Axillary space
The axillary space is an anatomic space.[1] It is further subdivided into quadrangular space, triangular space, and triangular interval. It is bounded by teres major, teres minor, medial border of the humerus, and long head of triceps brachii.[2]
| Axillary space | |
|---|---|
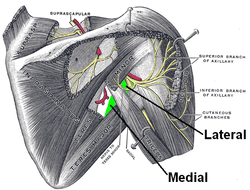 Axillary space, between the teres major and teres minor muscles, and split into a medial and lateral part by the triceps brachii muscle. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | spatium axillare |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
Quadrangular space
It is a quadrangular space bounded laterally by surgical neck of the humerus, medially by long head of triceps brachii and inferiorly by teres major. It is bounded superiorly by subscapularis in front, capsule of the shoulder joint in the middle, and behind by teres minor. The axillary nerve and posterior humeral circumflex artery and vein pass through this space.[2]
Triangular space
It is a triangular space bounded medially by teres minor, laterally by long head of triceps brachii, and inferiorly by teres major. The scapular circumflex artery and scapular circumflex vein pass through this space.[2]
Triangular interval
It is a triangular space bounded medially by long head of triceps brachii, laterally by medial border of humerus, and superiorly by teres major. The radial nerve and profunda brachii artery and vein passes through this space.[2]
References
- Scott L. Spear; Shawna C. Willey (2006). Surgery of the breast: principles and art. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 131–. ISBN 978-0-7817-4756-1. Retrieved 17 July 2010.
- Krishna, Garg (2010). "7 - Scapula". BD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy (Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical) Volume 1 - Upper limb and thorax (Fifth ed.). India: CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd. p. 81, 82. ISBN 978-81-239-1863-1.