ആൻതോസയാനിൻ
ആൻതോസയാനിൻ (anthocyans; from Greek: ἄνθος (anthos) ജലത്തിൽ ലയിക്കുന്നതും പിഎച്ചിനെ ആശ്രയിച്ച് ചുവപ്പ്, പർപ്പിൾ, നീല എന്നീ നിറങ്ങളിൽ ഫേനത്തിൽ കാണപ്പെടുന്ന വർണ്ണവസ്തുവാണിത്. ബ്ലൂബെറി, റാസ്ബെറി, ബ്ലാക്ക് റൈസ്, ബ്ലാക്ക് സോയ്ബീൻ തുടങ്ങിയ സസ്യാഹാരങ്ങളിൽ ധാരാളമായി ആൻതോസയാനിൻ കാണപ്പെടുന്നു. ശരത്കാലത്ത് കാണപ്പെടുന്ന ഇലകളുടെ നിറത്തിന് കാരണം ആൻതോസയാനിൻ ആണ്.[1] [2]

ആൻതോസയാനിൻ അടങ്ങിയ പർപ്പിൾ കോളീഫ്ളവർ

Anthocyanins give these pansies their dark purple pigmentation
രാസഗുണങ്ങൾ
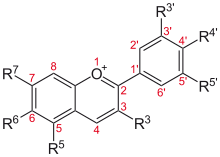
Anthocyanins are glycosides of anthocyanidins, the basic chemical structure of which is shown here
Superposition of spectra of chlorophyll a and b with oenin (malvidin 3O glucoside), a typical anthocyanin, in an acidic solution; while chlorophylls absorb in the blue and yellow/red parts of the visible spectrum, oenin absorbs mainly in the green part of the spectrum, where chlorophylls do not absorb at all

A selected purple-leaf cultivar of European beech tree
Flavylium cation derivatives
See Anthocyanidins article.
| Basic structure | Anthocyanidin | R3′ | R4′ | R5′ | R3 | R5 | R6 | R7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Aurantinidin | −H | −OH | −H | −OH | −OH | −OH | −OH |
| Cyanidin | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Delphinidin | −OH | −OH | −OH | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Europinidin | −OCH 3 |
−OH | −OH | −OH | −OCH 3 |
−H | −OH | |
| Pelargonidin | −H | −OH | −H | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Malvidin | −OCH 3 |
−OH | −OCH 3 |
−OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Peonidin | −OCH 3 |
−OH | −H | −OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Petunidin | −OH | −OH | −OCH 3 |
−OH | −OH | −H | −OH | |
| Rosinidin | −OCH 3 |
−OH | −H | −OH | −OH | −H | −OCH 3 |
അവലംബം
- Davies, Kevin M. (2004). Plant pigments and their manipulation. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 6. ISBN 1-4051-1737-0.
- Archetti, Marco; Döring, Thomas F.; Hagen, Snorre B.; et al. (2011). "Unravelling the evolution of autumn colours: an interdisciplinary approach". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 24 (3): 166–73. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2008.10.006. PMID 19178979.
പുറത്തേയ്ക്കുള്ള കണ്ണികൾ
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.