Posterior tibial artery
The posterior tibial artery of the lower limb carries blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and plantar surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery via the tibial-fibular trunk. It is accompanied by a deep vein, the posterior tibial vein, along its course.
| Posterior tibial artery | |
|---|---|
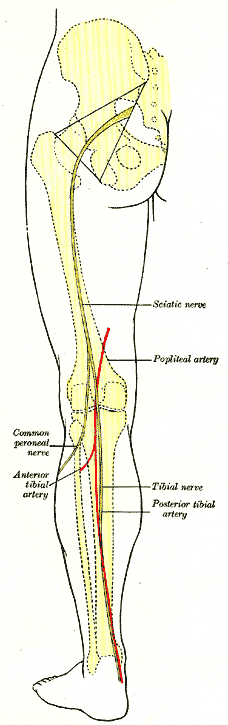 Back of left lower extremity, showing surface markings for bones, vessels, and nerves (posterior tibial artery labeled at bottom right). | |
| Details | |
| Source | Popliteal artery |
| Branches | Fibular artery, medial plantar artery, lateral plantar artery |
| Vein | Posterior tibial vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria tibialis posterior |
| TA | A12.2.16.055 |
| FMA | 43895 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Branches
The posterior tibial artery gives rise to the medial plantar artery, lateral plantar artery, and gives rise to the fibular artery. Often, the branch of the fibular artery is said to rise from the bifurcation of the tibial-fibular trunk and the posterior tibial artery.
In addition a calcaneal branch to the medial aspect of the calcaneus.
Palpation of the posterior tibial artery pulse
The posterior tibial artery pulse can be readily palpated halfway between the posterior border of the medial malleolus and the achilles tendon and is often examined by physicians when assessing a patient for peripheral vascular disease. It is very rarely absent in young and healthy individuals; in a study of 547 healthy individuals only one person did not have a palpable posterior tibial artery.[1] It is easily palpated over Pimenta's Point.
Additional images
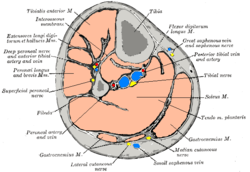 Cross-section through middle of leg.
Cross-section through middle of leg. Major arteries of the leg (posterior view).
Major arteries of the leg (posterior view).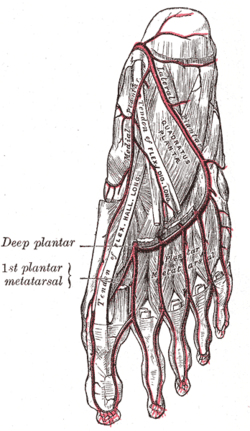 The plantar arteries. Deep view.
The plantar arteries. Deep view.
References
- Robertson GS, Ristic CD, Bullen BR. The incidence of congenitally absent foot pulses. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1990 Mar;72(2):99-100. PMID 2185683.
External links
- Gray's s157 - "The Arteries of the Lower Extremity"
- Gray's s95 - "Ankle joint"
- Anatomy figure: 12:04-14 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Arteries of the lower extremity shown in association with major landmarks."
- Image at umich.edu - pulse
- http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/figures/chapter_15/15-10.HTM
- http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/figures/chapter_17/17-3.HTM