Persistent left superior vena cava
In anatomy, a persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) is the most common variation of the thoracic venous system,[1][2] is prevalent in 0.3% of the population,[3] and an embryologic remnant that results from a failure to involute.
| Persistent left superior vena cava | |
|---|---|
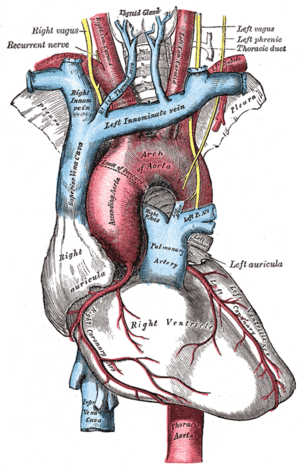 | |
| Superior vena cava(on left) |
Presentation
In PLSVC, the left brachiocephalic vein does not develop fully and the left upper limb and head & neck drain into the right atrium via the coronary sinus.
The variation, in isolation, is considered benign, but is very frequently associated with cardiac abnormalities (e.g. ventricular septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect) that have a significant mortality and morbidity.[4] It is more frequent in patients with congenital heart defects.[5]
Diagnosis
If an anomaly is detected during a routine ultrasound, a fetal echocardiogram is performed to determine whether a fetus has the condition. Otherwise it is often left unnoticed unless an extenuating circumstance warrants further examination of the heart, usually much later in life.
Treatment
References
- Pahwa R, Kumar A (May 2003). "Persistent left superior vena cava: an intensivist's experience and review of the literature". South. Med. J. 96 (5): 528–9. doi:10.1097/01.smj.0000060885.27846.91. PMID 12911199.
- Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Testa A, Vidan J, et al. (September 2004). "Persistent left superior vena cava draining into the coronary sinus: report of 10 cases and literature review". Clin Cardiol. 27 (9): 515–8. doi:10.1002/clc.4960270909. PMC 6654321. PMID 15471164.
- Freedom RM, Culham JAG, Moes CAF (1984). Angiography of Congenital Heart Disease. New York: Macmillan Publishing.
- Berg C, Knüppel M, Geipel A, et al. (March 2006). "Prenatal diagnosis of persistent left superior vena cava and its associated congenital anomalies". Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 27 (3): 274–80. doi:10.1002/uog.2704. PMID 16456841.
- Bjerregaard P, Laursen HB (January 1980). "Persistent left superior vena cava. Incidence, associated congenital heart defects and frontal plane P-wave axis in a paediatric population with congenital heart disease". Acta Paediatr Scand. 69 (1): 105–8. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1980.tb07039.x. PMID 7368902.