মিং রাজবংশ
মিং রাজবংশ (ইংরেজি: Ming Dynasty) চিনের একটি শাসক রাজবংশ যারা ১৩৬৮ সাল থেকে ১৬৪৪ সাল পর্যন্ত ২৭৬ বছর চিন রাজত্ব করে। মঙ্গোলদের দ্বারা পরিচালিত ইউয়ান সাম্রাজ্যের পতনের পর তারা চিনের শাসনভার গ্রহণ করে। মিং রাজবংশের শাসনকালকে অনেকেই অভিহিত করেন "মানব ইতিহাসের সবচেয়ে সুশৃঙ্খল সরকার ও সামাজিক স্থিতিশীলতা সর্বশ্রেষ্ঠ সময়গুলোর" অন্যতম যুগ হিসেবে। এটিই ছিল চিনের শেষ রাজবংশ যা জাতিগত হান চিনাদের শাসনাধীনে ছিল। ১৬৪৪ সালে লি জিচেং এর বিদ্রোহের ফলে এই সাম্রাজ্যের মূল রাজধানী বেইজিংয়ের পতন হয় এবং শুং রাজবংশের পত্তন ঘটে। শুং রাজবংশও অল্পসময় পরেই মানচু কর্তৃক পরিচালিত কিং রাজবংশের দ্বারা বিলুপ্ত হয়। তবে মিং রাজবংশের অনুগত কিছু কিছু অঞ্চল ১৬৬২ সাল পর্যন্ত টিকে ছিল যাদের একসাথে দক্ষিণ মিং বলা হয়।
| মহান মিং | |||||
| 大明 | |||||
| |||||
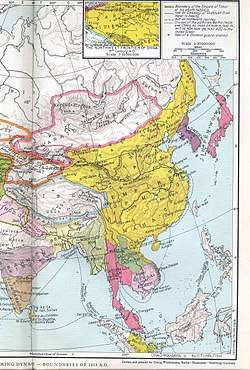 মিং রাজবংশের অবস্থান Ming China at its greatest extent under the reign of the Yongle Emperor | |||||
| রাজধানী | Nanjing (Yingtian prefecture) (১৩৬৮–১৬৪৪)[1] Beijing (Shuntian prefecture) (১৪০৩–১৬৪৪)[2][3] | ||||
| ভাষাসমূহ | অফিসিয়াল ভাষা: Guanhua Chinese Other Chinese dialects: Wu, Yue, Min, Xiang, Hakka, Gan Other languages: Turki (Modern Uyghur), Tibetan, Mongolian, Jurchen, others | ||||
| ধর্ম | Heaven worship, Taoism, Confucianism, Buddhism, Chinese folk religion, Islam | ||||
| সরকার | সম্পূর্ণ রাজতন্ত্র | ||||
| সম্রাট (皇帝) | |||||
| - | ১৩৬৮–১৩৯৮ | The Hongwu Emperor | |||
| - | ১৬২৭–১৬৪৪ | The Chongzhen Emperor | |||
| সিনিয়র গ্র্যান্ড সেক্রেটারি | |||||
| - | ১৪০২–১৪০৭ | Xie Jin | |||
| - | ১৬৪৪ | Wei Zaode | |||
| ইতিহাস | |||||
| - | নানজিং-এ প্রতিষ্ঠিত | ২৩শে জানুয়ারি ১৩৬৮ | |||
| - | Fall of Beijing to Li Zicheng | ২৫শে এপ্রিল ১৬৪৪ | |||
| - | দক্ষিণ মিং এর সমাপ্তি | ২২শে জানুয়ারি, ১৬৬২ | |||
| আয়তন | |||||
| - | ১৪১৫[4] | ৬৫,০০,০০০ বর্গ কি.মি. (২৫,০৯,৬৬৪ বর্গ মাইল) | |||
| জনসংখ্যা | |||||
| • | ১৩৯৩ আনুমানিক | ৬৫ | |||
| • | ১৪০৩ আনুমানিক | ৬৬ | |||
| • | ১৫০০ আনুমানিক | ১২৫ | |||
| • | ১৬০০ আনুমানিক | ১৬০ | |||
| মুদ্রা | Bimetallic: copper cashes (文, wén) in strings of coin and paper Silver taels (兩, liǎng) in sycees and by weight | ||||
| বর্তমানে অংশ | |||||
| Remnants of the Ming Dynasty ruled southern China until 1662, a dynastic period which is known as the Southern Ming. ¹The numbers are based on estimates made by CJ Peers in Late Imperial Chinese Armies: 1520–1840 ²According to A. G. Frank, ReOrient: global economy in the Asian Age, 1998, p. 109 ³According to A. Maddison, The World Economy Volume 1: A Millennial Perspective Volume 2, 2007, p. 238 | |||||
| সতর্কীকরণ: "মহাদেশের" জন্য উল্লিখিত মান সম্মত নয় | |||||
তথ্যসূত্র
- Primary capital after 1403; secondary capital after 1421.
- Secondary capital until 1421; primary capital afterwards.
- The capitals-in-exile of the Southern Ming were Nanjing (1644), Fuzhou (1645–6), Guangzhou (1646–7), Zhaoqing (১৬৪৬–৫২).
- Turchin, Peter; Adams, Jonathan M.; Hall, Thomas D (ডিসেম্বর ২০০৬)। "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires" (PDF)। Journal of world-systems research। 12 (2): 219–229। আইএসএসএন 1076–156x
|issn=এর মান পরীক্ষা করুন (সাহায্য)। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১২ আগস্ট ২০১০।
বহিঃসংযোগ
| উইকিমিডিয়া কমন্সে মিং রাজবংশ সংক্রান্ত মিডিয়া রয়েছে। |
- Notable Ming Dynasty Painters and Galleries at China Online Museum
- Ming Dynasty art at the Metropolitan Museum of Art
- Ming Dynasty With a total of 16 emperors, the Ming Dynasty lasted 276 years, from 1368 to 1644.
| পূর্বসূরী ইউয়ান রাজবংশ |
চীনা ইতিহাসে রাজবংশসমূহ ১৩৬৮–১৬৪৪ |
উত্তরসূরী চিং রাজবংশ (আরও দেখুন শুন রাজবংশ) |
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.