Arrector pili muscle
The arrector pili muscles are small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end,[1] known colloquially as goose bumps.
| Arrector pili muscle | |
|---|---|
Base of pilosebaceous unit: An arrector pili muscle can be seen as the pink-staining band of tissue at the bottom center and bottom left of image | |
| Details | |
| Nerve | Sympathetic postganglionic nerve fibers |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus arrector pili |
| TA | A16.0.00.024 |
| TH | H3.12.00.3.01041 |
| FMA | 67821 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
Each arrector pili is composed of a bundle of smooth muscle fibres which attach to several follicles (a follicular unit), and is innervated by the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system. The contraction of the muscle is then involuntary–stresses such as cold, fear etc. may stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, and thus cause contraction.
Contraction of the muscles has a number of different purposes. Its principal function in the majority of mammals is to provide insulation: air becomes trapped between the erect hairs, helping the animal retain heat. Erection of the porcupine's long, thick hairs causes the animal to become more intimidating, scaring predators. Pressure exerted by the muscle may cause sebum to be forced along the hair follicle towards the surface, protecting the hair.
Additional images
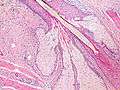 Insertion of sebaceous glands into hair shaft
Insertion of sebaceous glands into hair shaft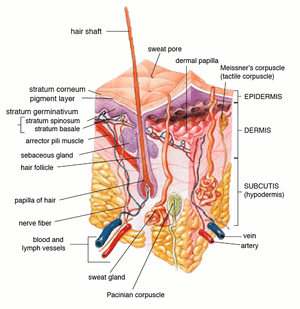 Cross-section of all skin layers
Cross-section of all skin layers
References
- David H. Cormack (1 June 2001). Essential histology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-0-7817-1668-0. Retrieved 15 May 2011.
- Myers, P., R. Espinosa, C. S. Parr, T. Jones, G. S. Hammond, and T. A. Dewey. 2006. The Animal Diversity Web; http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/topics/mammal_anatomy/hair.html
- Burkitt, Young; et al. (1993). Wheater's Functional Histology: a text and colour atlas. Heath. p. 162.