Metachondromatosis
Metachondromatosis is an autosomal dominant[2]incompletely penetrant[3] skeletal disorder affecting the growth of bones, leading to multiple enchondromas and osteochondromas.[3] This tumor syndrome affects mainly tubular bones, though it can also involve the vertebrae, small joints, and flat bones.[4]
| Metachondromatosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | METCDS[1] |
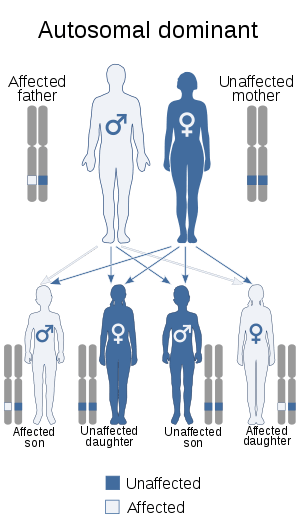 | |
| Metachondromatosis has an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. | |
Genetics
Metachondromatosis is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.[3] This means that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome, and only one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.
It has been associated with PTPN11.[3]
Diagnosis
Treatment
References
- "Metachondromatosis | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- Kennedy LA (1983). "metachondromatosis". Radiology. 148 (1): 117–8. doi:10.1148/radiology.148.1.6602353. PMID 6602353.
- Sobreira NL, Cirulli ET, Avramopoulos D, et al. (2010). "Whole-genome sequencing of a single proband together with linkage analysis identifies a Mendelian disease gene". PLoS Genet. 6 (6): e1000991. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000991. PMC 2887469. PMID 20577567.
- Hunter AG, Kozlowski K, Hochberger O (1995). "Metachondromatosis". Can Assoc Radiol J. 46 (3): 202–8. PMID 7538882.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.