Scheie syndrome
Scheie syndrome is a disease caused by a deficiency in the enzyme iduronidase, leading to the buildup of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in the body. It is the most mild subtype of mucopolysaccharidosis type I; the most severe subtype of this disease is called Hurler Syndrome.
| Scheie syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MPS I-S |
| Structure of dermatan sulfate, one of the molecules that accumulates in the lysosomes of Hurler syndrome patients | |
| Symptoms | Symptoms are variable, but may include: mild learning disabilities, psychiatric issues, visual problems, skeletal deformities, carpal tunnel syndrome, aortic valve disease, and/or sleep apnea |
| Usual onset | Symptoms may appear by age 5; diagnosis is usually made after age 10 |
| Causes | Deficiency of the alpha-L iduronidase enzyme |
| Differential diagnosis | Other forms of MPS I; Hunter Syndrome; other mucopolysaccharidoses |
| Treatment | Enzyme replacement therapy with iduronidase; surgery may be necessary |
| Prognosis | These patients may live to adulthood. |
| Frequency | 1 in 500,0000[1] |
Scheie syndrome is characterized by corneal clouding, facial dysmorphism, and normal lifespan.[2][3] People with this condition may have aortic regurgitation.[4]
Symptoms
The symptoms of Scheie syndrome are variable, but are milder than Hurler Syndrome. Symptoms may begin to appear by age 5, but affected children are often not diagnosed until after age 10. Patients with Scheie Syndrome may have normal intelligence, or they may have mild learning impairments or psychiatric problems. Glaucoma, retinal degeneration, and clouded corneas may cause visual impairments. Aortic valve disease may be present, along with carpal tunnel syndrome, deformed hands and feet, stiff joints, or sleep apnea. People with Scheie syndrome may live into adulthood.[1]
Genetics
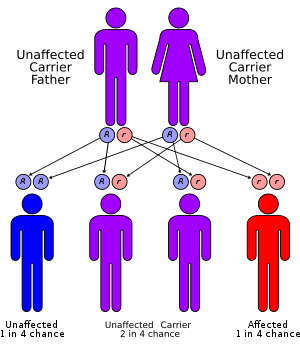
Children with Scheie Syndrome carry two defective copies of the IDUA gene, which has been mapped to the 4p16.3 site on chromosome 4. This is the gene which encodes for the protein iduronidase. All patients with subtypes of MPS I have mutations in the same gene, leading to deficiencies of the same enzyme. However, patients with Scheie Syndrome have a greater level of iduronidase activity than patients with Hurler Syndrome.
Because Scheie syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder, affected persons have two nonworking copies of the gene. A person born with one normal copy and one defective copy is called a carriers. They will produce less α-L-iduronidase than an individual with two normal copies of the gene. The reduced production of the enzyme in carriers, however, remains sufficient for normal function; the person should not show any symptoms of the disease.
History
In 1919, Gertrud Hurler, a German pediatrician, described a syndrome involving corneal clouding, skeletal abnormalities, and mental retardation. This became known as Hurler Syndrome.[5][6] In 1962, a milder variant of Hurler Syndrome was identified by Scheie, leading to the designation of Scheie syndrome.[7]
See also
- Hunter syndrome (MPS II)
- Sanfilippo syndrome (MPS III)
- Morquio syndrome (MPS IV)
References
- "Mucopolysaccharidoses Fact Sheet". National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. 15 Nov 2017. Retrieved 11 May 2018.
- Ropper AH, Samuels MA, "Chapter 37. Inherited Metabolic Diseases of the Nervous System" (Chapter). Ropper AH, Samuels MA: Adams and Victor's Principles of Neurology, 9e: http://www.accessmedicine.com/content.aspx?aID=3636356.
- Bonakdar-Pour, Akbar (2010-06-09). Diagnostic Imaging of Musculoskeletal Diseases: A Systematic Approach. ISBN 9781597453554.
- "Scheie syndrome - National Library of Medicine - PubMed Health". ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- Hurler's syndrome at Who Named It?
- Hurler, G. (1919). "Über einen Typ multipler Abartungen, vorwiegend am Skelettsystem". Zeitschrift für Kinderheilkunde. 24 (5–6): 220–234. doi:10.1007/BF02222956.
- Moore, David; Connock, Martin J.; Wraith, Ed; Lavery, Christine (2008-01-01). "The prevalence of and survival in Mucopolysaccharidosis I: Hurler, Hurler-Scheie and Scheie syndromes in the UK". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 3: 24. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-3-24. ISSN 1750-1172. PMC 2553763. PMID 18796143.