.
Geographic Distribution
Acanthocephalans are widely distributed and cases of acanthocephaliasis generally occur in areas where insects are eaten for dietary or medicinal purposes.
Clinical Presentation
Clinical symptoms of acanthocephaliasis are often severe, due in part to the mechanical damage caused by the insertion of the armed proboscis into the lumen of the host's intestine. Symptoms may include abdominal pain and distension, fever, decreased appetite, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, diarrhea, constipation or bloody stools.
Eggs of Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceous.
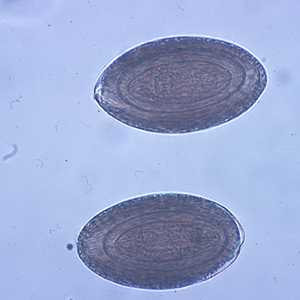
Figure A: Eggs of M. hirudinaceous in an unstained wet mount of stool.
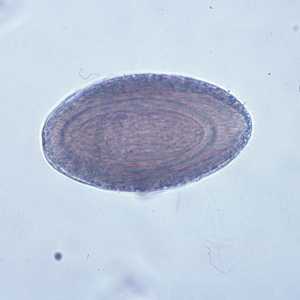
Figure B: Egg of M. hirudinaceous in an unstained wet mount of stool.
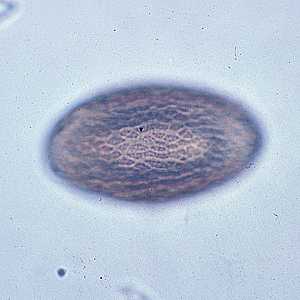
Figure C: Image of the same egg in Figure B, but in a different plane of focus, showing the textured exterior.
Eggs of Moniliformis moniliformis.

Figure A: Eggs of M. moniliformis liberated from an adult worm that was recovered from the stool of a patient.
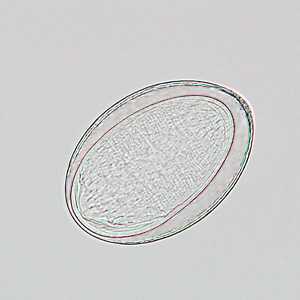
Figure B: Egg of M. moniliformis liberated from an adult worm that was recovered from the stool of a patient.
Adults of Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceous.

Figure A: Adult of M. hirudinaceous.
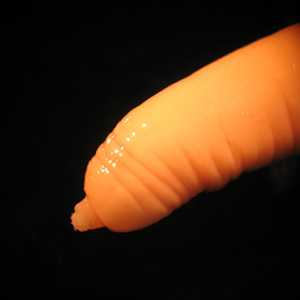
Figure B: Higher magnification of the specimen in Figure A, showing a close-up of the anterior end and the proboscis containing hooks.
Adults of Moniliformis moniliformis.

Figure A: Adult of M. moniliformis.

Figure B: Adult of M. moniliformis.

Figure C: Higher magnification of the anterior end of the specimen in Figures A and B, showing a close-up of the proboscis.

Figure D: Higher magnification of the anterior end of the specimen in Figures A and B, showing a close-up of the proboscis.
Acanthocephalans in tissue, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H & E).
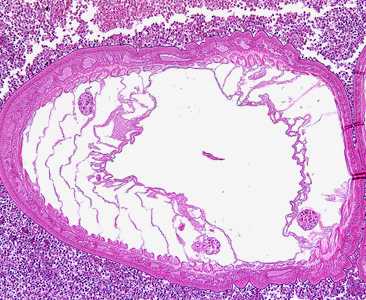
Figure A: Transverse section through the body wall of Bolbosoma sp. in an intestinal biopsy specimen, stained with H&E. Image taken at 100x magnification. Cetaceans are the normal definitive hosts for Bolbosoma spp., and humans usually become infected after eating under-cooked fish which serve as paratenic hosts for the parasite.
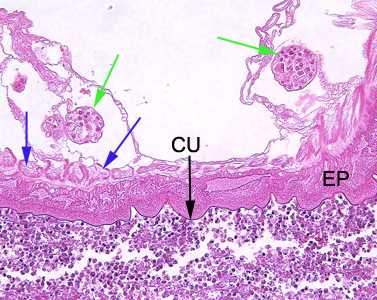
Figure B: Higher-magnification (200x) of the specimen in Figure A. Identifiable in this image are the characteristic thin cuticle (CU, black arrow), syncytial epidermis (EP), longitudinal muscles (blue arrows) and eggs (green arrows).
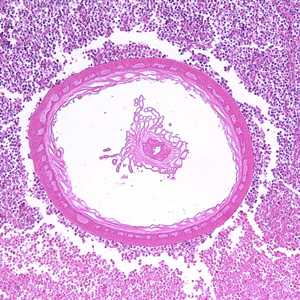
Figure C: Transverse section through the body wall of Bolbosoma sp. in an intestinal biopsy specimen, stained with H&E. Image taken at 100x magnification. In this image, a portion of the reproductive system is visible within the pseudocoelom.
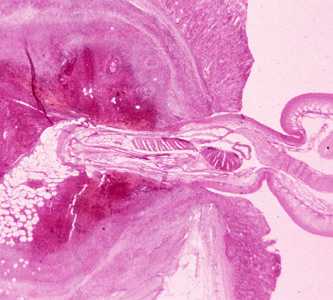
Figure D: Cross-section of the intestine of a pig, stained with H&E, showing the anterior end of an adult Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceous embedded within the intestinal wall.
Intermediate hosts of acanthocephalans.

Figure A: Larva of a melolonthine scarab beetle, also known as a "white grub". White grubs and dung beetle larvae are the most common intermediate hosts for M. hirudinaceous. Image courtesy of Parasite and Diseases Image Library, Australia (http://www.padil.gov.au/External Web Site Icon).

Figure B: American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. The American and Oriental cockroach (Blatta orientalis) are two of the more common intermediate hosts for M. moniliformis. Image courtesy of Parasite and Diseases Image Library, Australia (http://www.padil.gov.au/External Web Site Icon).
Laboratory Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by the observation of eggs or adults in stool. As humans are not the usual definitive host for acanthocephalans, the parasites often do not reach sexual maturity in the human host. Eggs in feces, especially in the absence of other symptoms, may indicate spurious passage.
Treatment Information
Few human cases of acanthocephaliasis have been reported, most of which have been caused by the parasitic worm Moniliformis moniliformis. Some experts consider pyrantel pamoate* the treatment of choice to expel the worm from the body. The treatment regimen consists of a total of 3 oral doses of pyrantel pamoate (11 mg/kg per dose) separated by 2-week intervals.
DPDx is an education resource designed for health professionals and laboratory scientists. For an overview including prevention and control visit www.cdc.gov/parasites/.
- Page last reviewed: May 3, 2016
- Page last updated: May 3, 2016
- Content source:
- Global Health – Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria
- Notice: Linking to a non-federal site does not constitute an endorsement by HHS, CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the site.
- Maintained By:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir