Supratrochlear lymph nodes
One or two supratrochlear lymph nodes are placed above the medial epicondyle of the humerus, medial to the basilic vein.
| Supratrochlear lymph nodes | |
|---|---|
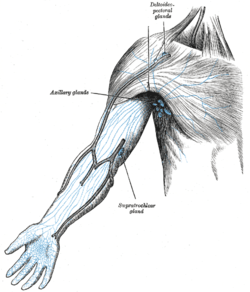 The superficial lymph glands and lymphatic vessels of the arm (supratrochlear gland labeled at bottom center) | |
 Regional lymph tissue | |
| Details | |
| System | Lymphatic system |
| Drains to | Lateral lymph nodes[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nodi lymphoidei supratrochleares |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Their afferents drain the middle, ring, and little fingers, the medial portion of the hand, and the superficial area over the ulnar side of the forearm; these vessels are, however, in free communication with the other lymphatic vessels of the forearm.
The nodes swell up when an infection is detected in the hand or forearm areas.
Their efferents accompany the basilic vein and join the deeper vessels.
They are distinguished in Terminologia anatomica from the "epitrochlear" (or "cubital") lymph nodes, but the region is similar.[2][3]
Additional images
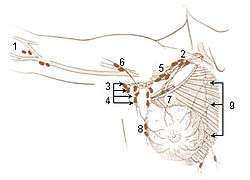 Lymph Nodes of the Upper Limb and Breast
Lymph Nodes of the Upper Limb and Breast
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 699 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- clinicalconsiderations at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Image at umich.edu
- Image at ucsd.edu
External links
- Patel D (2001). "The supratrochlear lymph nodes: their diagnostic significance in a swollen elbow joint". Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 83 (6): 425–6. PMC 2503686. PMID 11777140.
- clinicalconsiderations at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (lymphdrainageul)