Internal iliac lymph nodes
The internal iliac lymph nodes (or hypogastric) surround the internal iliac artery and its branches (the hypogastric vessels), and receive the lymphatics corresponding to the distribution of the branches of it, i. e., they receive lymphatics from all the pelvic viscera, from the deeper parts of the perineum, including the membranous and cavernous portions of the urethra, and from the buttock and back of the thigh. The internal iliac lymph nodes also drain the superior half of the rectum, above the pectinate line.[1][2]
| Internal iliac lymph nodes | |
|---|---|
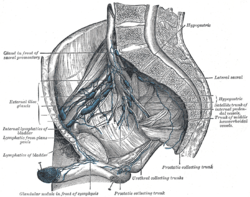 Iliopelvic glands, lateral view. (Hypogastric labeled at upper right.) | |
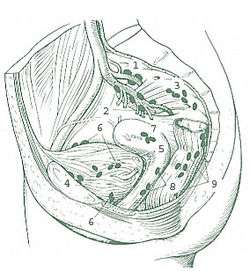 Internal Iliac Nodes 1: Superior gluteal 2: Inferior gluteal 3: Sacral Perivesical Lymph Nodes 4: Prevesicular 5: Postvesicular 6: Lateral vesicular 7: Parauterine 8: Paravaginal 9: Anorectal (pararectal) | |
| Details | |
| System | Lymphatic system |
| Drains to | common iliac lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nodi lymphoidei iliaci interni |
| Anatomical terminology | |
It does not receive lymph from the ovary or testis, which drain to the paraaortic lymph nodes.
Additional images
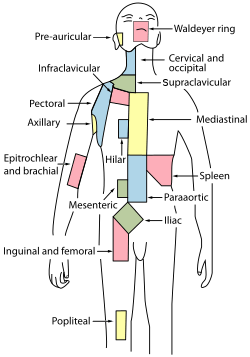 Regional lymph tissue
Regional lymph tissue Deep lymph nodes and vessels of the thorax and abdomen.
Deep lymph nodes and vessels of the thorax and abdomen.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 704 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- "Ano-Rectal Anatomy". University of Connecticut Health Center. Retrieved 18 October 2014.
- MD, Tao Le, MD, MHS, Vikas Bhushan, MD, Matthew Sochat, MD, Max Petersen, Goran Micevic, Kimberly Kallianos (2014). First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2014 : A Student-to-Student Guide. ISBN 978-0071831420.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.