Posterior tibial vein
In anatomy, there are two posterior tibial veins of the lower limb. They receive blood from the medial and lateral plantar veins and drain the posterior compartment of the leg and the plantar surface of the foot to the popliteal vein which it forms when it joins with the anterior tibial vein.[1]
| Posterior tibial vein | |
|---|---|
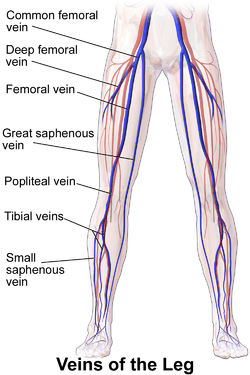 Veins of the leg, where the posterior tibial vein is the medial one of the "Tibial veins". | |
| Details | |
| Source | fibular veins |
| Drains to | popliteal vein |
| Artery | posterior tibial artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | venae tibiales posteriores |
| TA | A12.3.11.032 |
| FMA | 44332 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Like most deep veins, posterior tibial veins are accompanied by an homonym artery, the posterior tibial artery, along its course.
They receive the most important perforator veins: the Cockett perforators, superior, medial and inferior.[2]
Additional images
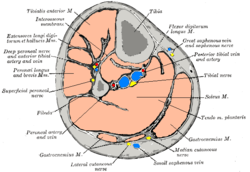 Cross-section through middle of leg.
Cross-section through middle of leg.
References
- Alcamo (2003). Anatomy Coloring Workbook. New York: Random House Inc. p. 196. ISBN 978-0375763427.
- Cavezzi, A.; Labropoulos, N.; Partsch, H.; Ricci, S.; Caggiati, A.; Myers, K.; Nicolaides, A.; Smith, P.C. (2006). "Duplex Ultrasound Investigation of the Veins in Chronic Venous Disease of the Lower Limbs—UIP Consensus Document. Part II. Anatomy". European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 31 (3): 288–99. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2005.07.020. PMID 16230038.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.